The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
The main purpose of waterquality is to quickly and
easily convert satellite-based reflectance imagery into one or many
well-known water quality indices designed for the detection of Harmful
Algal Blooms (HABs) using the following pigment proxies: chlorophyll-a,
blue-green algae (phycocyanin), and turbidity. Currently, this package
is able to process 40
algorithms for the following satellite-based imagers: WorldView-2,
Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, MODIS, MERIS, and OLCI. In order to improve the
aesthetics of the wq_calc() output, a series of
Map_WQ() functions were developed to help reduce technical
barriers and simplify the complexities in selecting a map layout.
Additional functionality of the package includes a series of
extract_lm() functions that wrap the “Fitting
Linear Models” and “caret” packages to
quickly generate crossvalidated linear models and standardized outputs
(r2, p-value, slope, intercept of the global lm model &
average r2, average RMSE, average MAE of crossvalidated
model) for any number of algorithm and water quality parameter
combinations. It is important to note that the extract_lm()
functions require ground-truth data in order to develop the models. For
a more detailed look into the full functionality of
waterquality, please view “Introduction
to the waterquality package”. For a broader look into how to apply
this tool into a research workflow or for more information on topics
such as data acquisition, image pre-processing, or results, see our
publication entitled “Waterquality:
An Open-Source R Package for the Detection and Quantification of
Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms and Water Quality”.
Additionally, we have recently developed and published a complementary python-based version of waterquality compatible with ESRI ArcGIS and ArcPro. For more information please visit “waterquality for ArcGIS Pro Toolbox”.
You can install the released version from CRAN with:
install.packages("waterquality")You can install waterquality from github with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("RAJohansen/waterquality")The main function in this package is wq_calc():
library(waterquality)
library(terra)
s2 = terra::rast(system.file("raster/S2_Harsha.tif", package = "waterquality"))
MM12NDCI = wq_calc(s2, alg = "MM12NDCI", sat = "sentinel2")Map_WQ_raster(WQ_raster = MM12NDCI,
map_title= "Water Quality Map",
raster_style = "quantile",
histogram = TRUE)
#> The legacy packages maptools, rgdal, and rgeos, underpinning the sp package,
#> which was just loaded, will retire in October 2023.
#> Please refer to R-spatial evolution reports for details, especially
#> https://r-spatial.org/r/2023/05/15/evolution4.html.
#> It may be desirable to make the sf package available;
#> package maintainers should consider adding sf to Suggests:.
#> The sp package is now running under evolution status 2
#> (status 2 uses the sf package in place of rgdal)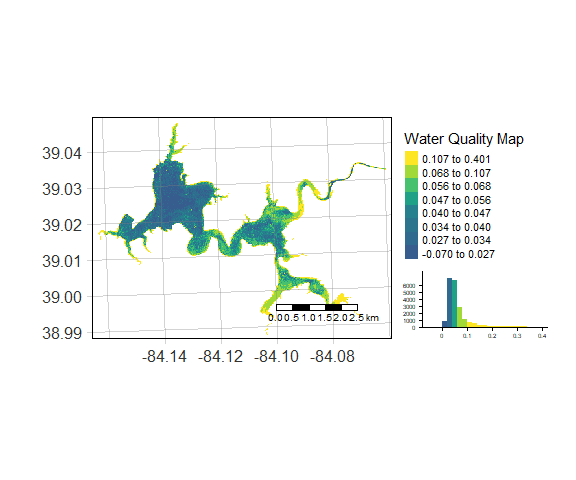
To cite waterquality in publications, please use:
Johansen R, Nowosad J, Reif M, Emery E (2023). waterquality: Satellite Derived Water Quality Detection Algorithms. U.S Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Vicksburg, MS, USA. R package version 1.0.0, https://github.com/RAJohansen/waterquality/.
We encourage users to submit issues and enhancement requests so we may continue to improve our package.
Furthermore, if you have a water quality algorithm that was not on our list, and you would like for it to be included in our package please email Richard.A.Johansen@erdc.dren.mil.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.