The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
saeczi is an R package that implements a small area
estimator that uses a two-stage modeling approach for zero-inflated
response variables. In particular, we are working with variables that
follow a semi-continuous distribution with a mixture of zeroes and
positive continuously distributed values. An example can be seen
below.
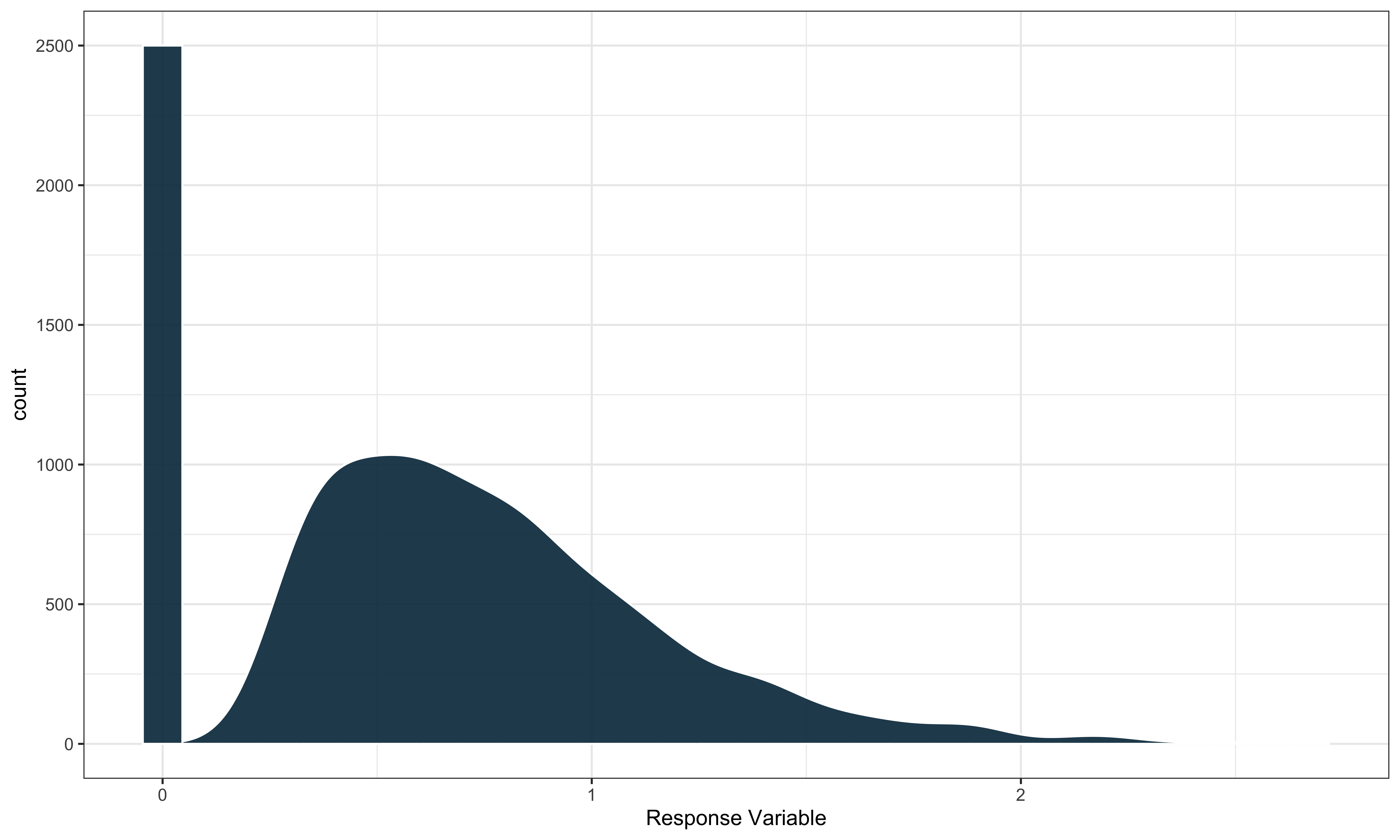
saeczi first fits a linear mixed model to the non-zero
portion of the response and then a generalized linear mixed model with
binomial response to classify the probability of zero for a given data
point. In estimation these models are each applied to new data points
and combined to compute a final prediction.
The package can also generate MSE estimates using a parametric bootstrap approach described in Chandra and Sud (2012) either in parallel or sequentially.
Install the latest CRAN release with:
install.packages("saeczi")You can also install the developmental version of saeczi
from GitHub with:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pkg_install("harvard-ufds/saeczi")We’ll use the internal package data to show an example of how to use
saeczi. The two data sets contained within the package
contain example forestry data collected by the Forestry Inventory and
Analysis (FIA) research program.
saeczi::samp: Example FIA plot-level sample data for
each county in Oregon.saeczi::pop: Example FIA pixel level population
auxiliary data for each county in Oregon.The main response variable included in samp is above
ground live biomass and our small areas in this case are the counties in
Oregon. To keep things simple we will use tree canopy cover (tcc16) and
elevation (elev) as our predictors in both of the models. We can use
saeczi to get estimates for the mean biomass in each county
as well as the corresponding bootstrapped (B = 500) MSE estimate as
follows.
library(saeczi)
data(pop)
data(samp)
result <- saeczi(samp_dat = samp,
pop_dat = pop,
lin_formula = DRYBIO_AG_TPA_live_ADJ ~ tcc16 + elev,
log_formula = DRYBIO_AG_TPA_live_ADJ ~ tcc16,
domain_level = "COUNTYFIPS",
mse_est = TRUE,
B = 1000L)The function returns the following objects:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
call |
The original function call |
res |
A data.frame containing the estimates |
lin_mod |
The linear model object of class
merMod used to compute the estimates |
log_mod |
The logistic model object of class
merMod used to compute the estimates |
As there are 36 total counties in Oregon, we will just look at the first few rows of the results:
result$res |> head()
#> COUNTYFIPS mse est
#> 1 41001 38.30647 14.57288
#> 2 41003 122.90662 103.33016
#> 3 41005 1069.30963 86.08616
#> 4 41007 4691.01214 78.79615
#> 5 41009 356.53805 73.98920
#> 6 41011 273.34697 90.44174saeczi supports parallelization through the
future package to speed up the bootstrapping process, but
requires a small amount of additional work on the part of the user. It
is not enough just to specify parallel = TRUE in the
function signature as a future::plan must also be
specified.
Below is an example that uses multisession’ future resolution with 6 threads:
future::plan("multisession", workers = 6)
result_par <- saeczi(samp_dat = samp,
pop_dat = pop,
lin_formula = DRYBIO_AG_TPA_live_ADJ ~ tcc16 + elev,
log_formula = DRYBIO_AG_TPA_live_ADJ ~ tcc16,
domain_level = "COUNTYFIPS",
mse_est = TRUE,
parallel = TRUE,
B = 1000L)These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.