
The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.

Statistical methods for analytical method comparison and validation studies. The package implements Bland-Altman analysis, Passing-Bablok regression, Deming regression, and quality goal specifications based on biological variation — approaches commonly used in clinical laboratory method validation.
Install valytics from CRAN:
install.packages("valytics")Or install the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("marcellogr/valytics")valytics provides tools for analytical method
validation:
Method Comparison - Bland-Altman analysis: Assess agreement through bias and limits of agreement - Passing-Bablok regression: Non-parametric regression robust to outliers - Deming regression: Errors-in-variables regression for method comparison
Quality Specifications - Biological variation-based goals: Calculate allowable total error from CVI and CVG - Sigma metrics: Six Sigma quality assessment - Performance assessment: Evaluate methods against quality specifications
All methods produce publication-ready plots and comprehensive statistical summaries.
library(valytics)
# Compare two creatinine measurement methods
data(creatinine_serum)
ba <- ba_analysis(
x = creatinine_serum$enzymatic,
y = creatinine_serum$jaffe
)
ba
#>
#> Bland-Altman Analysis
#> ----------------------------------------
#> n = 80 paired observations
#>
#> Difference type: Absolute (y - x)
#> Confidence level: 95%
#>
#> Results:
#> Bias (mean difference): 0.174
#> 95% CI: [0.127, 0.220]
#> SD of differences: 0.209
#>
#> Limits of Agreement:
#> Lower LoA: -0.236
#> 95% CI: [-0.316, -0.156]
#> Upper LoA: 0.584
#> 95% CI: [0.504, 0.663]plot(ba)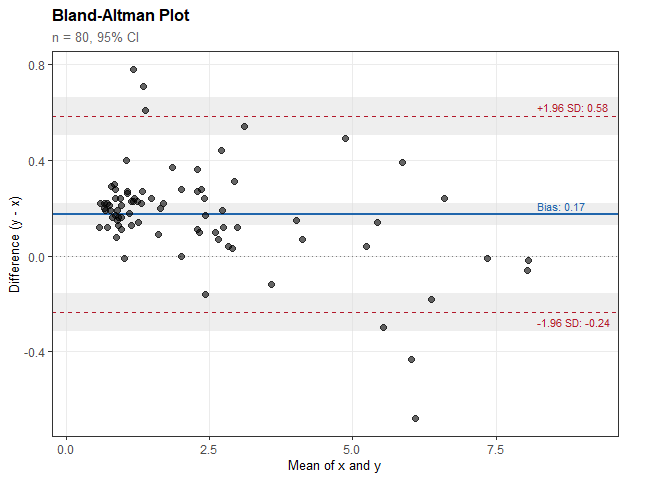
pb <- pb_regression(
x = creatinine_serum$enzymatic,
y = creatinine_serum$jaffe
)
pb
#>
#> Passing-Bablok Regression
#> ----------------------------------------
#> n = 80 paired observations
#>
#> CI method: Analytical (Passing-Bablok 1983)
#> Confidence level: 95%
#>
#> Regression equation:
#> creatinine_serum$jaffe = 0.234 + 0.971 * creatinine_serum$enzymatic
#>
#> Results:
#> Intercept: 0.234
#> 95% CI: [0.229, 0.239]
#> (excludes 0: significant constant bias)
#>
#> Slope: 0.971
#> 95% CI: [0.966, 0.974]
#> (excludes 1: significant proportional bias)plot(pb)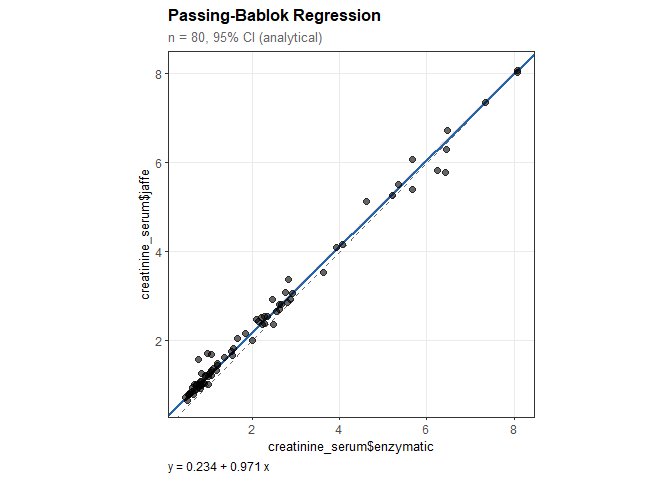
dm <- deming_regression(
x = creatinine_serum$enzymatic,
y = creatinine_serum$jaffe
)
dm
