| Title: | Policy Learning |
| Version: | 1.6.2 |
| Description: | Package for learning and evaluating (subgroup) policies via doubly robust loss functions. Policy learning methods include doubly robust blip/conditional average treatment effect learning and sequential policy tree learning. Methods for (subgroup) policy evaluation include doubly robust cross-fitting and online estimation/sequential validation. See Nordland and Holst (2022) <doi:10.48550/arXiv.2212.02335> for documentation and references. |
| License: | Apache License (≥ 2) |
| Encoding: | UTF-8 |
| Depends: | R (≥ 4.1), SuperLearner |
| Imports: | data.table (≥ 1.14.5), lava (≥ 1.7.2.1), future.apply, progressr, methods, policytree (≥ 1.2.0), survival, targeted (≥ 0.6), DynTxRegime |
| Suggests: | DTRlearn2, glmnet (≥ 4.1-6), mets, mgcv, xgboost, knitr, ranger, rmarkdown, testthat (≥ 3.0), ggplot2 |
| RoxygenNote: | 7.3.3 |
| BugReports: | https://github.com/AndreasNordland/polle/issues |
| VignetteBuilder: | knitr |
| NeedsCompilation: | no |
| Packaged: | 2025-12-04 12:51:45 UTC; oano |
| Author: | Andreas Nordland [aut, cre],
Klaus Holst |
| Maintainer: | Andreas Nordland <andreasnordland@gmail.com> |
| Repository: | CRAN |
| Date/Publication: | 2025-12-04 14:40:08 UTC |
polle: Policy Learning
Description

Package for learning and evaluating (subgroup) policies via doubly robust loss functions. Policy learning methods include doubly robust blip/conditional average treatment effect learning and sequential policy tree learning. Methods for (subgroup) policy evaluation include doubly robust cross-fitting and online estimation/sequential validation. See Nordland and Holst (2022) doi:10.48550/arXiv.2212.02335 for documentation and references.
Author(s)
Maintainer: Andreas Nordland andreasnordland@gmail.com
Authors:
Klaus Holst klaus@holst.it (ORCID)
See Also
Useful links:
Report bugs at https://github.com/AndreasNordland/polle/issues
c_model class object
Description
Provides constructors for right-censoring models. Main constructors include:
-
c_cox(): Cox proportional hazards model -
c_no_censoring(): Model for scenarios without censoring The constructors are used as input forpolicy_eval()andpolicy_learn().
Usage
c_cox(formula = ~., offset = NULL, weights = NULL, ...)
c_no_censoring()
Arguments
formula |
An object of class formula specifying the design matrix for
the right-censoring model. Use |
offset |
offsets for Cox model, see |
weights |
weights for Cox score equations, see |
... |
Additional arguments passed to the model. |
Details
c_cox() is a wrapper of mets::phreg() (Cox proportional hazard model).
Value
A c-model object (function) with arguments:
event: censoring events
time: start time
time2: end time
H: history matrix
See Also
Conditional Policy Evaluation
Description
conditional() is used to calculate the
policy value for each group defined by a given baseline variable.
Usage
conditional(object, policy_data, baseline)
Arguments
object |
Policy evaluation object created by |
policy_data |
Policy data object created by |
baseline |
Character string. |
Value
object of inherited class 'estimate', see lava::estimate.default. The object is a list with elements 'coef' (policy value estimate for each group) and 'IC' (influence curve estimate matrix).
Examples
library("polle")
library("data.table")
setDTthreads(1)
d <- sim_single_stage(n=2e3)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = "A",
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = c("Z","L"),
utility = "U")
# static policy:
p <- policy_def(1)
pe <- policy_eval(pd,
policy = p)
# conditional value for each group defined by B
conditional(pe, pd, "B")
Control arguments for doubly robust blip-learning
Description
control_blip sets the default control arguments
for doubly robust blip-learning, type = "blip".
Usage
control_blip(blip_models = q_glm(~.), quantile_prob_threshold = NULL)
Arguments
blip_models |
Single element or list of V-restricted blip-models created
by |
quantile_prob_threshold |
Numeric vector. Quantile probabilities for adaptively setting the threshold for the conditional average treatment effect. |
Value
list of (default) control arguments.
Control arguments for doubly robust Q-learning
Description
control_drql sets the default control arguments
for doubly robust Q-learning, type = "drql".
Usage
control_drql(qv_models = q_glm(~.))
Arguments
qv_models |
Single element or list of V-restricted Q-models created
by |
Value
list of (default) control arguments.
Control arguments for Efficient Augmentation and Relaxation Learning
Description
control_earl sets the default control arguments
for efficient augmentation and relaxation learning , type = "earl".
The arguments are passed directly to DynTxRegime::earl() if not
specified otherwise.
Usage
control_earl(
moPropen,
moMain,
moCont,
regime,
iter = 0L,
fSet = NULL,
lambdas = 0.5,
cvFolds = 0L,
surrogate = "hinge",
kernel = "linear",
kparam = NULL,
verbose = 0L
)
Arguments
moPropen |
Propensity model of class "ModelObj", see modelObj::modelObj. |
moMain |
Main effects outcome model of class "ModelObj". |
moCont |
Contrast outcome model of class "ModelObj". |
regime |
An object of class formula specifying the design of the policy/regime. |
iter |
Maximum number of iterations for outcome regression. |
fSet |
A function or NULL defining subset structure. |
lambdas |
Numeric or numeric vector. Penalty parameter. |
cvFolds |
Integer. Number of folds for cross-validation of the parameters. |
surrogate |
The surrogate 0-1 loss function. The options are
|
kernel |
The options are |
kparam |
Numeric. Kernel parameter |
verbose |
Integer. |
Value
list of (default) control arguments.
Control arguments for Outcome Weighted Learning
Description
control_owl() sets the default control arguments
for backwards outcome weighted learning, type = "owl".
The arguments are passed directly to DTRlearn2::owl() if not
specified otherwise.
Usage
control_owl(
policy_vars = NULL,
reuse_scales = TRUE,
res.lasso = TRUE,
loss = "hinge",
kernel = "linear",
augment = FALSE,
c = 2^(-2:2),
sigma = c(0.03, 0.05, 0.07),
s = 2^(-2:2),
m = 4
)
Arguments
policy_vars |
Character vector/string or list of character
vectors/strings. Variable names used to restrict the policy.
The names must be a subset of the history names, see get_history_names().
Not passed to |
reuse_scales |
The history matrix passed to |
res.lasso |
If |
loss |
Loss function. The options are |
kernel |
Type of kernel used by the support vector machine. The
options are |
augment |
If |
c |
Regularization parameter. |
sigma |
Tuning parameter. |
s |
Slope parameter. |
m |
Number of folds for cross-validation of the parameters. |
Value
list of (default) control arguments.
Control arguments for Policy Tree Learning
Description
control_ptl sets the default control arguments
for doubly robust policy tree learning, type = "ptl".
The arguments are passed directly to policytree::policy_tree() (or
policytree::hybrid_policy_tree()) if not specified otherwise.
Usage
control_ptl(
policy_vars = NULL,
hybrid = FALSE,
depth = 2,
search.depth = 2,
split.step = 1,
min.node.size = 1
)
Arguments
policy_vars |
Character vector/string or list of character
vectors/strings. Variable names used to
construct the V-restricted policy tree.
The names must be a subset of the history names, see get_history_names().
Not passed to |
hybrid |
If |
depth |
Integer or integer vector. The depth of the fitted policy tree for each stage. |
search.depth |
(only used if |
split.step |
Integer or integer vector. The number of possible splits to consider when performing policy tree search at each stage. |
min.node.size |
Integer or integer vector. The smallest terminal node size permitted at each stage. |
Value
list of (default) control arguments.
Control arguments for Residual Weighted Learning
Description
control_rwl sets the default control arguments
for residual learning , type = "rwl".
The arguments are passed directly to DynTxRegime::rwl() if not
specified otherwise.
Usage
control_rwl(
moPropen,
moMain,
regime,
fSet = NULL,
lambdas = 2,
cvFolds = 0L,
kernel = "linear",
kparam = NULL,
responseType = "continuous",
verbose = 2L
)
Arguments
moPropen |
Propensity model of class "ModelObj", see modelObj::modelObj. |
moMain |
Main effects outcome model of class "ModelObj". |
regime |
An object of class formula specifying the design of the policy/regime. |
fSet |
A function or NULL defining subset structure. |
lambdas |
Numeric or numeric vector. Penalty parameter. |
cvFolds |
Integer. Number of folds for cross-validation of the parameters.
|
kernel |
The options are |
kparam |
Numeric. Kernel parameter |
responseType |
Character string. Options are |
verbose |
Integer. |
Value
list of (default) control arguments.
Copy Policy Data Object
Description
Objects of class policy_data contains elements of
class data.table::data.table.
data.table provide functions that operate on objects by reference.
Thus, the policy_data object is not copied when modified by reference,
see examples. An explicit copy can be made by copy_policy_data. The
function is a wrapper of data.table::copy().
Usage
copy_policy_data(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
Value
Object of class policy_data.
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage case: Wide data
d1 <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
head(d1, 5)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd1 <- policy_data(d1,
action="A",
covariates=c("Z", "B", "L"),
utility="U")
pd1
# True copy
pd2 <- copy_policy_data(pd1)
# manipulating the data.table by reference:
pd2$baseline_data[, id := id + 1]
head(pd2$baseline_data$id - pd1$baseline_data$id)
# False copy
pd2 <- pd1
# manipulating the data.table by reference:
pd2$baseline_data[, id := id + 1]
head(pd2$baseline_data$id - pd1$baseline_data$id)
Fit Censoring Functions
Description
Fits right-censoring models for each stage or a single model across all stages.
