
The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
The goal of samplr is to provide tools to understand human performance from the perspective of sampling, both looking at how people generate samples and how people use the samples they have generated. A longer overview and other resources can be found at sampling.warwick.ac.uk.
You can install samplr from CRAN:
install.packages("samplr")or install the development version from Github with:
devtools::install_github("lucas-castillo/samplr")or alternatively using the remotes package
remotes::install_github("lucas-castillo/samplr")If you are installing the development version on MacOS, you will need the following prior to installation:
xcode-select --install in a terminal. You may also check if
those are already installed by running
pkgbuild::check_build_tools() in
/usr/local/gfortran.Read more about it on the macOS Prerequisites section in the R Installation and Administration Manual.
If you are installing the development version on Windows, you will need to have RTools installed, which you can find here. Please make sure you install the version corresponding to your R version (i.e. for R 4.3.3, you’d need RTools 4.3).
The samplr package provides tools to generate samples following particular algorithms
library(samplr)
set.seed(1)
chain <- sampler_mh(start = 1, distr_name = "norm", distr_params = c(0,1), sigma_prop = diag(1) * .5, iterations = 2048)
r <- plot_series(chain[[1]], change = FALSE)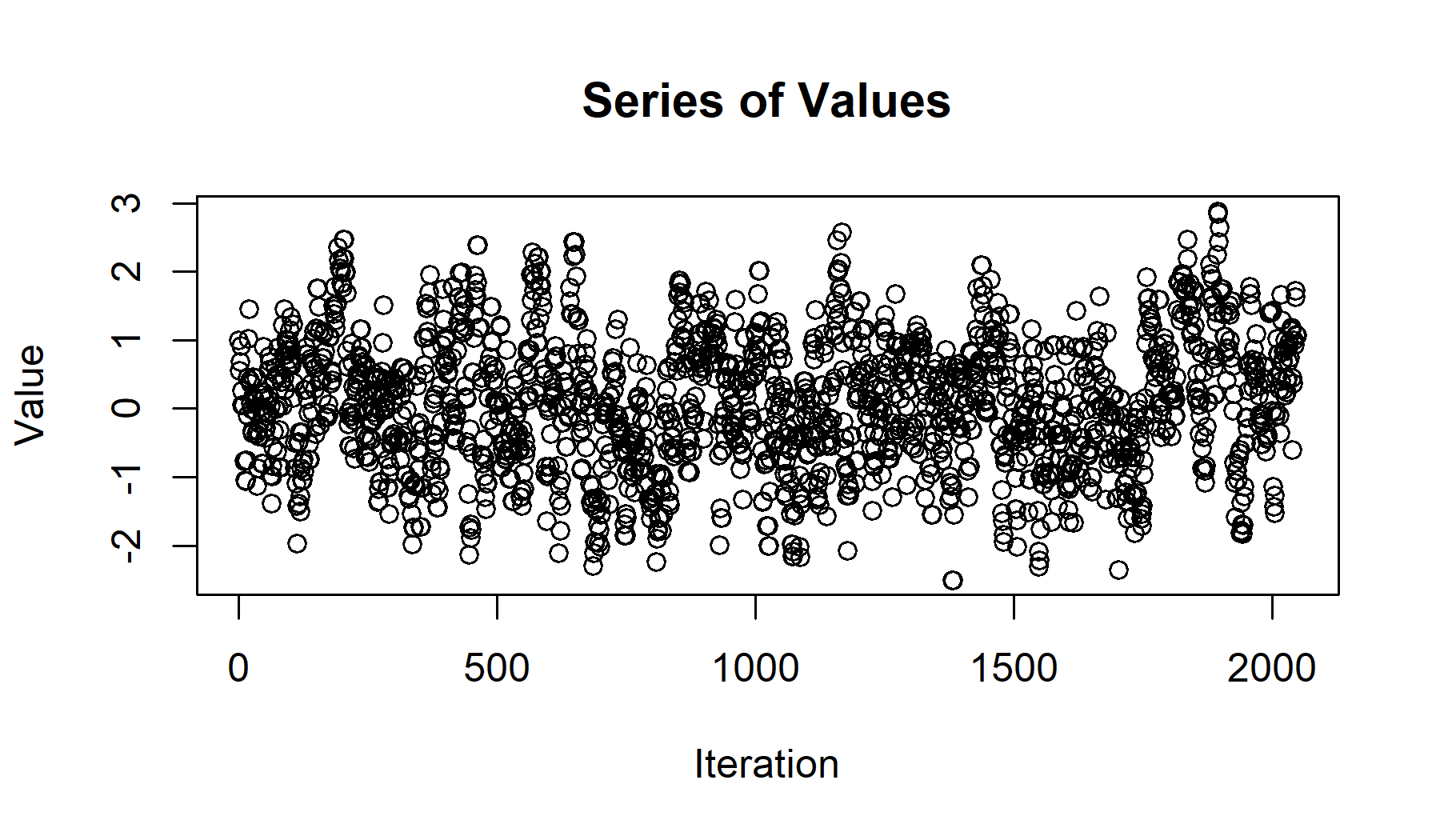
As well as tools to diagnose the patterns both from samplers and participants:
v <- calc_all(chain[[1]][1:200])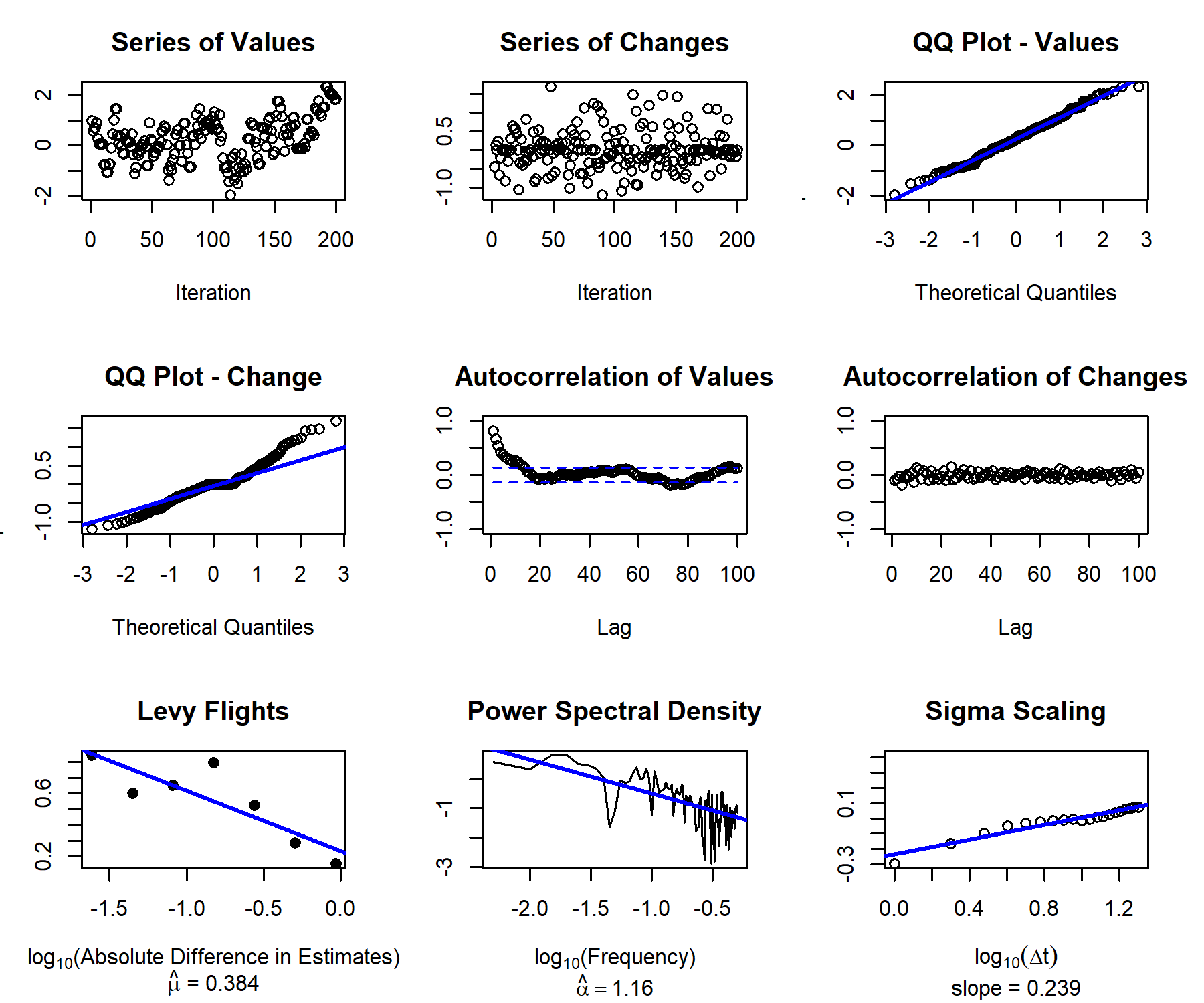
Please cite the corresponding preprint:
APA: Castillo, L., Li, Y.-X., & Sanborn, A. N. (2025). The samplr package: A tool for modeling human cognition with sampling algorithms. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/ax8hm_v1
BibLaTeX:
@online{castillo2025SamplrPackageTool,
title = {The Samplr Package: {{A}} Tool for Modeling Human Cognition with Sampling Algorithms},
author = {Castillo, Lucas and Li, Yun-Xiao and Sanborn, Adam N},
date = {2025},
doi = {10.31234/osf.io/ax8hm_v1},
pubstate = {in preparation}
}These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.