#>
#> Deming Regression
#> ----------------------------------------
#> n = 80 paired observations
#>
#> Error ratio (lambda): 1.000
#> CI method: Jackknife
#> Confidence level: 95%
#>
#> Regression equation:
#> creatinine_serum$jaffe = 0.277 + 0.953 * creatinine_serum$enzymatic
#>
#> Results:
#> Intercept: 0.277 (SE = 0.028)
#> 95% CI: [0.222, 0.332]
#> (excludes 0: significant constant bias)
#>
#> Slope: 0.953 (SE = 0.014)
#> 95% CI: [0.925, 0.982]
#> (excludes 1: significant proportional bias)plot(dm)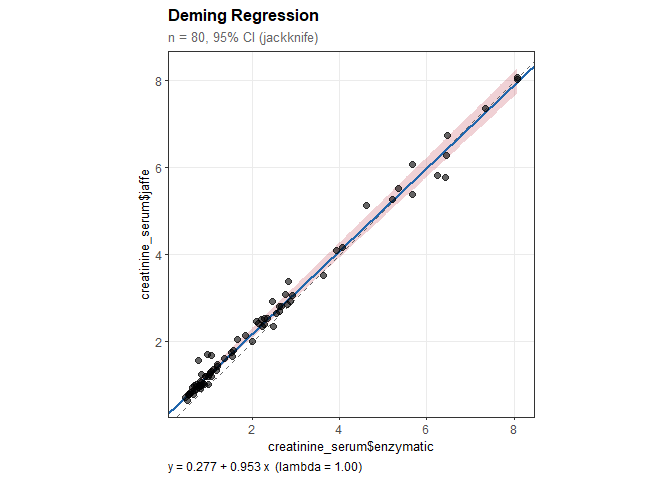
Calculate performance goals based on within-subject (CVI) and between-subject (CVG) biological variation:
# Creatinine biological variation (from EFLM database)
# CV_I = 5.95%, CV_G = 14.7%
ate <- ate_from_bv(cvi = 5.95, cvg = 14.7)
ate
#>
#> Analytical Performance Specifications from Biological Variation
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#>
#> Input:
#> Within-subject CV (CV_I): 5.95%
#> Between-subject CV (CV_G): 14.70%
#> Performance level: desirable
#> Coverage factor (k): 1.65
#>
#> Specifications:
#> Allowable imprecision (CV_A): 2.98%
#> Allowable bias: 3.96%
#> Total allowable error (TEa): 8.87%# Evaluate method performance
sm <- sigma_metric(bias = 1.5, cv = 2.5, tea = 10)
sm
#>
#> Six Sigma Metric
#> ----------------------------------------
#>
#> Input:
#> Observed bias: 1.50%
#> Observed CV: 2.50%
#> Total allowable error (TEa): 10.00%
#>
#> Result:
#> Sigma: 3.40
#> Performance: Marginal
#> Defect rate: ~66,800 per million# Full quality assessment
assess <- ate_assessment(
bias = 1.5,
cv = 2.5,
tea = 10,
allowable_bias = 4.0,
allowable_cv = 3.0
)
assess
#>
#> Analytical Performance Assessment
#> --------------------------------------------------
#>
#> >>> METHOD ACCEPTABLE <<<
#>
#> Performance Summary:
#> Parameter Observed Allowable Status
#> -------------------- ---------- ---------- ----------
#> Bias 1.50% 4.00% PASS
#> CV (Imprecision) 2.50% 3.00% PASS
#> Total Error 5.62% 10.00% PASS
#>
#> Sigma Metric: 3.40 (Marginal)method1 ~ method2)The package includes three realistic clinical datasets:
| Dataset | Description | n |
|---|---|---|
glucose_methods |
POC meter vs. laboratory analyzer | 60 |
creatinine_serum |
Enzymatic vs. Jaffe methods | 80 |
troponin_cardiac |
Two hs-cTnI platforms | 50 |
Bland-Altman:
Passing-Bablok:
Deming:
Biological Variation:
GPL-3
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.