
The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.

osfr provides a suite of functions for interacting with the Open Science Framework (OSF).
What is OSF?
OSF is a free and open source project management repository designed to support researchers across their entire project lifecycle. The service includes unlimited cloud storage and file version history, providing a centralized location for all your research materials that can be kept private, shared with select collaborators, or made publicly available with citable DOIs.
You can install the current release of osfr from CRAN (recommended):
install.packages("osfr")Or the development version from GitHub with the remotes package:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("ropensci/osfr")Note: You need to setup an OSF personal access token (PAT) to use osfr to manage projects or upload files.
Many researchers use OSF to archive and share their work. You can use osfr to explore publicly accessible projects and download the associated files—all you need to get started is the project’s URL or GUID (global unique identifier).
Every user, project, component, and file on OSF is assigned a GUID
that is embedded in the corresponding entity’s URL. For example, you can
access the main OSF project for the Cancer Reproducibility
Project at https://osf.io/e81xl/. The GUID for this project is
e81xl.
We can then use osfr to retrieve this project and load it into R by providing the GUID:
library(osfr)
cr_project <- osf_retrieve_node("e81xl")
cr_project
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> name id meta
#> <chr> <chr> <list>
#> 1 Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology e81xl <named list [3]>This returns an osf_tbl object with a single row
representing the retrieved project. Let’s list the files that have been
uploaded to this project.
osf_ls_files(cr_project)
#> # A tibble: 4 × 3
#> name id meta
#> <chr> <chr> <list>
#> 1 papers_and_keywords.xlsx 553e671b8c5e4a219919… <named list>
#> 2 Full_dataset_of_papers_formatted.xls 553e671b8c5e4a219919… <named list>
#> 3 METHOD_to_select_papers.txt 553e671b8c5e4a219919… <named list>
#> 4 Adjustment of 50 studies to 37 studies.docx 565602398c5e4a3877d7… <named list>This returns another osf_tbl with 1 row for each of the
files and directories in the project. We can examine any of these files
directly on OSF with osf_open(), which opens the
corresponding file’s view in your default browser.
This project contains 2 components:
Replication Studies and Data collection and publishing
guidelines. We can list these components with osfr using
osf_ls_nodes().
osf_ls_nodes(cr_project)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 3
#> name id meta
#> <chr> <chr> <list>
#> 1 Meta-analysis paper figures and tables squy7 <named list>
#> 2 Replication Data from the Reproducibility Project: Cancer … e5nvr <named list>
#> 3 Process paper figures and reported statistics 35ut8 <named list>
#> 4 Replication Studies p7ayb <named list>
#> 5 Data collection and publishing guidelines a5imq <named list>osfr is compatible with the pipe operator and dplyr, providing a powerful set
of tools for working with osf_tbls. Here, we’re listing the
sub-components nested within the Replication Studies component,