Usage
fit_c_functions(policy_data, c_models, full_history = FALSE)
Arguments
policy_data |
Policy data object created by |
c_models |
Single c_model or list of K+1 c_models |
full_history |
Logical; use full history (TRUE) or Markov-type history (FALSE) |
Details
The function handles two scenarios:
Multiple models: One model per stage (length K+1)
Single model: Same model applied across all stages
Value
List of fitted censoring functions with class "c_functions"
Fit g-functions
Description
fit_g_functions is used to fit a list of g-models.
Usage
fit_g_functions(policy_data, g_models, full_history = FALSE)
Arguments
policy_data |
Policy data object created by |
g_models |
List of action probability models/g-models for each stage
created by |
full_history |
If TRUE, the full history is used to fit each g-model. If FALSE, the single stage/"Markov type" history is used to fit each g-model. |
Examples
library("polle")
### Simulating two-stage policy data
d <- sim_two_stage(2e3, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# fitting a single g-model across all stages:
g_functions <- fit_g_functions(policy_data = pd,
g_models = g_glm(),
full_history = FALSE)
g_functions
# fitting a g-model for each stage:
g_functions <- fit_g_functions(policy_data = pd,
g_models = list(g_glm(), g_glm()),
full_history = TRUE)
g_functions
g_model class object
Description
Use g_glm(), g_empir(),
g_glmnet(), g_rf(), g_sl(), g_xgboost to construct
an action probability model/g-model object.
The constructors are used as input for policy_eval() and policy_learn().
Usage
g_empir(formula = ~1, ...)
g_glm(
formula = ~.,
family = "binomial",
model = FALSE,
na.action = na.pass,
...
)
g_glmnet(formula = ~., family = "binomial", alpha = 1, s = "lambda.min", ...)
g_rf(
formula = ~.,
num.trees = c(500),
mtry = NULL,
cv_args = list(nfolds = 5, rep = 1),
...
)
g_sl(
formula = ~.,
SL.library = c("SL.mean", "SL.glm"),
family = binomial(),
env = parent.frame(),
onlySL = TRUE,
...
)
g_xgboost(
formula = ~.,
objective = "binary:logistic",
nrounds,
max_depth = 6,
learning_rate = NULL,
nthread = 1,
cv_args = list(nfolds = 3, rep = 1),
...
)
Arguments
formula |
An object of class formula specifying the design matrix for
the propensity model/g-model. Use |
... |
Additional arguments passed to |
family |
A description of the error distribution and link function to be used in the model. |
model |
(Only used by |
na.action |
(Only used by |
alpha |
(Only used by |
s |
(Only used by |
num.trees |
(Only used by |
mtry |
(Only used by |
cv_args |
(Only used by |
SL.library |
(Only used by |
env |
(Only used by |
onlySL |
(Only used by |
objective |
(Only used by |
nrounds |
(Only used by |
max_depth |
(Only used by |
learning_rate |
(Only used by |
nthread |
(Only used by |
Details
g_glm() is a wrapper of glm() (generalized linear model).
g_empir() calculates the empirical probabilities within the groups
defined by the formula.
g_glmnet() is a wrapper of glmnet::glmnet() (generalized linear model via
penalized maximum likelihood).
g_rf() is a wrapper of ranger::ranger() (random forest).
When multiple hyper-parameters are given, the
model with the lowest cross-validation error is selected.
g_sl() is a wrapper of SuperLearner::SuperLearner (ensemble model).
g_xgboost() is a wrapper of xgboost::xgboost.
Value
g-model object: function with arguments 'A' (action vector), 'H' (history matrix) and 'action_set'.
See Also
get_history_names(), get_g_functions().
Examples
library("polle")
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(2e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# available state history variable names:
get_history_names(pd)
# defining a g-model:
g_model <- g_glm(formula = ~B+C)
# evaluating the static policy (A=1) using inverse propensity weighting
# based on a state glm model across all stages:
pe <- policy_eval(type = "ipw",
policy_data = pd,
policy = policy_def(1, reuse = TRUE),
g_models = g_model)
# inspecting the fitted g-model:
get_g_functions(pe)
# available full history variable names at each stage:
get_history_names(pd, stage = 1)
get_history_names(pd, stage = 2)
# evaluating the same policy based on a full history
# glm model for each stage:
pe <- policy_eval(type = "ipw",
policy_data = pd,
policy = policy_def(1, reuse = TRUE),
g_models = list(g_glm(~ L_1 + B),
g_glm(~ A_1 + L_2 + B)),
g_full_history = TRUE)
# inspecting the fitted g-models:
get_g_functions(pe)
Get Maximal Stages
Description
get_K returns the maximal number of stages for the observations in
the policy data object.
Usage
get_K(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
Value
Integer.
Examples
d <- sim_multi_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
pd <- policy_data(data = d$stage_data,
baseline_data = d$baseline_data,
type = "long",
id = "id",
stage = "stage",
event = "event",
action = "A",
utility = "U")
pd
# getting the maximal number of stages:
get_K(pd)
Get Action Set
Description
get_action_set returns the action set, i.e., the possible
actions at each stage for the policy data object.
Usage
get_action_set(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
Value
Character vector.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# getting the actions set:
get_action_set(pd)
Get Actions
Description
get_actions returns the actions at every stage for every observation
in the policy data object.
Usage
get_actions(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
Value
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage and character variable A.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# getting the actions:
head(get_actions(pd))
Get event indicators
Description
get_event returns the event indicators for given IDs
stages
Usage
get_event(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data or history. |
Value
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage.
Get g-functions
Description
get_g_functions() returns a list of (fitted) g-functions
associated with each stage.
Usage
get_g_functions(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_eval or policy_object. |
Value
List of class nuisance_functions.
See Also
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# evaluating the static policy a=1 using inverse propensity weighting
# based on a GLM model at each stage
pe <- policy_eval(type = "ipw",
policy_data = pd,
policy = policy_def(1, reuse = TRUE, name = "A=1"),
g_models = list(g_glm(), g_glm()))
pe
# getting the g-functions
g_functions <- get_g_functions(pe)
g_functions
# getting the fitted g-function values
head(predict(g_functions, pd))
Get history variable names
Description
get_history_names() returns the state covariate names of the history data
table for a given stage. The function is useful when specifying
the design matrix for g_model and q_model objects.
Usage
get_history_names(object, stage)
Arguments
object |
Policy data object created by |
stage |
Stage number. If NULL, the state/Markov-type history variable names are returned. |
Value
Character vector.
Examples
library("polle")
### Multiple stages:
d3 <- sim_multi_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
pd3 <- policy_data(data = d3$stage_data,
baseline_data = d3$baseline_data,
type = "long",
id = "id",
stage = "stage",
event = "event",
action = "A",
utility = "U")
pd3
# state/Markov type history variable names (H):
get_history_names(pd3)
# full history variable names (H_k) at stage 2:
get_history_names(pd3, stage = 2)
Get IDs
Description
get_id returns the ID for every observation in the policy data object.
Usage
get_id(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data or history. |
Value
Character vector.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# getting the IDs:
head(get_id(pd))
Get IDs and Stages
Description
get_id_stage returns the ID and stage number differnt types of events.
Usage
get_id_stage(object, event_set = c(0))
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data or history. |
event_set |
Integer vector. Subset of c(0,1,2). |
Value
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# getting the IDs and stages:
head(get_id_stage(pd))
Get Number of Observations
Description
get_n returns the number of observations in
the policy data object.
Usage
get_n(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
Value
Integer.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# getting the number of observations:
get_n(pd)
Get Policy
Description
get_policy extracts the policy from a policy object
or a policy evaluation object The policy is a function which take a
policy data object as input and returns the policy actions.
Usage
get_policy(object, threshold = NULL)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_object or policy_eval. |
threshold |
Numeric vector. Thresholds for the first stage policy function. |
Value
function of class policy.
Examples
library("polle")
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("BB"),
covariates = list(
L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")
),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3")
)
pd
### V-restricted (Doubly Robust) Q-learning
# specifying the learner:
pl <- policy_learn(
type = "drql",
control = control_drql(qv_models = q_glm(formula = ~C))
)
# fitting the policy (object):
po <- pl(
policy_data = pd,
q_models = q_glm(),
g_models = g_glm()
)
# getting and applying the policy:
head(get_policy(po)(pd))
# the policy learner can also be evaluated directly:
pe <- policy_eval(
policy_data = pd,
policy_learn = pl,
q_models = q_glm(),
g_models = g_glm()
)
# getting and applying the policy again:
head(get_policy(pe)(pd))
Get Policy Actions
Description
get_policy_actions() extract the actions dictated by the
(learned and possibly cross-fitted) policy a every stage.
Usage
get_policy_actions(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_eval. |
Value
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage and action variable
d.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# defining a policy learner based on cross-fitted doubly robust Q-learning:
pl <- policy_learn(type = "drql",
control = control_drql(qv_models = list(q_glm(~C_1), q_glm(~C_1+C_2))),
full_history = TRUE,
L = 2) # number of folds for cross-fitting
# evaluating the policy learner using 2-fold cross fitting:
pe <- policy_eval(type = "dr",
policy_data = pd,
policy_learn = pl,
q_models = q_glm(),
g_models = g_glm(),
M = 2) # number of folds for cross-fitting
# Getting the cross-fitted actions dictated by the fitted policy:
head(get_policy_actions(pe))
Get Policy Functions
Description
get_policy_functions() returns a function defining the policy at
the given stage. get_policy_functions() is useful when implementing
the learned policy.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'blip'
get_policy_functions(
object,
stage,
threshold = NULL,
include_g_values = FALSE,
...
)
## S3 method for class 'drql'
get_policy_functions(
object,
stage,
threshold = NULL,
include_g_values = FALSE,
...
)
get_policy_functions(object, stage, threshold, ...)
## S3 method for class 'ptl'
get_policy_functions(object, stage, threshold = NULL, ...)
## S3 method for class 'ql'
get_policy_functions(
object,
stage,
threshold = NULL,
include_g_values = FALSE,
...
