The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
The goal of ravetools is to provide memory-efficient
signal & image processing toolbox for
intracranial Electroencephalography. Highlighted features
include:
Notch filter (remove electrical line
frequencies)Welch Periodogram (averaged power over
frequencies)Wavelet (frequency-time
decomposition)FFTCT/MRI to MRI image alignmentThe package is available on CRAN. To install the
compiled version, simply run:
install.packages("ravetools")Installing the package from source requires installation of proper
compilers and some C libraries; see this
document for details.
iEEG preprocess
pipelineThis is a basic example which shows you how to preprocess an
iEEG signal. The goal here is to:
* Channel referencing is not included
library(ravetools)
# Generate 20 second data at 2000 Hz
time <- seq(0, 20, by = 1 / 2000)
signal <- sin( 120 * pi * time) +
sin(time * 20*pi) +
exp(-time^2) *
cos(time * 10*pi) +
rnorm(length(time))
diagnose_channel(signal, srate = 2000)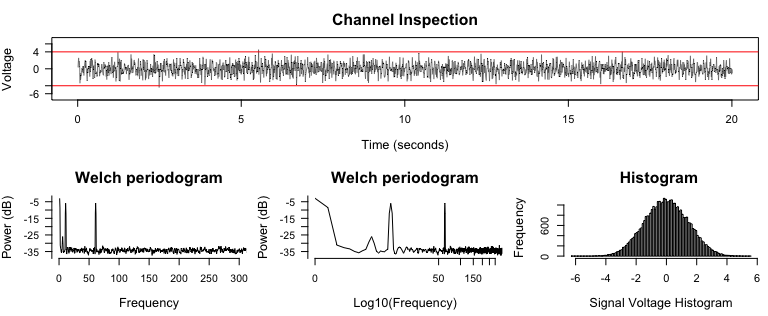
Notch filters and inspect Periodograms## ------- Notch filter --------
signal2 <- notch_filter(signal, sample_rate = 2000)
diagnose_channel(signal, signal2, srate = 2000,
name = c("Raw", "Filtered"))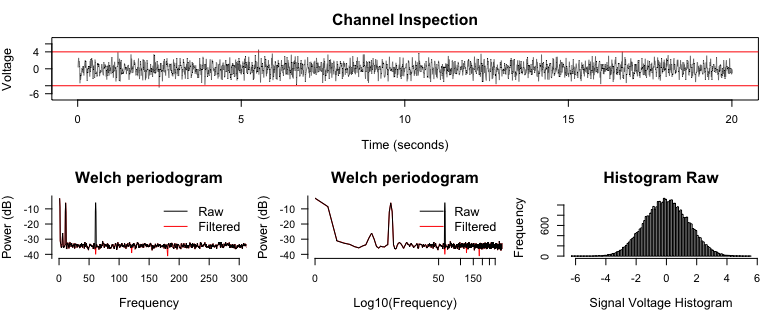
Current version of ravetools provides two approaches:
Wavelet and Multi-taper. Wavelet
uses the Morlet wavelet
and obtains both amplitude and phase data, while
Multi-taper does not generate phase data. However, the
amplitude obtained from Multi-taper is smoother than
Wavelet.
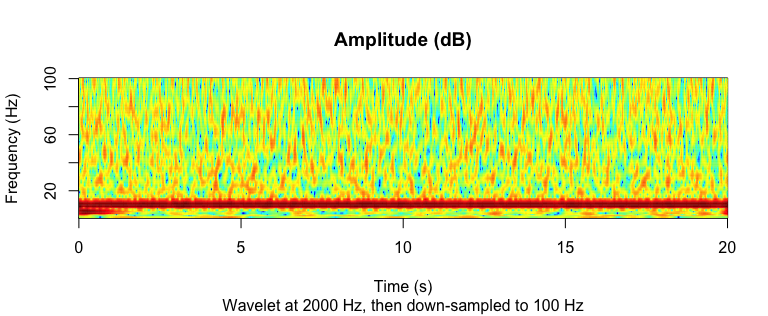
Wavelet:## ---------- Wavelet -----------
coef <- morlet_wavelet(
signal2, freqs = seq(1, 100, by = 1),
srate = 2000, wave_num = c(2, 15))
amplitude <- 20 * log10(Mod(coef[]))
# For each frequency, decimate to 100 Hz
downsample_amp <- apply(amplitude, 2, decimate, q = 20)
downsample_time <- decimate(time, q = 20)
par(mfrow = c(1,1))
image(
z = downsample_amp,
x = downsample_time,
y = seq(1, 100, by = 1),
xlab = "Time (s)",
ylab = "Frequency (Hz)",
main = "Amplitude (dB)",
sub = "Wavelet at 2000 Hz, then down-sampled to 100 Hz",
col = matlab_palette()
)
Multi-taperAlternatively you can use Multi-tapers to obtain
amplitude data. The algorithm is modified from source code here. Please
credit them as well if you adopt this approach.