filtering for a specific study (Study 19) and then listing the
files uploaded to that study’s component.
library(dplyr)
cr_project %>%
osf_ls_nodes() %>%
filter(name == "Replication Studies") %>%
osf_ls_nodes(pattern = "Study 19") %>%
osf_ls_files()
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> name id meta
#> <chr> <chr> <list>
#> 1 Replication_Study_19.Rmd 578e2b23594d9001f48164… <named list>
#> 2 Study_19_Correction_Letter.docx 5a56569125719b000ff28b… <named list>
#> 3 Replication_Study_19.docx 57c9e8ed594d9001e7a240… <named list>
#> 4 Response_letter_Replication_Study_19.docx 58755747b83f6901ff066a… <named list>
#> 5 Replication_Study_19_track_changes.docx 581a27b76c613b02233228… <named list>
#> 6 Replication_Study_19_track_changes_2.docx 58714d46594d9001f801f4… <named list>We could continue this pattern of exploration and even download local
copies of project files using osf_download(). Or, if you
come across a publication that directly references a file’s OSF URL, you
could quickly download it to your project directory by providing the URL
or simply the GUID:
osf_retrieve_file("https://osf.io/btgx3/") %>%
osf_download()
#> # A tibble: 1 × 4
#> name id local_path meta
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <list>
#> 1 Study_19_Figure_1.pdf btgx3 ./Study_19_Figure_1.pdf <named list [3]>You can use osfr to create projects, add sub-components or directories, and upload files. See Getting Started to learn more about building projects with osfr, but here is a quick example in which we:
mtcars.csv) to the new directory# create an external data file
write.csv(mtcars, "mtcars.csv")
osf_create_project(title = "Motor Trend Car Road Tests") %>%
osf_create_component("Car Data") %>%
osf_mkdir("rawdata") %>%
osf_upload("mtcars.csv") %>%
osf_open()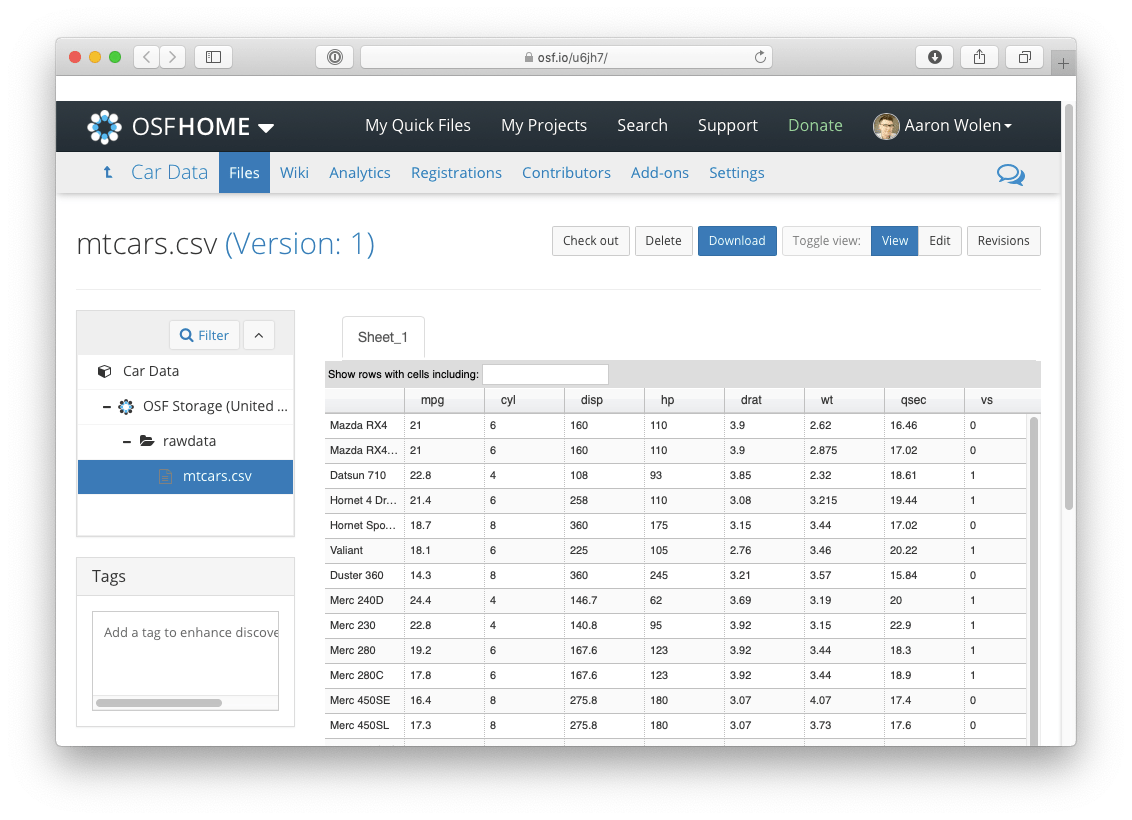
osf_tblsThere are 3 main types of OSF entities that osfr can work with:
osfr represents these entities within
osf_tbls—specialized data frames built on the tibble class
that provide useful information about the entities like their
name and unique id for users, and API data in
the meta column that’s necessary for osfr’s internal
functions. Otherwise, they’re just data.frames and can be
manipulated using standard functions from base R or dplyr.
OSF is developed by the Center for Open Science in Charlottesville, VA.
The original version of osfr was developed by Chris Chartgerink and further developed by Brian Richards and Ryan Hafen. The current version was developed by Aaron Wolen and is heavily inspired by Jennifer Bryan and Lucy D’Agostino McGowan’s excellent googledrive package. Seriously, we borrowed a lot of great ideas from them. Other important resources include http testing by Scott Chamberlain and R Packages by Hadley Wickham. Development was also greatly facilitated by OSF’s excellent API documentation.
Big thanks to Rusty Speidel for designing our logo and Tim Errington for his feedback during development.
Check out the Contributing Guidelines to get started with osfr development and note that by contributing to this project, you agree to abide by the terms outlined in the Contributor Code of Conduct.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.