)
Arguments
object |
Object of class "policy_object" or "policy_eval", see policy_learn and policy_eval. |
stage |
Integer. Stage number. |
threshold |
Numeric, threshold for not choosing the reference action at stage 1. |
include_g_values |
If TRUE, the g-values are included as an attribute. |
... |
Additional arguments. |
Value
Functions with arguments:
Hdata.table::data.table containing the variables needed to evaluate the policy (and g-function).
Examples
library("polle")
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = "BB",
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
### Realistic V-restricted Policy Tree Learning
# specifying the learner:
pl <- policy_learn(type = "ptl",
control = control_ptl(policy_vars = list(c("C_1", "BB"),
c("L_1", "BB"))),
full_history = TRUE,
alpha = 0.05)
# evaluating the learner:
pe <- policy_eval(policy_data = pd,
policy_learn = pl,
q_models = q_glm(),
g_models = g_glm())
# getting the policy function at stage 2:
pf2 <- get_policy_functions(pe, stage = 2)
args(pf2)
# applying the policy function to new data:
set.seed(1)
L_1 <- rnorm(n = 10)
new_H <- data.frame(C = rnorm(n = 10),
L = L_1,
L_1 = L_1,
BB = "group1")
d2 <- pf2(H = new_H)
head(d2)
Get Policy Object
Description
Extract the fitted policy object.
Usage
get_policy_object(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_eval. |
Value
Object of class policy_object.
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage:
d1 <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd1 <- policy_data(d1, action="A", covariates=list("Z", "B", "L"), utility="U")
pd1
# evaluating the policy:
pe1 <- policy_eval(policy_data = pd1,
policy_learn = policy_learn(type = "drql",
control = control_drql(qv_models = q_glm(~.))),
g_models = g_glm(),
q_models = q_glm())
# extracting the policy object:
get_policy_object(pe1)
Get Q-functions
Description
get_q_functions() returns a list of (fitted) Q-functions
associated with each stage.
Usage
get_q_functions(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_eval or policy_object. |
Value
List of class nuisance_functions.
See Also
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(
L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")
),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3")
)
pd
# evaluating the static policy a=1 using outcome regression
# based on a GLM model at each stage.
pe <- policy_eval(
type = "or",
policy_data = pd,
policy = policy_def(1, reuse = TRUE, name = "A=1"),
q_models = list(q_glm(), q_glm())
)
pe
# getting the Q-functions
q_functions <- get_q_functions(pe)
# getting the fitted g-function values
head(predict(q_functions, pd))
Get Stage Action Sets
Description
get_stage_action_sets returns the action sets at each stage, i.e.,
the possible actions at each stage for the policy data object.
Usage
get_stage_action_sets(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
Value
List of character vectors.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage_multi_actions(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# getting the stage actions set:
get_stage_action_sets(pd)
Get the Utility
Description
get_utility() returns the utility, i.e., the sum of the rewards,
for every observation in the policy data object.
Usage
get_utility(object)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
Value
data.table::data.table with key id and numeric variable U.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# getting the utility:
head(get_utility(pd))
Get History Object
Description
get_history summarizes the history and action at a given stage from a
policy_data object.
Usage
get_history(object, stage = NULL, full_history = FALSE, event_set = c(0))
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
stage |
Stage number. If NULL, the state/Markov-type history across all stages is returned. |
full_history |
Logical. If TRUE, the full history is returned If FALSE, only the state/Markov-type history is returned. |
event_set |
Integer vector. Subset of c(0,1,2). |
Details
Each observation has the sequential form
O= {B, U_1, X_1, A_1, ..., U_K, X_K, A_K, U_{K+1}},
for a possibly stochastic number of stages K.
-
Bis a vector of baseline covariates. -
U_kis the reward at stage k (not influenced by the actionA_k). -
X_kis a vector of state covariates summarizing the state at stage k. -
A_kis the categorical action at stage k.
Value
Object of class history. The object is a list containing the following elements:
H |
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage and with variables
{ |
A |
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage and variable |
action_name |
Name of the action variable in |
action_set |
Sorted character vector defining the action set. |
U |
(If |
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage:
d1 <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd1 <- policy_data(d1, action="A", covariates=list("Z", "B", "L"), utility="U")
pd1
# In the single stage case, set stage = NULL
h1 <- get_history(pd1)
head(h1$H)
head(h1$A)
### Two stages:
d2 <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd2 <- policy_data(d2,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd2
# getting the state/Markov-type history across all stages:
h2 <- get_history(pd2)
head(h2$H)
head(h2$A)
# getting the full history at stage 2:
h2 <- get_history(pd2, stage = 2, full_history = TRUE)
head(h2$H)
head(h2$A)
head(h2$U)
# getting the state/Markov-type history at stage 2:
h2 <- get_history(pd2, stage = 2, full_history = FALSE)
head(h2$H)
head(h2$A)
### Multiple stages
d3 <- sim_multi_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd3 <- policy_data(data = d3$stage_data,
baseline_data = d3$baseline_data,
type = "long",
id = "id",
stage = "stage",
event = "event",
action = "A",
utility = "U")
pd3
# getting the full history at stage 2:
h3 <- get_history(pd3, stage = 2, full_history = TRUE)
head(h3$H)
# note that not all observations have two stages:
nrow(h3$H) # number of observations with two stages.
get_n(pd3) # number of observations in total.
Nuisance Functions
Description
The fitted g-functions and Q-functions are stored in an object of class "nuisance_functions". The object is a list with a fitted model object for every stage. Information on whether the full history or the state/Markov-type history is stored as an attribute ("full_history").
S3 generics
The following S3 generic functions are available for an object of class
nuisance_functions:
predictPredict the values of the g- or Q-functions based on a policy_data object.
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
# evaluating the static policy a=1:
pe <- policy_eval(policy_data = pd,
policy = policy_def(1, reuse = TRUE),
g_models = g_glm(),
q_models = q_glm())
# getting the fitted g-functions:
(g_functions <- get_g_functions(pe))
# getting the fitted Q-functions:
(q_functions <- get_q_functions(pe))
# getting the fitted values:
head(predict(g_functions, pd))
head(predict(q_functions, pd))
Trim Number of Stages
Description
partial creates a partial policy data object by trimming
the maximum number of stages in the policy data object to a fixed
given number.
Usage
partial(object, K)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
K |
Maximum number of stages. |
Value
Object of class policy_data.
Examples
library("polle")
### Multiple stage case
d <- sim_multi_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(data = d$stage_data,
baseline_data = d$baseline_data,
type = "long",
id = "id",
stage = "stage",
event = "event",
action = "A",
utility = "U")
pd
# Creating a partial policy data object with 3 stages
pd3 <- partial(pd, K = 3)
pd3
Plot policy data for given policies
Description
Plot policy data for given policies
Usage
## S3 method for class 'policy_data'
plot(
x,
policy = NULL,
which = c(1),
stage = 1,
history_variables = NULL,
jitter = 0.05,
...
)
Arguments
x |
Object of class policy_data |
policy |
An object or list of objects of class policy |
which |
A subset of the numbers 1:2
|
stage |
Stage number for plot 2 |
history_variables |
character vector of length 2 for plot 2 |
jitter |
numeric |
... |
Additional arguments |
Examples
library("polle")
library("data.table")
setDTthreads(1)
d3 <- sim_multi_stage(2e2, seed = 1)
pd3 <- policy_data(data = d3$stage_data,
baseline_data = d3$baseline_data,
type = "long",
id = "id",
stage = "stage",
event = "event",
action = "A",
utility = "U")
pd3 <- partial(pd3, K = 3)
# specifying two static policies:
p0 <- policy_def(c(1,1,0), name = "p0")
p1 <- policy_def(c(1,0,0), name = "p1")
plot(pd3)
plot(pd3, policy = list(p0, p1))
# learning and plotting a policy:
pe3 <- policy_eval(pd3,
policy_learn = policy_learn(),
q_models = q_glm(formula = ~t + X + X_lead))
plot(pd3, list(get_policy(pe3), p0))
# plotting the recommended actions at a specific stage:
plot(pd3, get_policy(pe3),
which = 2,
stage = 2,
history_variables = c("t","X"))
Plot histogram of the influence curve for a policy_eval object
Description
Plot histogram of the influence curve for a policy_eval object
Usage
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
plot(x, ...)
Arguments
x |
Object of class policy_eval |
... |
Additional arguments |
Examples
d <- sim_two_stage(2e3, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = "BB",
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pe <- policy_eval(pd,
policy_learn = policy_learn())
plot(pe)
Policy-class
Description
A function of inherited class "policy" takes a policy data object as input and returns the policy actions for every observation for every (observed) stage.
Details
A policy can either be defined directly by the user using policy_def or a policy can be fitted using policy_learn (or policy_eval). policy_learn returns a policy_object from which the policy can be extracted using get_policy.
Value
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage and
action variable d.
S3 generics
The following S3 generic functions are available for an object of class
policy:
printBaisc print function
Examples
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
# defining a dynamic policy:
p <- policy_def(
function(L) (L>0)*1,
reuse = TRUE
)
p
head(p(pd), 5)
# V-restricted (Doubly Robust) Q-learning:
# specifying the learner:
pl <- policy_learn(type = "drql",
control = control_drql(qv_models = q_glm(formula = ~ C)))
# fitting the policy (object):
po <- pl(policy_data = pd,
q_models = q_glm(),
g_models = g_glm())
p <- get_policy(po)
p
head(p(pd))
Create Policy Data Object
Description
policy_data() creates a policy data object which
is used as input to policy_eval() and policy_learn() for policy
evaluation and data adaptive policy learning.
Usage
policy_data(
data,
baseline_data,
type = "wide",
action,
covariates,
utility,
baseline = NULL,
deterministic_rewards = NULL,
id = NULL,
stage = NULL,
event = NULL,
time = NULL,
time2 = NULL,
action_set = NULL,
verbose = FALSE
)
## S3 method for class 'policy_data'
print(x, digits = 2, ...)
## S3 method for class 'policy_data'
summary(object, probs = seq(0, 1, 0.25), ...)
