The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
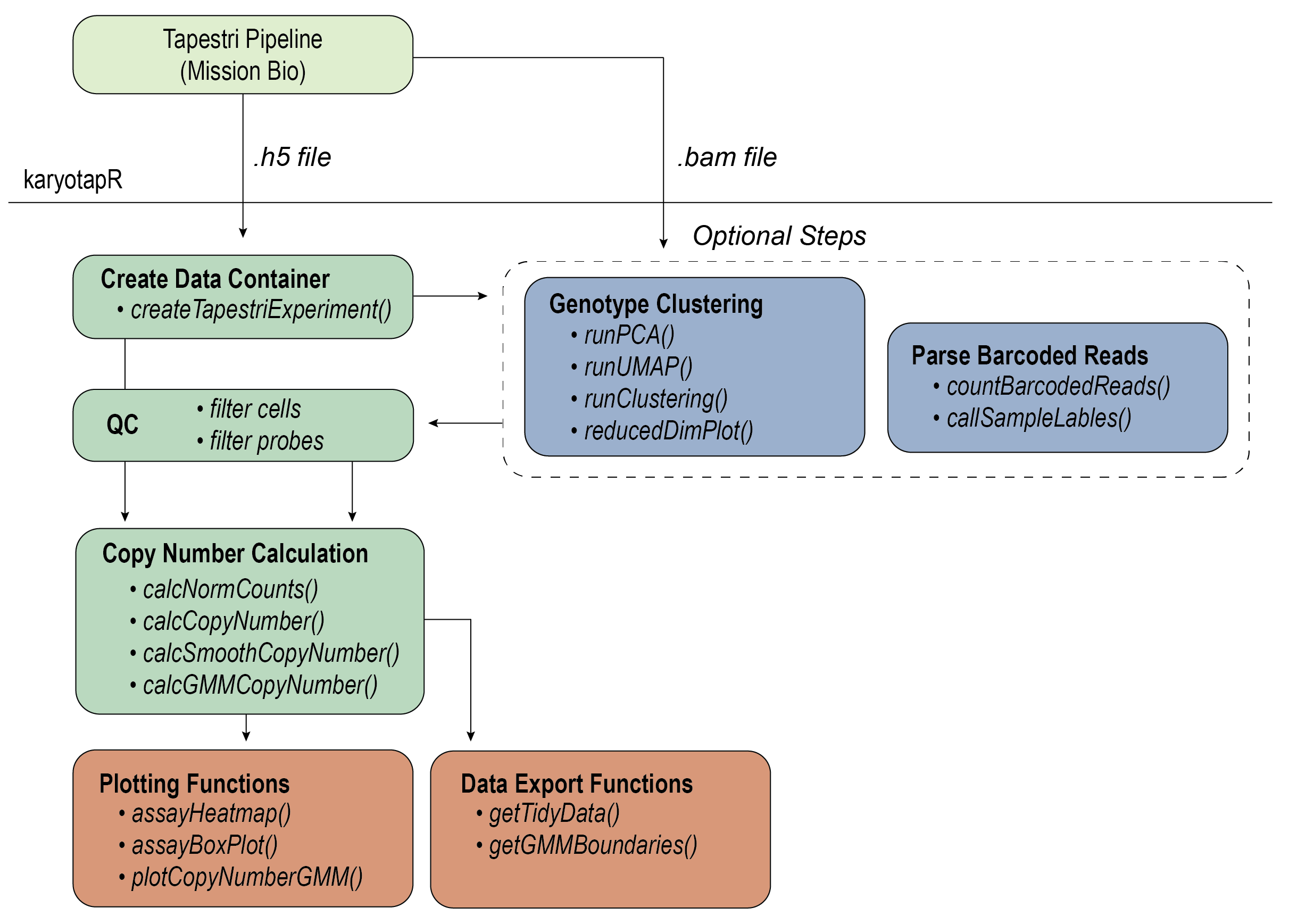
karyotapR enables analysis of DNA copy number (aneuploidy) using data produced by the KaryoTap method. Users can easily parse, manipulate, and visualize datasets produced from the automated ‘Tapestri Pipeline’, with support for normalization, clustering, and copy number calling. Functions are also available to deconvolute multiplexed samples by genotype and parsing barcoded reads from exogenous lentiviral constructs.
KaryoTap combines custom genome-wide targeted DNA sequencing panels for the Mission Bio Tapestri system with a Gaussian mixture model framework for calling copy number.
Mays JC et al., 2023. KaryoTap Enables Aneuploidy Detection in Thousands of Single Human Cells. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.09.08.555746v1.
You can install the current stable version of karyotapR from CRAN with:
install.packages('karyotapR')You can install the development version of karyotapR from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("joeymays/karyotapR")For details on the workflow, see the Getting Started guide, articles on this site, and the package reference/documentation.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.