
The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.

The goal of vital is to allow analysis of demographic data using tidy tools.
You can install the stable version from CRAN:
pak::pak("vital")You can install the development version from Github:
pak::pak("robjhyndman/vital")First load the necessary packages.
library(vital)
library(tsibble)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)The basic data object is a vital, which is time-indexed
tibble that contains vital statistics such as births, deaths, population
counts, and mortality and fertility rates.
Here is an example of a vital object containing
mortality data for Norway.
norway_mortality <- norway_mortality |>
collapse_ages(max_age = 100)We can use functions to see which variables are index, key or vital:
index_var(norway_mortality)
#> [1] "Year"
key_vars(norway_mortality)
#> [1] "Age" "Sex"
vital_vars(norway_mortality)
#> age sex deaths population
#> "Age" "Sex" "Deaths" "Population"norway_mortality |>
filter(Sex != "Total", Year < 1980, Age < 90) |>
autoplot(Mortality) + scale_y_log10()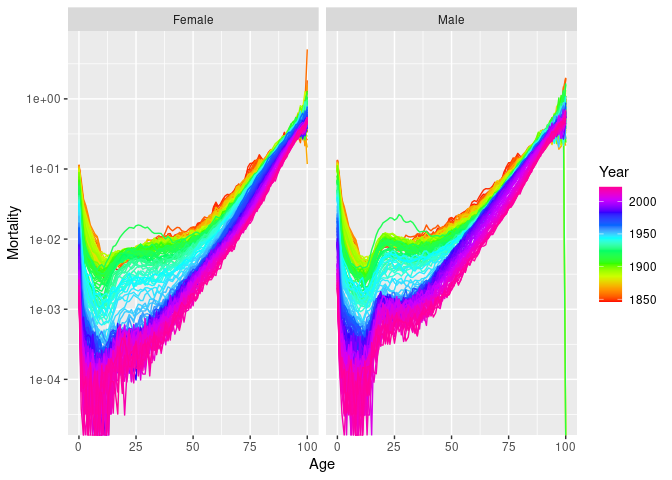
# Life table for Norwegian males in 2000
norway_mortality |>
filter(Sex == "Male", Year == 2000) |>
life_table()
#> # A vital: 101 x 13 [?]
#> # Key: Age x Sex [101 x 1]
#> Year Age Sex mx qx lx dx Lx Tx ex rx nx
#> <int> <int> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2000 0 Male 4.26e-3 4.24e-3 1 4.24e-3 0.996 76.0 76.0 0.996 1
#> 2 2000 1 Male 5.93e-4 5.93e-4 0.996 5.90e-4 0.995 75.0 75.3 0.999 1
#> 3 2000 2 Male 2.29e-4 2.29e-4 0.995 2.28e-4 0.995 74.0 74.3 1.000 1
#> 4 2000 3 Male 1.57e-4 1.57e-4 0.995 1.56e-4 0.995 73.0 73.3 1.000 1
#> 5 2000 4 Male 2.21e-4 2.21e-4 0.995 2.20e-4 0.995 72.0 72.3 1.000 1
#> 6 2000 5 Male 1.89e-4 1.89e-4 0.995 1.88e-4 0.994 71.0 71.4 1.000 1
#> 7 2000 6 Male 1.28e-4 1.28e-4 0.994 1.27e-4 0.994 70.0 70.4 1.000 1