Arguments
data |
data.frame or data.table::data.table; see Examples. |
baseline_data |
data.frame or data.table::data.table; see Examples. |
type |
Character string. If "wide", |
action |
Action variable name(s). Character vector or character string.
|
covariates |
Stage specific covariate name(s). Character vector or named list of character vectors.
|
utility |
Utility/Reward variable name(s). Character string or vector.
|
baseline |
Baseline covariate name(s). Character vector. |
deterministic_rewards |
Deterministic reward variable name(s). Named list of character vectors of length K. The name of each element must be on the form "U_Aa" where "a" corresponds to an action in the action set. |
id |
ID variable name. Character string. |
stage |
Stage number variable name. |
event |
Event indicator name. |
time |
Character string |
time2 |
Character string |
action_set |
Character string. Action set across all stages. |
verbose |
Logical. If TRUE, formatting comments are printed to the console. |
x |
Object to be printed. |
digits |
Minimum number of digits to be printed. |
... |
Additional arguments passed to print. |
object |
Object of class policy_data |
probs |
numeric vector (probabilities) |
Details
Each observation has the sequential form
O= {B, U_1, X_1, A_1,
..., U_K, X_K, A_K, U_{K+1}},
for a possibly stochastic number of stages K.
-
Bis a vector of baseline covariates. -
U_kis the reward at stage k (not influenced by the actionA_k). -
X_kis a vector of state covariates summarizing the state at stage k. -
A_kis the categorical action at stage k.
The utility is given by the sum of the rewards, i.e., U = \sum_{k =
1}^{K+1} U_k.
Value
policy_data() returns an object of class "policy_data". The
object is a list containing the following elements:
stage_data |
data.table::data.table containing the id, stage
number, event indicator, action ( |
baseline_data |
data.table::data.table containing the id and
baseline covariates ( |
colnames |
List containing the state covariate names, baseline covariate names, and the deterministic reward variable names. |
action_set |
Sorted character vector describing the action set, i.e., the possible actions at all stages. |
stage_action_sets |
List of sorted character vectors describing the observed actions at each stage. |
dim |
List containing the number of observations (n) and the number of stages (K). |
S3 generics
The following S3 generic functions are available for an
object of class policy_data:
partial()Trim the maximum number of stages in a
policy_dataobject.subset_id()Subset a a
policy_dataobject on ID.get_history()Summarize the history and action at a given stage.
get_history_names()Get history variable names.
get_actions()Get the action at every stage.
get_utility()Get the utility.
plot()Plot method.
See Also
policy_eval(), policy_learn(), copy_policy_data()
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage: Wide data
d1 <- sim_single_stage(n = 5e2, seed=1)
head(d1, 5)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd1 <- policy_data(d1,
action="A",
covariates=c("Z", "B", "L"),
utility="U")
pd1
# associated S3 methods:
methods(class = "policy_data")
head(get_actions(pd1), 5)
head(get_utility(pd1), 5)
head(get_history(pd1)$H, 5)
### Two stage: Wide data
d2 <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
head(d2, 5)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd2 <- policy_data(d2,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("B"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd2
head(get_history(pd2, stage = 2)$H, 5) # state/Markov type history and action, (H_k,A_k).
head(get_history(pd2, stage = 2, full_history = TRUE)$H, 5) # Full history and action, (H_k,A_k).
### Multiple stages: Long data
d3 <- sim_multi_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
head(d3$stage_data, 10)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd3 <- policy_data(data = d3$stage_data,
baseline_data = d3$baseline_data,
type = "long",
id = "id",
stage = "stage",
event = "event",
action = "A",
utility = "U")
pd3
head(get_history(pd3, stage = 3)$H, 5) # state/Markov type history and action, (H_k,A_k).
head(get_history(pd3, stage = 2, full_history = TRUE)$H, 5) # Full history and action, (H_k,A_k).
Define Policy
Description
policy_def returns a function of class policy.
The function input is a policy_data object and it returns a data.table::data.table
with keys id and stage and action variable d.
Usage
policy_def(policy_functions, full_history = FALSE, reuse = FALSE, name = NULL)
Arguments
policy_functions |
A single function/character string or a list of functions/character strings. The list must have the same length as the number of stages. |
full_history |
If TRUE, the full history at each stage is used as input to the policy functions. |
reuse |
If TRUE, the policy function is reused at every stage. |
name |
Character string. |
Value
Function of class "policy". The function takes a
policy_data object as input and returns a data.table::data.table
with keys id and stage and action variable d.
See Also
get_history_names(), get_history().
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage"
d1 <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd1 <- policy_data(d1, action="A", covariates=list("Z", "B", "L"), utility="U")
pd1
# defining a static policy (A=1):
p1_static <- policy_def(1)
# applying the policy:
p1_static(pd1)
# defining a dynamic policy:
p1_dynamic <- policy_def(
function(Z, L) ((3*Z + 1*L -2.5)>0)*1
)
p1_dynamic(pd1)
### Two stages:
d2 <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed = 1)
pd2 <- policy_data(d2,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
# defining a static policy (A=0):
p2_static <- policy_def(0,
reuse = TRUE)
p2_static(pd2)
# defining a reused dynamic policy:
p2_dynamic_reuse <- policy_def(
function(L) (L > 0)*1,
reuse = TRUE
)
p2_dynamic_reuse(pd2)
# defining a dynamic policy for each stage based on the full history:
# available variable names at each stage:
get_history_names(pd2, stage = 1)
get_history_names(pd2, stage = 2)
p2_dynamic <- policy_def(
policy_functions = list(
function(L_1) (L_1 > 0)*1,
function(L_1, L_2) (L_1 + L_2 > 0)*1
),
full_history = TRUE
)
p2_dynamic(pd2)
Policy Evaluation
Description
policy_eval() is used to estimate
the value of a given fixed policy
or a data adaptive policy (e.g. a policy
learned from the data). policy_eval()
is also used to estimate the average
treatment effect among the subjects who would
get the treatment under the policy.
Usage
policy_eval(
policy_data,
policy = NULL,
policy_learn = NULL,
g_functions = NULL,
g_models = g_glm(),
g_full_history = FALSE,
save_g_functions = TRUE,
q_functions = NULL,
q_models = q_glm(),
q_full_history = FALSE,
save_q_functions = TRUE,
c_functions = NULL,
c_models = NULL,
c_full_history = FALSE,
save_c_functions = TRUE,
m_function = NULL,
m_model = NULL,
m_full_history = FALSE,
save_m_function = TRUE,
target = "value",
type = "dr",
cross_fit_type = "pooled",
variance_type = "pooled",
M = 1,
nrep = 1,
min_subgroup_size = 1,
future_args = list(future.seed = TRUE),
name = NULL
)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
coef(object, ...)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
IC(x, ...)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
vcov(object, ...)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
print(
x,
digits = 4L,
width = 35L,
std.error = TRUE,
level = 0.95,
p.value = TRUE,
...
)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
summary(object, ...)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
estimate(
x,
labels = get_element(x, "name", check_name = FALSE),
level = 0.95,
...
)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
merge(x, y, ..., paired = TRUE)
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval'
x + ...
## S3 method for class 'policy_eval_online'
vcov(object, ...)
Arguments
policy_data |
Policy data object created by |
policy |
Policy object created by |
policy_learn |
Policy learner object created by |
g_functions |
Fitted g-model objects, see nuisance_functions.
Preferably, use |
g_models |
List of action probability models/g-models for each stage
created by |
g_full_history |
If TRUE, the full history is used to fit each g-model. If FALSE, the state/Markov type history is used to fit each g-model. |
save_g_functions |
If TRUE, the fitted g-functions are saved. |
q_functions |
Fitted Q-model objects, see nuisance_functions.
Only valid if the Q-functions are fitted using the same policy.
Preferably, use |
q_models |
Outcome regression models/Q-models created by
|
q_full_history |
Similar to g_full_history. |
save_q_functions |
Similar to save_g_functions. |
c_functions |
Fitted c-model/censoring probability model objects. Preferably, use |
c_models |
List of right-censoring probability models, see c_model. |
c_full_history |
Similar to g_full_history. |
save_c_functions |
Similar to save_g_functions. |
m_function |
Fitted outcome model object for stage K+1. Preferably, use |
m_model |
Outcome model for the utility at stage K+1. Only used if the final utility contribution is missing/has been right-censored |
m_full_history |
Similar to g_full_history. |
save_m_function |
Similar to save_g_functions. |
target |
Character string. Either "value" or "subgroup". If "value",
the target parameter is the policy value.
If "subgroup", the target parameter
is the average treatement effect among
the subgroup of subjects that would receive
treatment under the policy, see details.
"subgroup" is only implemented for |
type |
Character string. Type of evaluation. Either |
cross_fit_type |
Character string.
Either "stacked", or "pooled", see details. (Only used if |
variance_type |
Character string. Either "pooled" (default),
"stacked" or "complete", see details. (Only used if |
M |
Number of folds for cross-fitting. |
nrep |
Number of repetitions of cross-fitting (estimates averaged over repeated cross-fittings) |
min_subgroup_size |
Minimum number of observations in the evaluated subgroup (Only used if target = "subgroup"). |
future_args |
Arguments passed to |
name |
Character string. |
object, x, y |
Objects of class "policy_eval". |
... |
Additional arguments. |
digits |
Integer. Number of printed digits. |
width |
Integer. Width of printed parameter name. |
std.error |
Logical. Should the std.error be printed. |
level |
Numeric. Level of confidence limits. |
p.value |
Logical. Should the p.value for associated confidence level be printed. |
labels |
Name(s) of the estimate(s). |
paired |
|
Details
Each observation has the sequential form
O= {B, U_1, X_1, A_1, ..., U_K, X_K, A_K, U_{K+1}},
for a possibly stochastic number of stages K.
-
Bis a vector of baseline covariates. -
U_kis the reward at stage k (not influenced by the actionA_k). -
X_kis a vector of state covariates summarizing the state at stage k. -
A_kis the categorical action within the action set\mathcal{A}at stage k.
