The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.

The goal of grasps is to provide a collection of statistical methods that incorporate both element-wise and group-wise penalties to estimate a precision matrix, making them user-friendly and useful for researchers and practitioners.
\[\hat{\Omega}(\lambda,\alpha,\gamma) = {\arg\min}_{\Omega \succ 0} \{ -\log\det(\Omega) + \text{tr}(S\Omega) + \lambda P_{\alpha,\gamma}(\Omega) \},\]
\[P_{\alpha,\gamma}(\Omega) = \alpha P^\text{idv}_\gamma(\Omega) + (1-\alpha) P^\text{grp}_\gamma(\Omega),\]
\[P^\text{idv}_\gamma(\Omega) = \sum_{i,j} p_\gamma(\vert\omega_{ij}\vert),\]
\[P^\text{grp}_\gamma(\Omega) = \sum_{g,g^\prime} p_\gamma(\Vert\Omega_{gg^\prime}\Vert_F).\]
For more details, see the vignette Penalized Precision Matrix Estimation in grasps.
The package grasps provides functions to estimate precision matrices using the following penalties:
| Penalty | Reference |
|---|---|
Lasso
(penalty = "lasso") |
Tibshirani (1996); Friedman et al. (2008) |
Adaptive lasso
(penalty = "adapt") |
Zou (2006); Fan et al. (2009) |
Atan (penalty = "atan") |
Wang and Zhu (2016) |
Exp (penalty = "exp") |
Wang et al. (2018) |
Lq (penalty = "lq") |
Frank and Friedman (1993); Fu (1998); Fan and Li (2001) |
LSP (penalty = "lsp") |
Candès et al. (2008) |
MCP (penalty = "mcp") |
Zhang (2010) |
SCAD (penalty = "scad") |
Fan and Li (2001); Fan et al. (2009) |
See the vignette Penalized Precision Matrix Estimation in grasps for more details.
You can install the development version of grasps from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("Carol-seven/grasps")library(grasps)
## reproducibility for everything
set.seed(1234)
## block-structured precision matrix based on SBM
sim <- gen_prec_sbm(d = 30, K = 3,
within.prob = 0.25, between.prob = 0.05,
weight.dists = list("gamma", "unif"),
weight.paras = list(c(shape = 20, rate = 10),
c(min = 0, max = 5)),
cond.target = 100)
## synthetic data
library(MASS)
X <- mvrnorm(n = 20, mu = rep(0, 30), Sigma = sim$Sigma)
## solution
res <- grasps(X = X, membership = sim$membership, penalty = "adapt", crit = "HBIC")
## visualization
plot(res)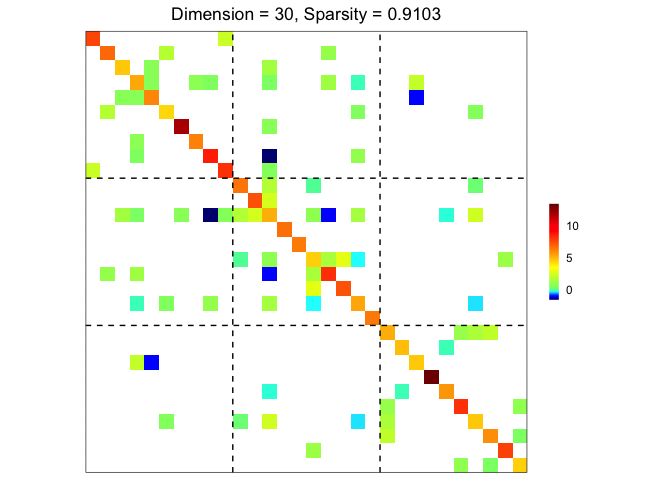
## performance
performance(hatOmega = res$hatOmega, Omega = sim$Omega)
#> measure value
#> 1 sparsity 0.9103
#> 2 Frobenius 24.6796
#> 3 KL 7.2063
#> 4 quadratic 54.1949
#> 5 spectral 13.1336
#> 6 TP 22.0000
#> 7 TN 370.0000
#> 8 FP 17.0000
#> 9 FN 26.0000
#> 10 TPR 0.4583
#> 11 FPR 0.0439
#> 12 F1 0.5057
#> 13 MCC 0.4545These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.