#> 8 2000 7 Male 1.27e-4 1.27e-4 0.994 1.26e-4 0.994 69.0 69.4 1.000 1
#> 9 2000 8 Male 9.40e-5 9.40e-5 0.994 9.34e-5 0.994 68.0 68.4 1.000 1
#> 10 2000 9 Male 2.17e-4 2.17e-4 0.994 2.16e-4 0.994 67.0 67.4 1.000 1
#> # ℹ 91 more rows
#> # ℹ 1 more variable: ax <dbl># Life expectancy
norway_mortality |>
filter(Sex != "Total") |>
life_expectancy() |>
ggplot(aes(x = Year, y = ex, color = Sex)) +
geom_line()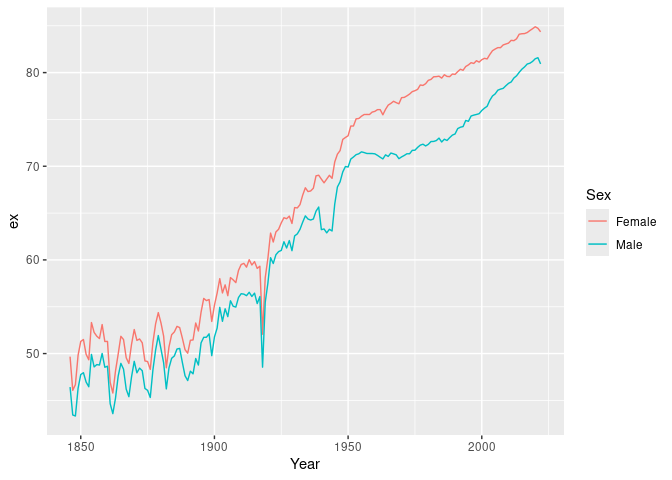
Several smoothing functions are provided:
smooth_spline(), smooth_mortality(),
smooth_fertility(), and smooth_loess(), each
smoothing across the age variable for each year.
# Smoothed data
norway_mortality |>
filter(Sex != "Total", Year == 1967) |>
smooth_mortality(Mortality) |>
autoplot(Mortality) +
geom_line(aes(y = .smooth), col = "#0072B2") +
ylab("Mortality rate") +
scale_y_log10()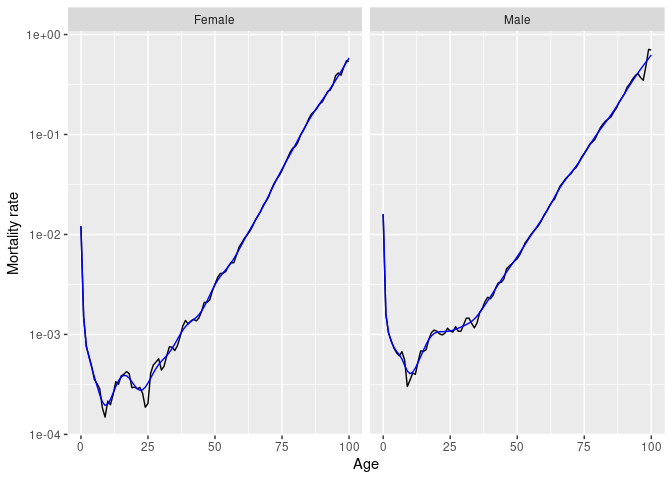
Several mortality models are available including variations on Lee-Carter models (Lee & Carter, JASA, 1992), and functional data models (Hyndman & Ullah, CSDA, 2007).
fit <- norway_mortality |>
filter(Sex != "Total") |>
model(
lee_carter = LC(log(Mortality)),
fdm = FDM(log(Mortality))
)
fit
#> # A mable: 2 x 3
#> # Key: Sex [2]
#> Sex lee_carter fdm
#> <chr> <model> <model>
#> 1 Female <LC> <FDM>
#> 2 Male <LC> <FDM>Models are fitted for all combinations of key variables excluding age.
fit |>
select(lee_carter) |>
filter(Sex == "Female") |>
report()
#> Series: Mortality
#> Model: LC
#> Transformation: log(Mortality)
#>
#> Options:
#> Adjust method: dt
#> Jump choice: fit
#>
#> Age functions
#> # A tibble: 101 × 3
#> Age ax bx
#> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0 -4.33 0.0155
#> 2 1 -6.16 0.0223
#> 3 2 -6.77 0.0193
#> 4 3 -7.14 0.0187
#> 5 4 -7.18 0.0165
#> # ℹ 96 more rows
#>
#> Time coefficients
#> # A tsibble: 124 x 2 [1Y]
#> Year kt
#> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 1900 115.