The utility is given by the sum of the rewards, i.e.,
U = \sum_{k = 1}^{K+1} U_k.
A policy is a set of functions
d = \{d_1, ..., d_K\},
where d_k for k\in \{1, ..., K\}
maps \{B, X_1, A_1, ..., A_{k-1}, X_k\} into the
action set.
Recursively define the Q-models (q_models):
Q^d_K(h_K, a_K) = E[U|H_K = h_K, A_K = a_K]
Q^d_k(h_k, a_k) = E[Q_{k+1}(H_{k+1},
d_{k+1}(B,X_1, A_1,...,X_{k+1}))|H_k = h_k, A_k = a_k].
If q_full_history = TRUE,
H_k = \{B, X_1, A_1, ..., A_{k-1}, X_k\}, and if
q_full_history = FALSE, H_k = \{B, X_k\}.
The g-models (g_models) are defined as
g_k(h_k, a_k) = P(A_k = a_k|H_k = h_k).
If g_full_history = TRUE,
H_k = \{B, X_1, A_1, ..., A_{k-1}, X_k\}, and if
g_full_history = FALSE, H_k = \{B, X_k\}.
Furthermore, if g_full_history = FALSE and g_models is a
single model, it is assumed that g_1(h_1, a_1) = ... = g_K(h_K, a_K).
If target = "value" and type = "or"
policy_eval() returns the empirical estimate of
the value (coef):
E\left[Q^d_1(H_1, d_1(\cdot))\right]
If target = "value" and type = "ipw" policy_eval()
returns the empirical estimates of
the value (coef) and influence curve (IC):
E\left[\left(\prod_{k=1}^K I\{A_k = d_k(\cdot)\}
g_k(H_k, A_k)^{-1}\right) U\right].
\left(\prod_{k=1}^K I\{A_k =
d_k(\cdot)\} g_k(H_k, A_k)^{-1}\right) U -
E\left[\left(\prod_{k=1}^K
I\{A_k = d_k(\cdot)\} g_k(H_k, A_k)^{-1}\right) U\right].
If target = "value" and
type = "dr" policy_eval returns the empirical estimates of
the value (coef) and influence curve (IC):
E[Z_1(d,g,Q^d)(O)],
Z_1(d, g, Q^d)(O) - E[Z_1(d,g, Q^d)(O)],
where
Z_1(d, g, Q^d)(O) = Q^d_1(H_1 , d_1(\cdot)) +
\sum_{r = 1}^K \prod_{j = 1}^{r}
\frac{I\{A_j = d_j(\cdot)\}}{g_{j}(H_j, A_j)}
\{Q_{r+1}^d(H_{r+1} , d_{r+1}(\cdot)) - Q_{r}^d(H_r , d_r(\cdot))\}.
If target = "subgroup", type = "dr", K = 1,
and \mathcal{A} = \{0,1\}, policy_eval()
returns the empirical estimates of the subgroup average
treatment effect (coef) and influence curve (IC):
E[Z_1(1,g,Q)(O) - Z_1(0,g,Q)(O) | d_1(\cdot) = 1],
\frac{1}{P(d_1(\cdot) = 1)} I\{d_1(\cdot) = 1\}
\Big\{Z_1(1,g,Q)(O) - Z_1(0,g,Q)(O) - E[Z_1(1,g,Q)(O)
- Z_1(0,g,Q)(O) | d_1(\cdot) = 1]\Big\}.
Applying M-fold cross-fitting using the {M} argument, let
\mathcal{Z}_{1,m}(a) = \{Z_1(a, g_m, Q_m^d)(O): O\in \mathcal{O}_m \}.
If target = "subgroup", type = "dr", K = 1,
\mathcal{A} = \{0,1\}, and cross_fit_type = "pooled",
policy_eval() returns the estimate
\frac{1}{{N^{-1} \sum_{i =
1}^N I\{d(H_i) = 1\}}} N^{-1} \sum_{m=1}^M \sum_{(Z, H) \in \mathcal{Z}_{1,m}
\times \mathcal{H}_{1,m}} I\{d_1(H) = 1\} \left\{Z(1)-Z(0)\right\}
If
cross_fit_type = "stacked" the returned estimate is
M^{-1}
\sum_{m = 1}^M \frac{1}{{n^{-1} \sum_{h \in \mathcal{H}_{1,m}} I\{d(h) =
1\}}} n^{-1} \sum_{(Z, H) \in \mathcal{Z}_{1,m} \times \mathcal{H}_{1,m}}
I\{d_1(H) = 1\} \left\{Z(1)-Z(0)\right\},
where for ease of notation we let
the integer n be the number of oberservations in each fold.
Value
policy_eval() returns an object of class "policy_eval".
The object is a list containing the following elements:
coef |
Numeric vector. The estimated target parameter: policy value or subgroup average treatment effect. |
IC |
Numeric matrix. Estimated influence curve associated with
|
type |
Character string. The type of evaluation ("dr", "ipw", "or"). |
target |
Character string. The target parameter ("value" or "subgroup") |
id |
Character vector. The IDs of the observations. |
name |
Character vector. Names for the each element in |
coef_ipw |
(only if |
coef_or |
(only if |
policy_actions |
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage. Actions associated with the policy for every observation and stage. |
policy_object |
(only if |
g_functions |
(only if |
g_values |
The fitted g-function values. |
q_functions |
(only if |
q_values |
The fitted Q-function values. |
Z |
(only if |
subgroup_indicator |
(only if |
cross_fits |
(only if |
folds |
(only if |
cross_fit_type |
Character string. |
variance_type |
Character string. |
S3 generics
The following S3 generic functions are available for an object of
class policy_eval:
get_g_functions()Extract the fitted g-functions.
get_q_functions()Extract the fitted Q-functions.
get_policy()Extract the fitted policy object.
get_policy_functions()Extract the fitted policy function for a given stage.
get_policy_actions()Extract the (fitted) policy actions.
plot.policy_eval()Plot diagnostics.
References
van der Laan, Mark J., and Alexander R. Luedtke.
"Targeted learning of the mean outcome under an optimal dynamic treatment rule."
Journal of causal inference 3.1 (2015): 61-95.
doi:10.1515/jci-2013-0022
Tsiatis, Anastasios A., et al. Dynamic
treatment regimes: Statistical methods for precision medicine. Chapman and
Hall/CRC, 2019. doi:10.1201/9780429192692.
Victor Chernozhukov, Denis
Chetverikov, Mert Demirer, Esther Duflo, Christian Hansen, Whitney Newey,
James Robins, Double/debiased machine learning for treatment and structural
parameters, The Econometrics Journal, Volume 21, Issue 1, 1 February 2018,
Pages C1–C68, doi:10.1111/ectj.12097.
See Also
lava::IC, lava::estimate.default.
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage:
d1 <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd1 <- policy_data(d1,
action = "A",
covariates = list("Z", "B", "L"),
utility = "U")
pd1
# defining a static policy (A=1):
pl1 <- policy_def(1)
# evaluating the policy:
pe1 <- policy_eval(policy_data = pd1,
policy = pl1,
g_models = g_glm(),
q_models = q_glm(),
name = "A=1 (glm)")
# summarizing the estimated value of the policy:
# (equivalent to summary(pe1)):
pe1
coef(pe1) # value coefficient
sqrt(vcov(pe1)) # value standard error
# getting the g-function and Q-function values:
head(predict(get_g_functions(pe1), pd1))
head(predict(get_q_functions(pe1), pd1))
# getting the fitted influence curve (IC) for the value:
head(IC(pe1))
# evaluating the policy using random forest nuisance models:
set.seed(1)
pe1_rf <- policy_eval(policy_data = pd1,
policy = pl1,
g_models = g_rf(),
q_models = q_rf(),
name = "A=1 (rf)")
# merging the two estimates (equivalent to pe1 + pe1_rf):
(est1 <- merge(pe1, pe1_rf))
coef(est1)
head(IC(est1))
### Two stages:
d2 <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd2 <- policy_data(d2,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd2
# defining a policy learner based on cross-fitted doubly robust Q-learning:
pl2 <- policy_learn(
type = "drql",
control = control_drql(qv_models = list(q_glm(~C_1),
q_glm(~C_1+C_2))),
full_history = TRUE,
L = 2) # number of folds for cross-fitting
# evaluating the policy learner using 2-fold cross fitting:
pe2 <- policy_eval(type = "dr",
policy_data = pd2,
policy_learn = pl2,
q_models = q_glm(),
g_models = g_glm(),
M = 2, # number of folds for cross-fitting
name = "drql")
# summarizing the estimated value of the policy:
pe2
# getting the cross-fitted policy actions:
head(get_policy_actions(pe2))
Online/Sequential Policy Evaluation
Description
policy_eval_online() is used to estimate
the value of a given fixed policy
or a data adaptive policy (e.g. a policy
learned from the data). policy_eval_online()
is also used to estimate the subgroup average
treatment effect as defined by the (learned) policy.
The evaluation is based on a online/sequential validation
estimation scheme making the estimation approach valid for a
non-converging policy under no heterogenuous treatment effect
(exceptional law), see details.
Usage
policy_eval_online(
policy_data,
policy = NULL,
policy_learn = NULL,
g_functions = NULL,
g_models = g_glm(),
g_full_history = FALSE,
save_g_functions = TRUE,
q_functions = NULL,
q_models = q_glm(),
q_full_history = FALSE,
save_q_functions = TRUE,
c_functions = NULL,
c_models = NULL,
c_full_history = FALSE,
save_c_functions = TRUE,
m_function = NULL,
m_model = NULL,
m_full_history = FALSE,
save_m_function = TRUE,
target = "value",
M = 4,
train_block_size = get_n(policy_data)/5,
name = NULL,
min_subgroup_size = 1
)
Arguments
policy_data |
Policy data object created by |
policy |
Policy object created by |
policy_learn |
Policy learner object created by |
g_functions |
Fitted g-model objects, see nuisance_functions.