## ---------- Multitaper -----------
res <- multitaper(
data = signal2,
fs = 2000,
frequency_range = c(1, 100),
time_bandwidth = 1.5,
window_params = c(2, 0.01),
nfft = 100
)
par(mfrow = c(1,1))
image(
x = res$time,
y = res$frequency,
z = 10 * log10(res$spec),
xlab = "Time (s)",
ylab = 'Frequency (Hz)',
col = matlab_palette(),
main = "Amplitude (dB)"
)
ravetools provides imaging co-registration via
NiftyReg (doi.org/10.1117/1.JMI.1.2.024003).
You can align CT to MRI, or MRI
(T2) to MRI (T1). The method can be body
rigid, affine, or non-linear.
source <- system.file("extdata", "epi_t2.nii.gz", package="RNiftyReg")
target <- system.file("extdata", "flash_t1.nii.gz", package="RNiftyReg")
aligned <- register_volume(source, target, verbose = FALSE)
source_img <- aligned$source[[1]]
target_img <- aligned$target
aligned_img <- aligned$image
par(mfrow = c(2, 2), mar = c(0.1, 0.1, 3.1, 0.1))
pal <- grDevices::grey.colors(256, alpha = 1)
image(source_img[,,30], asp = 1, axes = FALSE,
col = pal, main = "Source image")
image(target_img[,,64], asp = 1, axes = FALSE,
col = pal, main = "Target image")
image(aligned_img[,,64], asp = 1, axes = FALSE,
col = pal, main = "Aligned image")
# bucket fill and calculate differences
aligned_img[is.nan(aligned_img) | aligned_img <= 1] <- 1
target_img[is.nan(target_img) | aligned_img <= 1] <- 1
diff <- abs(aligned_img / target_img - 1)
image(diff[,,64], asp = 1, axes = FALSE,
col = pal, main = "Percentage Difference")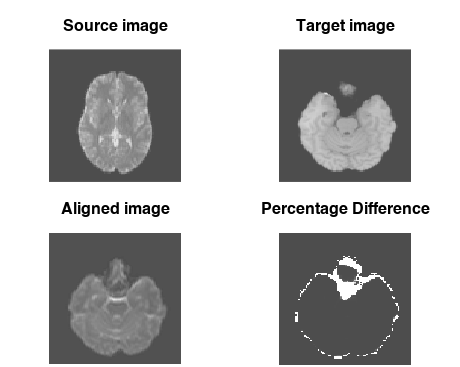
RAVE
paper from Beauchamp's labMagnotti, JF, and Wang, Z, and Beauchamp, MS. RAVE: comprehensive
open-source software for reproducible analysis and visualization of
intracranial EEG data. NeuroImage, 223, p.117341.The multitaper function (MIT License) uses the script
derived from Prerau's lab. The TinyParallel
script is derived from RcppParallel package (GPL License)
with TBB features removed (only use
tinythreads). The register_volume function
uses NiftyReg (BSD License) developed by CMIC
at University College London, UK (its R implementation is released under
GPL license).
[1] Magnotti, JF, and Wang, Z, and Beauchamp, MS. RAVE: comprehensive
open-source software for reproducible analysis and visualization of
intracranial EEG data. NeuroImage, 223, p.117341.
[2] Prerau, Michael J, and Brown, Ritchie E, and Bianchi, Matt T, and
Ellenbogen, Jeffrey M, and Purdon, Patrick L. Sleep Neurophysiological
Dynamics Through the Lens of Multitaper Spectral Analysis. Physiology,
December 7, 2016, 60-92.
[3] Modat, M., Cash, D.M., Daga, P., Winston, G.P., Duncan, J.S. and
Ourselin, S., 2014. Global image registration using a symmetric
block-matching approach. Journal of medical imaging, 1(2), pp.024003-024003.
[4] JJ Allaire, Romain Francois, Kevin Ushey, Gregory Vandenbrouck, Marcus
Geelnard and Intel (2022). RcppParallel: Parallel Programming Tools for
'Rcpp'. R package version 5.1.5.
https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RcppParallelThese binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.