#> 2 1901 109.
#> 3 1902 103.
#> 4 1903 109.
#> 5 1904 106.
#> # ℹ 119 more rows
#>
#> Time series model: RW w/ drift
#>
#> Variance explained: 66.33%fit |>
select(lee_carter) |>
autoplot()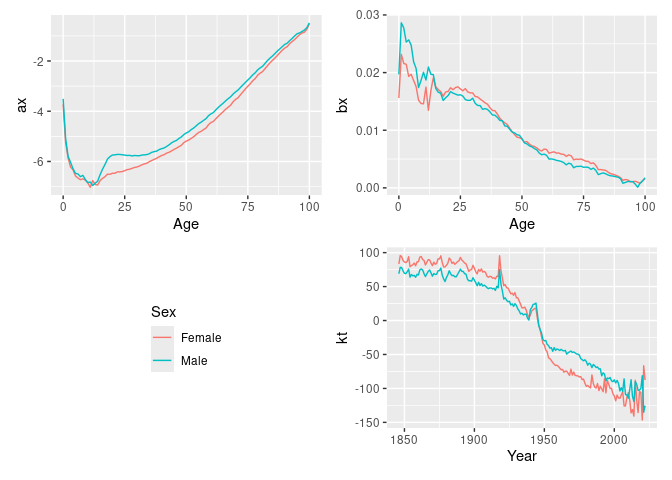
fit |>
select(lee_carter) |>
age_components()
#> # A tibble: 202 × 4
#> Sex Age ax bx
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Female 0 -4.33 0.0155
#> 2 Female 1 -6.16 0.0223
#> 3 Female 2 -6.77 0.0193
#> 4 Female 3 -7.14 0.0187
#> 5 Female 4 -7.18 0.0165
#> 6 Female 5 -7.41 0.0174
#> 7 Female 6 -7.45 0.0165
#> 8 Female 7 -7.48 0.0155
#> 9 Female 8 -7.37 0.0125
#> 10 Female 9 -7.39 0.0124
#> # ℹ 192 more rows
fit |>
select(lee_carter) |>
time_components()
#> # A tsibble: 248 x 3 [1Y]
#> # Key: Sex [2]
#> Sex Year kt
#> <chr> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Female 1900 115.
#> 2 Female 1901 109.
#> 3 Female 1902 103.
#> 4 Female 1903 109.
#> 5 Female 1904 106.
#> 6 Female 1905 110.
#> 7 Female 1906 101.
#> 8 Female 1907 106.
#> 9 Female 1908 105.
#> 10 Female 1909 99.6
#> # ℹ 238 more rowsfit |> forecast(h = 20)
#> # A vital fable: 8,080 x 6 [1Y]
#> # Key: Age x (Sex, .model) [101 x 4]
#> Sex .model Year Age Mortality .mean
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dist> <dbl>
#> 1 Female lee_carter 2024 0 t(N(-6.8, 0.0088)) 0.00110
#> 2 Female lee_carter 2025 0 t(N(-6.9, 0.018)) 0.00106
#> 3 Female lee_carter 2026 0 t(N(-6.9, 0.027)) 0.00103
#> 4 Female lee_carter 2027 0 t(N(-6.9, 0.036)) 0.00100
#> 5 Female lee_carter 2028 0 t(N(-7, 0.045)) 0.000972
#> 6 Female lee_carter 2029 0 t(N(-7, 0.055)) 0.000944
#> 7 Female lee_carter 2030 0 t(N(-7, 0.064)) 0.000916
#> 8 Female lee_carter 2031 0 t(N(-7.1, 0.074)) 0.000889
#> 9 Female lee_carter 2032 0 t(N(-7.1, 0.084)) 0.000863
#> 10 Female lee_carter 2033 0 t(N(-7.1, 0.094)) 0.000838
#> # ℹ 8,070 more rowsThe forecasts are returned as a distribution column (here transformed
normal because of the log transformation used in the model). The
.mean column gives the point forecasts equal to the mean of
the distribution column.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.