Preferably, use |
g_models |
List of action probability models/g-models for each stage
created by |
g_full_history |
If TRUE, the full history is used to fit each g-model. If FALSE, the state/Markov type history is used to fit each g-model. |
save_g_functions |
If TRUE, the fitted g-functions are saved. |
q_functions |
Fitted Q-model objects, see nuisance_functions.
Only valid if the Q-functions are fitted using the same policy.
Preferably, use |
q_models |
Outcome regression models/Q-models created by
|
q_full_history |
Similar to g_full_history. |
save_q_functions |
Similar to save_g_functions. |
c_functions |
Fitted c-model/censoring probability model objects. Preferably, use |
c_models |
List of right-censoring probability models, see c_model. |
c_full_history |
Similar to g_full_history. |
save_c_functions |
Similar to save_g_functions. |
m_function |
Fitted outcome model object for stage K+1. Preferably, use |
m_model |
Outcome model for the utility at stage K+1. Only used if the final utility contribution is missing/has been right-censored |
m_full_history |
Similar to g_full_history. |
save_m_function |
Similar to save_g_functions. |
target |
Character string. Either "value" or "subgroup". If "value",
the target parameter is the policy value.
If "subgroup", the target parameter
is the subgroup average treatement effect given by the policy, see details.
"subgroup" is only implemented for |
M |
Number of folds for online estimation/sequential validation excluding the initial training block, see details. |
train_block_size |
Integer. Size of the initial training block only used for training of the policy and nuisance models, see details. |
name |
Character string. |
min_subgroup_size |
Minimum number of observations in the evaluated subgroup (Only used if target = "subgroup"). |
Details
Setup
Each observation has the sequential form
O= {B, U_1, X_1, A_1, ..., U_K, X_K, A_K, U_{K+1}},
for a possibly stochastic number of stages K.
-
Bis a vector of baseline covariates. -
U_kis the reward at stage k (not influenced by the actionA_k). -
X_kis a vector of state covariates summarizing the state at stage k. -
A_kis the categorical action within the action set\mathcal{A}at stage k.
The utility is given by the sum of the rewards, i.e.,
U = \sum_{k = 1}^{K+1} U_k.
A (subgroup) policy is a set of functions
d = \{d_1, ..., d_K\},
where d_k for k\in \{1, ..., K\}
maps a subset or function V_1 of \{B, X_1, A_1, ..., A_{k-1}, X_k\} into the
action set (or set of subgroups).
Recursively define the Q-models (q_models):
Q^d_K(h_K, a_K) = \mathbb{E}[U|H_K = h_K, A_K = a_K]
Q^d_k(h_k, a_k) = \mathbb{E}[Q_{k+1}(H_{k+1},
d_{k+1}(V_{k+1}))|H_k = h_k, A_k = a_k].
If q_full_history = TRUE,
H_k = \{B, X_1, A_1, ..., A_{k-1}, X_k\}, and if
q_full_history = FALSE, H_k = \{B, X_k\}.
The g-models (g_models) are defined as
g_k(h_k, a_k) = \mathbb{P}(A_k = a_k|H_k = h_k).
If g_full_history = TRUE,
H_k = \{B, X_1, A_1, ..., A_{k-1}, X_k\}, and if
g_full_history = FALSE, H_k = \{B, X_k\}.
Furthermore, if g_full_history = FALSE and g_models is a
single model, it is assumed that g_1(h_1, a_1) = ... = g_K(h_K, a_K).
Target parameters
If target = "value", policy_eval_online
returns the estimates of
the value, i.e., the expected potential utility under the policy, (coef):
\mathbb{E}[U^{(d)}]
If target = "subgroup", K = 1, \mathcal{A} = \{0,1\},
and d_1(V_1) \in \{s_1, s_2\} , policy_eval()
returns the estimates of the subgroup average
treatment effect (coef):
\mathbb{E}[U^{(1)} - U^{(0)}| d_1(\cdot) = s]\quad s\in \{s_1,s_2\},
Online estimation/sequential validation
Estimation of the target parameter is based online estimation/sequential
validation using the doubly robust score. The following figure illustrate
online estimation using M = 5 steps and an initial training block of
size train_block_size = l.
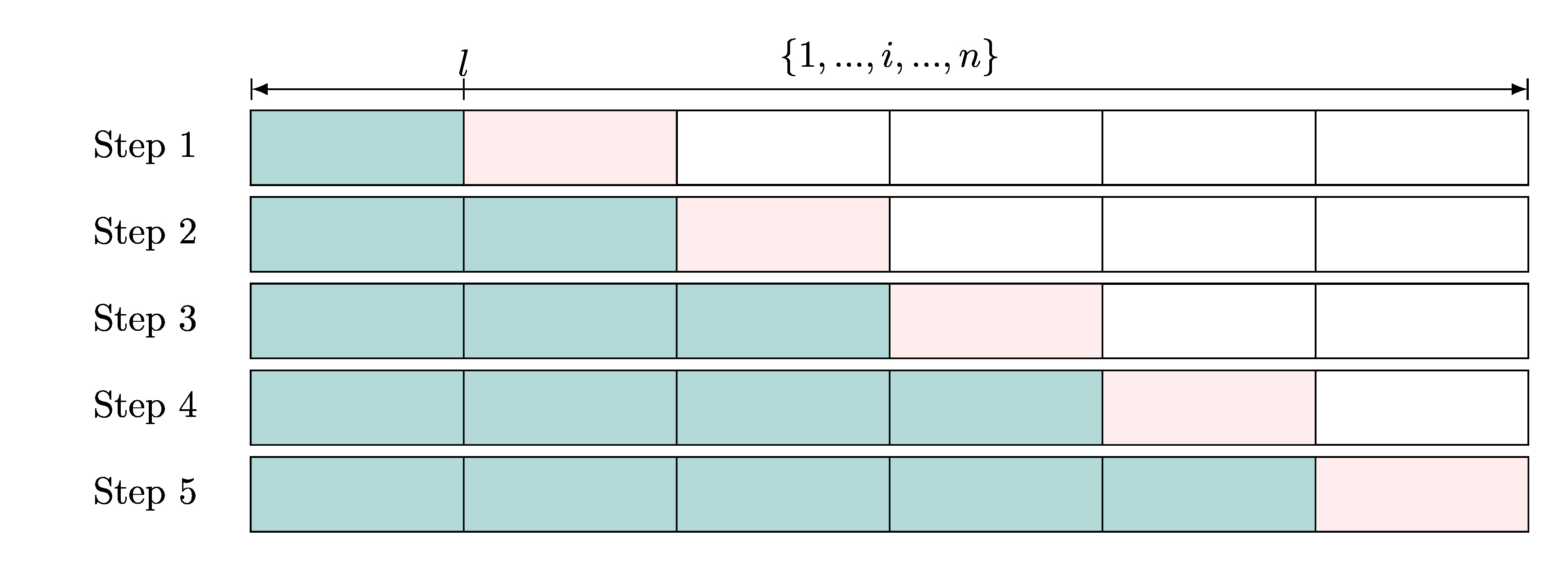
Step 1:
The n observations are randomly ordered. In step 1,
the first \{1,...,l\} observations, highlighted in teal/blue, are used to fit the
Q-models, g-models, the policy (if using the policy_learn argument), and other required models.
We denote the collection of these fitted models as P.
The remaining observations are split into M blocks of size m = (n-l)/M, which
we for simplicity assume to be a whole number. In step 1, the target
parameter is estimated using the associated doubly robust score Z(P)
evaluated on the first validation fold
highlighted in pink \{l+1,...,l+m\}:
\frac{\sum_{i = l+1}^{l+m} {\widehat \sigma_{i}^{-1}}
Z(\widehat P_i)(O_i)}
{\sum_{i = l+1}^{l+m} \widehat \sigma_{i}^{-1}},
where \widehat P_i for i \in \{l+1,...,l+m\}
refer to the fitted models trained on \{1,...,l\}, and \widehat \sigma_i
is the insample estimate for the standard deviation based on the training observations \{1,...,l\}.
We will later give an exact expression for \widehat \sigma_i for each target parameter.
Note that \widehat \sigma_i is constant for i \in \{l+1,...,l+m\}, but it will be
convenient to keep the same index for \widehat \sigma.
Step 2 to M:
In step 2, observations with index \{1,...,l+m\} are used to fit the model collection P,
as well as the insample estimate for the standard deviation. For i \in \{l+m+1,...,l+2m\} these are
denoted as \widehat P_i, \widehat \sigma_i.
This sequential model fitting is repeated for all M
steps and the updated online estimator is given by
\frac{\sum_{i = l+1}^{n} {\widehat \sigma_{i}^{-1}}
Z(\widehat P_i)(O_i)}
{\sum_{i = l+1}^n \widehat \sigma_{i}^{-1}},
with an associated standard error estimate given by
\frac{\left(\frac{1}{n-l}\sum_{i = l+1}^n \widehat \sigma_{i}^{-1}\right)^{-1}}{\sqrt{n-l}}.
Doubly robust scores
target = "value":
For a policy value target the doubly robust score is given by
Z(d, g, Q^d)(O) = Q^d_1(H_1 , d_1(V_1)) +
\sum_{r = 1}^K \prod_{j = 1}^{r}
\frac{I\{A_j = d_j(\cdot)\}}{g_{j}(H_j, A_j)}
\{Q_{r+1}^d(H_{r+1} , d_{r+1}(V_1)) - Q_{r}^d(H_r , d_r(V_1))\}.
The influence function(/curve) for the associated onestep etimator is
Z(d, g, Q^d)(O) - \mathbb{E}[Z(d,g, Q^d)(O)],
which is used to estimate the insample stadard deviation. For example,
in step 2, i.e., for i \in \{l+m+1,...,l+2m\}
\widehat \sigma_i^2 = \frac{1}{l+m}\sum_{j=1}^{l+m} \left(Z(\widehat d_i,\widehat Q_i,\widehat{g}_i)(O_j) - \frac{1}{l+m}\sum_{r=1}^{l+m} Z(\widehat d_i,\widehat Q_i,\widehat{g}_i)(O_r) \right)^2
target = "subgroup":
For a subgroup average treatment effect target,
where K = 1 (single-stage),
\mathcal{A} = \{0,1\} (binary treatment), and
d_1(V_1) \in \{s_1, s_2\} (dichotomous subgroup policy) the
doubly robust score is given by
Z(d,g,Q, D) = \frac{I\{d_1(\cdot) = s\}}{D}
\Big\{Z_1(1,g,Q)(O) - Z_1(0,g,Q)(O) \Big\}.
Z_1(a, g, Q)(O) = Q_1(H_1 , a) +
\frac{I\{A = a\}}{g_1(H_1, a)}
\{U - Q_{1}(H_1 , a)\},
where D is \mathbb{P}(d_1(V_1) = s).
The associated onestep/estimating equation estimator has influence function
\frac{ I\{d_1(\cdot) = s\}}{D}
\Big\{Z_1(1,g,Q)(O) - Z_1(0,g,Q)(O) - E[Z_1(1,g,Q)(O)
- Z_1(0,g,Q)(O) | d_1(\cdot) = s]\Big\},
which is used to estimate the standard deviation \widehat \sigma.
Value
policy_eval_online() returns an object of inherited class "policy_eval_online", "policy_eval".
The object is a list containing the following elements:
coef |
Numeric vector. The estimated target parameters: policy value or subgroup average treatment effect. |
vcov |
Numeric vector. The estimated squared standard deviation associated with
|
target |
Character string. The target parameter ("value" or "subgroup") |
id |
Character vector. The IDs of the observations. |
name |
Character vector. Names for the each element in |
train_sequential_index |
list of indexes used for training at each step. |
valid_sequential_index |
list of indexes used for validation at each step. |
References
Luedtke, Alexander R, and Mark J van der Laan. “STATISTICAL INFERENCE FOR THE MEAN OUTCOME UNDER A POSSIBLY NON-UNIQUE OPTIMAL TREATMENT STRATEGY.” Annals of statistics vol. 44,2 (2016): 713-742. doi:10.1214/15-AOS1384
Create Policy Learner
Description
policy_learn() is used to specify a policy
learning method (Q-learning,
doubly robust Q-learning, policy tree
learning and outcome weighted learning).
Evaluating the policy learner returns a policy object.
Usage
policy_learn(
type = "blip",
control = control_blip(),
alpha = 0,
threshold = NULL,
full_history = FALSE,
L = 1,
cross_fit_g_models = TRUE,
cross_fit_c_models = TRUE,
save_cross_fit_models = FALSE,
future_args = list(future.seed = TRUE),
name = type
)
## S3 method for class 'policy_learn'
print(x, ...)
## S3 method for class 'policy_object'
print(x, ...)
Arguments
type |
Type of policy learner method:
|
control |
List of control arguments.
Values (and default values) are set using
|
alpha |
Probability threshold for determining realistic actions. |
threshold |
Numeric vector, thresholds for not choosing the reference action at stage 1. |
full_history |
If |
L |
Number of folds for cross-fitting nuisance models. |
cross_fit_g_models |
If |
cross_fit_c_models |
If |
save_cross_fit_models |
If |
future_args |
Arguments passed to |
name |
Character string. |
x |
Object of class "policy_object" or "policy_learn". |
... |
Additional arguments passed to print. |
Value
Function of inherited class "policy_learn".
Evaluating the function on a policy_data object returns an object of
class policy_object. A policy object is a list containing all or
some of the following elements:
q_functionsFitted Q-functions. Object of class "nuisance_functions".
g_functionsFitted g-functions. Object of class "nuisance_functions".
action_setSorted character vector describing the action set, i.e., the possible actions at each stage.
alphaNumeric. Probability threshold to determine realistic actions.
KInteger. Maximal number of stages.
qv_functions(only if
type = "drql") Fitted V-restricted Q-functions. Contains a fitted model for each stage and action.ptl_objects(only if
type = "ptl") Fitted V-restricted policy trees. Contains a policytree::policy_tree for each stage.ptl_designs(only if
type = "ptl") Specification of the V-restricted design matrix for each stage
S3 generics
The following S3 generic functions are available for an object of class "policy_object":
get_g_functions()Extract the fitted g-functions.
get_q_functions()Extract the fitted Q-functions.
get_policy()Extract the fitted policy object.
get_policy_functions()Extract the fitted policy function for a given stage.
get_policy_actions()Extract the (fitted) policy actions.
References
Doubly Robust Q-learning (type = "drql"): Luedtke, Alexander R., and
Mark J. van der Laan. "Super-learning of an optimal dynamic treatment rule."
The international journal of biostatistics 12.1 (2016): 305-332.
doi:10.1515/ijb-2015-0052.
Policy Tree Learning (type = "ptl"): Zhou, Zhengyuan, Susan Athey,
and Stefan Wager. "Offline multi-action policy learning: Generalization and
optimization." Operations Research (2022). doi:10.1287/opre.2022.2271.
(Augmented) Outcome Weighted Learning: Liu, Ying, et al. "Augmented
outcome‐weighted learning for estimating optimal dynamic treatment regimens."
Statistics in medicine 37.26 (2018): 3776-3788. doi:10.1002/sim.7844.
See Also
Examples
library("polle")
### Two stages:
d <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
baseline = c("BB"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd
### V-restricted (Doubly Robust) Q-learning
# specifying the learner:
pl <- policy_learn(
type = "drql",
control = control_drql(qv_models = list(q_glm(formula = ~ C_1 + BB),
q_glm(formula = ~ L_1 + BB))),
full_history = TRUE
)
# evaluating the learned policy
pe <- policy_eval(policy_data = pd,
policy_learn = pl,
q_models = q_glm(),
g_models = g_glm())
pe
# getting the policy object:
po <- get_policy_object(pe)
# inspecting the fitted QV-model for each action strata at stage 1:
po$qv_functions$stage_1
head(get_policy(pe)(pd))
Predict g-functions and Q-functions
Description
predict() returns the fitted values of the g-functions and
Q-functions when applied to a (new) policy data object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'nuisance_functions'
predict(object, new_policy_data, event_set = c(0), ...)
Arguments
object |
Object of class "nuisance_functions". Either |
new_policy_data |
Policy data object created by |
event_set |
Subset of the events considered. Action events (0), terminal events (1), or right-censoring events (2) |
... |
Additional arguments. |
Value
data.table::data.table with keys id and stage and variables g_a or Q_a for
each action a in the actions set.
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage:
d <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd <- policy_data(d, action="A", covariates=list("Z", "B", "L"), utility="U")
pd
# defining a static policy (A=1):
pl <- policy_def(1, name = "A=1")
# doubly robust evaluation of the policy:
pe <- policy_eval(policy_data = pd,
policy = pl,
g_models = g_glm(),
q_models = q_glm())
# summarizing the estimated value of the policy:
pe
# getting the fitted g-function values:
head(predict(get_g_functions(pe), pd))
# getting the fitted Q-function values:
head(predict(get_q_functions(pe), pd))
q_model class object
Description
Use q_glm(), q_glmnet(), q_rf(), and q_sl() to construct
an outcome regression model/Q-model object.
The constructors are used as input for policy_eval() and policy_learn().
Usage
q_glm(
formula = ~A * .,
family = gaussian(),
model = FALSE,
na.action = na.pass,
...
)
q_glmnet(
formula = ~A * .,
family = "gaussian",
alpha = 1,
s = "lambda.min",
...
)
q_rf(
formula = ~.,
num.trees = c(250, 500, 750),
mtry = NULL,
cv_args = list(nfolds = 3, rep = 1),
...
)
q_sl(
formula = ~.,
SL.library = c("SL.mean", "SL.glm"),
env = parent.frame(),
onlySL = TRUE,
discreteSL = FALSE,
...
)
q_xgboost(
formula = ~.,
objective = "reg:squarederror",
nrounds,
max_depth = 6,
learning_rate = NULL,
nthread = 1,
cv_args = list(nfolds = 3, rep = 1),
...
)
Arguments
formula |
An object of class formula specifying the design matrix for
the outcome regression model/Q-model at the given stage. The action at the
given stage is always denoted 'A', see examples. Use
|
family |
A description of the error distribution and link function to be used in the model. |
model |
(Only used by |
na.action |
(Only used by |
... |
Additional arguments passed to |
alpha |
(Only used by |
s |
(Only used by |
num.trees |
(Only used by |
mtry |
(Only used by |
cv_args |
(Only used by |
SL.library |
(Only used by |
env |
(Only used by |
onlySL |
(Only used by |
discreteSL |
(Only used by |
objective |
(Only used by |
nrounds |
(Only used by |
max_depth |
(Only used by |
learning_rate |
(Only used by |
nthread |
(Only used by |
Details
q_glm() is a wrapper of glm() (generalized linear model).
q_glmnet() is a wrapper of glmnet::glmnet() (generalized linear model via
penalized maximum likelihood).
q_rf() is a wrapper of ranger::ranger() (random forest).
When multiple hyper-parameters are given, the
model with the lowest cross-validation error is selected.
q_sl() is a wrapper of SuperLearner::SuperLearner (ensemble model).
q_xgboost() is a wrapper of xgboost::xgboost.
Value
q_model object: function with arguments 'AH' (combined action and history matrix) and 'V_res' (residual value/expected utility).
See Also
get_history_names(), get_q_functions().
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage case
d1 <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd1 <- policy_data(d1,
action="A",
covariates=list("Z", "B", "L"),
utility="U")
pd1
# available history variable names for the outcome regression:
get_history_names(pd1)
# evaluating the static policy a=1 using inverse
# propensity weighting based on the given Q-model:
pe1 <- policy_eval(type = "or",
policy_data = pd1,
policy = policy_def(1, name = "A=1"),
q_model = q_glm(formula = ~A*.))
pe1
# getting the fitted Q-function values
head(predict(get_q_functions(pe1), pd1))
### Two stages:
d2 <- sim_two_stage(5e2, seed=1)
pd2 <- policy_data(d2,
action = c("A_1", "A_2"),
covariates = list(L = c("L_1", "L_2"),
C = c("C_1", "C_2")),
utility = c("U_1", "U_2", "U_3"))
pd2
# available full history variable names at each stage:
get_history_names(pd2, stage = 1)
get_history_names(pd2, stage = 2)
# evaluating the static policy a=1 using outcome
# regression based on a glm model for each stage:
pe2 <- policy_eval(type = "or",
policy_data = pd2,
policy = policy_def(1, reuse = TRUE, name = "A=1"),
q_model = list(q_glm(~ A * L_1),
q_glm(~ A * (L_1 + L_2))),
q_full_history = TRUE)
pe2
# getting the fitted Q-function values
head(predict(get_q_functions(pe2), pd2))
Objects exported from other packages
Description
These objects are imported from other packages. Follow the links below to see their documentation.
Simulate Multi-Stage Data
Description
Simulate Multi-Stage Data
Usage
sim_multi_stage(
n,
par = list(tau = 10, gamma = c(0, -0.2, 0.3), alpha = c(0, 0.5, 0.2, -0.5, 0.4), beta =
c(3, -0.5, -0.5), psi = 1, xi = 0.3),
a = function(t, x, beta, ...) {
prob <- lava::expit(beta[1] + (beta[2] * t^2) +
(beta[3] * x))
stats::rbinom(n = 1, size = 1, prob = prob)
},
seed = NULL
)
Arguments
n |
Number of observations. |
par |
Named list with distributional parameters.
|
a |
Function used to specify the action/treatment at every stage. |
seed |
Integer. |
Details
sim_multi_stage samples n iid observation
O with the following distribution:
W \sim \mathcal{N}(0, 1)\\
B \sim Ber(\xi)
For k\geq 1 let
(T_k - T_{k-1})| X_{k-1}, A_{k-1}, W \sim
\begin{cases}
Exp\Big\{\exp\left(\gamma^T [1, X_{k-1}, W] \right) \Big\} + \psi \quad A_{k-1} = 1\\
\infty \quad A_{k-1} = 0
\end{cases}\\
X_{k}\mid T_k, X_{k-1}, B \sim
\begin{cases}
\mathcal{N}\left\{ \alpha^T [1, T_k, T^2_k, X_{k-1}, B], 1\right\} \quad T_k < \infty \\
0 \quad T_k = \infty
\end{cases}\\
A_k \mid X_k, T_k \sim
\begin{cases}
Ber\left\{ expit\left(\beta^T[1, T_{k}^2, X_k] \right)\right\} \quad T_k < \infty\\
0 \quad T_k = \infty,
\end{cases}
Note that \psi is the minimum increment.
Value
list with elements stage_data (data.table::data.table) and
baseline_data (data.table::data.table).
Simulate Single-Stage Data
Description
Simulate Single-Stage Data
Usage
sim_single_stage(
n = 10000,
par = c(k = 0.1, d = 0.5, a = 1, b = -2.5, c = 3, p = 0.3),
action_model = function(Z, L, B, k, d) {
k * (Z + L - 1) * Z^(-2) + d * (B == 1)
},
utility_model = function(Z, L, A, a, b, c) {
Z + L + A * (c * Z + a * L + b)
},
seed = NULL,
return_model = FALSE,
...
)
Arguments
n |
Number of observations. |
par |
Named vector with distributional parameters.
|
action_model |
Function used to specify the action/treatment probability (logit link). |
utility_model |
Function used to specify the conditional mean utility. |
seed |
Integer. |
return_model |
If TRUE, the lava::lvm model is returned. |
... |
Additional arguments passed to |
Details
sim_single_stage samples n iid observation
O = (B, Z, L, A, U) with the following distribution:
B \sim Bernoulli(\pi)\\
Z, L \sim Uniform([0,1])\\
A\mid Z,L,B \sim Bernoulli(expit\{\kappa Z^{-2}(Z+L-1) + \delta B)\\
U\mid Z,L,A \sim \mathcal{N}(Z+L+A\cdot\{\gamma Z + \alpha L + \beta\}, 1)
Value
data.frame with n rows and columns Z, L, B, A, and U.
Simulate Single-Stage Multi-Action Data
Description
Simulate Single-Stage Multi-Action Data
Usage
sim_single_stage_multi_actions(n = 1000, seed = NULL)
Arguments
n |
Number of observations. |
seed |
Integer. |
Details
sim_single_stage_multi_actions samples n iid observation
O = (z, x, a, u) with the following distribution:
z, x \sim Uniform([0,1])\\
\tilde a \sim \mathcal{N}(0,1)\\
a \mid \tilde a \sim
\begin{cases}
0 \quad if \quad \tilde a < -1\\
1 \quad if \quad \tilde a -1 \leq a < 0.5\\
2 \quad otherwise
\end{cases}\\
u \mid z, x \sim \mathcal{N}(x + z + I\{a=2\}(x-0.5) + I\{a=1\}(x^2 + z -0.5), 1)
Value
data.frame with n rows and columns z, x, a, and u.
Simulate Two-Stage Data
Description
Simulate Two-Stage Data
Usage
sim_two_stage(
n = 10000,
par = c(gamma = 0.5, beta = 1),
seed = NULL,
action_model_1 = function(C_1, beta, ...) stats::rbinom(n = NROW(C_1), size = 1, prob =
lava::expit(beta * C_1)),
action_model_2 = function(C_2, beta, ...) stats::rbinom(n = NROW(C_2), size = 1, prob =
lava::expit(beta * C_2)),
deterministic_rewards = FALSE
)
Arguments
n |
Number of observations. |
par |
Named vector with distributional parameters.
|
seed |
Integer. |
action_model_1 |
Function used to specify the action/treatment at stage 1. |
action_model_2 |
Function used to specify the action/treatment at stage 2. |
deterministic_rewards |
Logical. If TRUE, the deterministic reward contributions are returned as well (columns U_1_A0, U_1_A1, U_2_A0, U_2_A1). |
Details
sim_two_stage samples n iid observation
O with the following distribution:
BB is a random categorical variable with levels group1,
group2, and group3. Furthermore,
B \sim \mathcal{N}(0,1)\\
L_{1} \sim \mathcal{N}(0, 1)\\
C_{1} \mid L_{1} \sim \mathcal{N}(L_1, 1)\\
A_1 \mid C_1 \sim Bernoulli(expit(\beta C_1))\\
L_{2} \sim \mathcal{N} (0, 1)\\
C_{2} \mid A_1, L_1 \sim \mathcal{N}(\gamma L_1 + A_1, 1)\\
A_2 \mid C_2 \sim Bernoulli(expit(\beta C_2))\\
L_{3} \sim \mathcal{N} (0, 1)
The rewards are calculated as
U_1 = L_1\\
U_2 = A_1\cdot C_1 + L_2 \\
U_3 = A_2\cdot C_2 + L_3.
Value
data.table::data.table with n rows and columns B, BB, L_1, C_1, A_1, L_2, C_2, A_2, L_3, U_1, U_2, U_3 (,U_1_A0, U_1_A1, U_2_A0, U_2_A1).
Simulate Two-Stage Multi-Action Data
Description
Simulate Two-Stage Multi-Action Data
Usage
sim_two_stage_multi_actions(
n = 1000,
par = list(gamma = 0.5, beta = 1, prob = c(0.2, 0.4, 0.4)),
seed = NULL,
action_model_1 = function(C_1, beta, ...) stats::rbinom(n = NROW(C_1), size = 1, prob =
lava::expit(beta * C_1))
)
Arguments
n |
Number of observations. |
par |
Named vector with distributional parameters.
|
seed |
Integer. |
action_model_1 |
Function used to specify the dichotomous action/treatment at stage 1. |
Details
sim_two_stage_multi_actions samples n iid observation
O with the following distribution:
BB is a random categorical variable with levels group1,
group2, and group3. Furthermore,
B \sim \mathcal{N}(0,1)\\
L_{1} \sim \mathcal{N}(0, 1)\\
C_{1} \mid L_{1} \sim \mathcal{N}(L_1, 1)\\
P(A_1='yes'\mid C_1) = expit(\beta C_1)\\
P(A_1='no'\mid C_1) = 1 - P(A_1='yes' \mid C_1)\\
L_{2} \sim \mathcal{N} (0, 1)\\
C_{2} \mid A_1, L_1 \sim \mathcal{N}(\gamma L_1 + A_1, 1)\\
P(A_2='yes') = p_1\\
P(A_2='no') = p_2\\
P(A_2='default') = p_3\\
L_{3} \sim \mathcal{N} (0, 1)
The rewards are calculated as
U_1 = L_1\\
U_2 = A_1\cdot C_1 + L_2 \\
U_3 = A_2\cdot C_2 + L_3.
Value
data.table::data.table with n rows and columns B, BB, L_1, C_1, A_1, L_2, C_2, A_2, L_3, U_1, U_2, U_3.
Subset Policy Data on ID
Description
subset_id returns a policy data object containing the given IDs.
Usage
subset_id(object, id, preserve_action_set = TRUE)
Arguments
object |
Object of class policy_data. |
id |
character vectors of IDs. |
preserve_action_set |
If TRUE, the action sets must be preserved. |
Value
Object of class policy_data.
Examples
library("polle")
### Single stage:
d <- sim_single_stage(5e2, seed=1)
# constructing policy_data object:
pd <- policy_data(d, action="A", covariates=list("Z", "B", "L"), utility="U")
pd
# getting the observation IDs:
get_id(pd)[1:10]
# subsetting on IDs:
pdsub <- subset_id(pd, id = 250:500)
pdsub
get_id(pdsub)[1:10]