The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.

The ggalign package provides an integrative framework
for composable visualization, enabling the construction of complex
multi-plot layouts—including insets, circular arrangements, and
multi-panel compositions. Built on the grammar of graphics, it
introduces tools to align, stack, and nest plots, making it easy to link
related views, overlay clustering results, or highlight shared patterns.
Designed for high-dimensional data contexts such as genomics,
transcriptomics, and microbiome studies, it simplifies the creation of
richly annotated, publication-ready figures from diverse visual
components.
ggalign?ggalign focuses on aligning observations across multiple
plots. If you’ve ever struggled with aligning plots with self-contained
ordering (like dendrogram), or applying consistent grouping or ordering
across multiple plots (e.g., with k-means clustering),
ggalign is designed to make this easier. The package
integrates seamlessly with ggplot2, providing the flexibility to use its
geoms, scales, and other components for complex visualizations.
You can install ggalign from CRAN
using:
install.packages("ggalign")Alternatively, install the development version from r-universe with:
install.packages("ggalign",
repos = c("https://yunuuuu.r-universe.dev", "https://cloud.r-project.org")
)or from GitHub with:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("Yunuuuu/ggalign")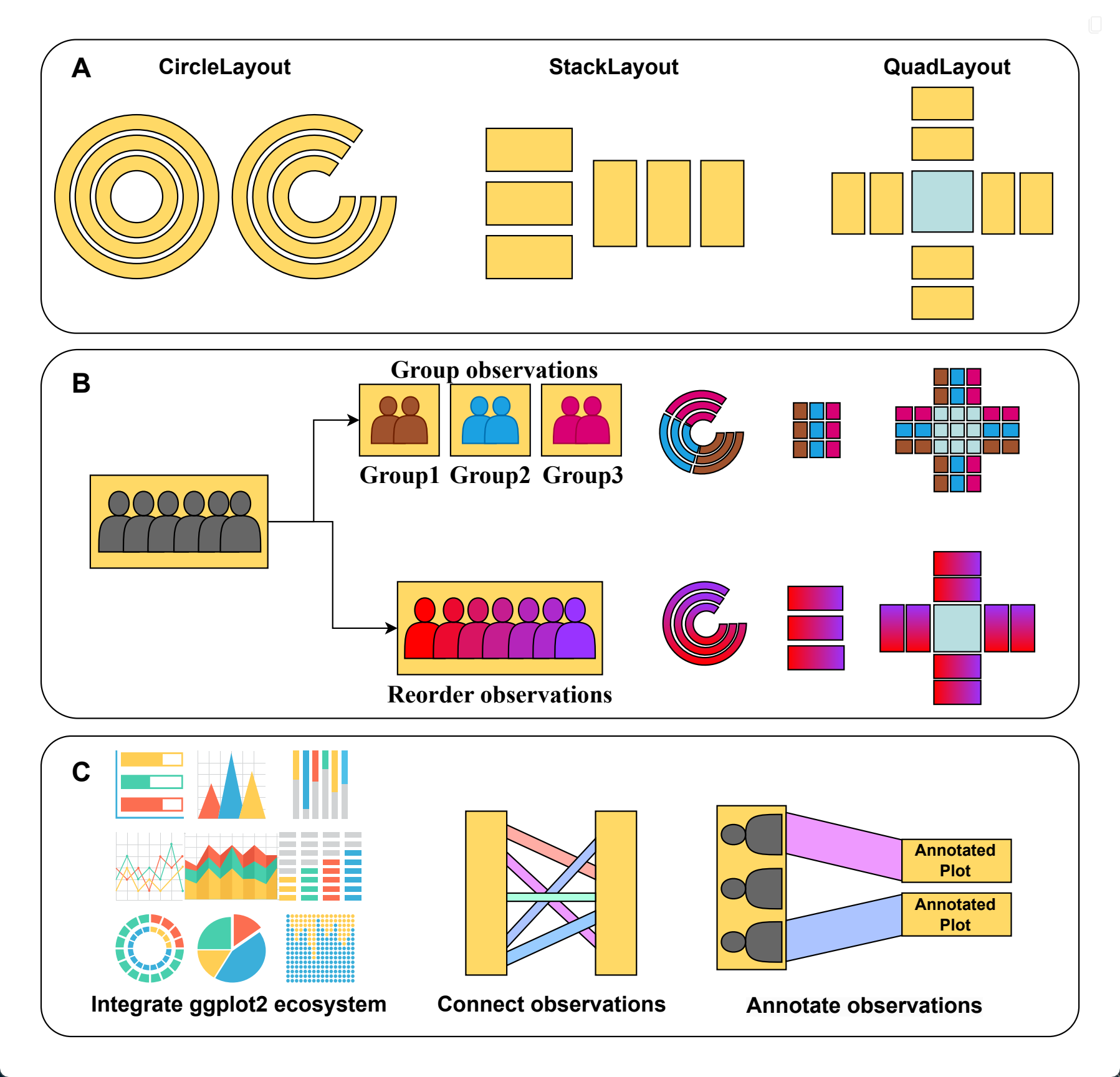
ggalign
|
marsilea
|
ComplexHeatmap
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | R | Python | R | |
| User Interface | Declarative | Declarative | Functional | |
| Plot System | ggplot2 (Advanced plot system built on grid system) | Matplotlib | grid | |
| Focus | General-purpose composable visualization | Grid-based composable visualization | Heatmap | |
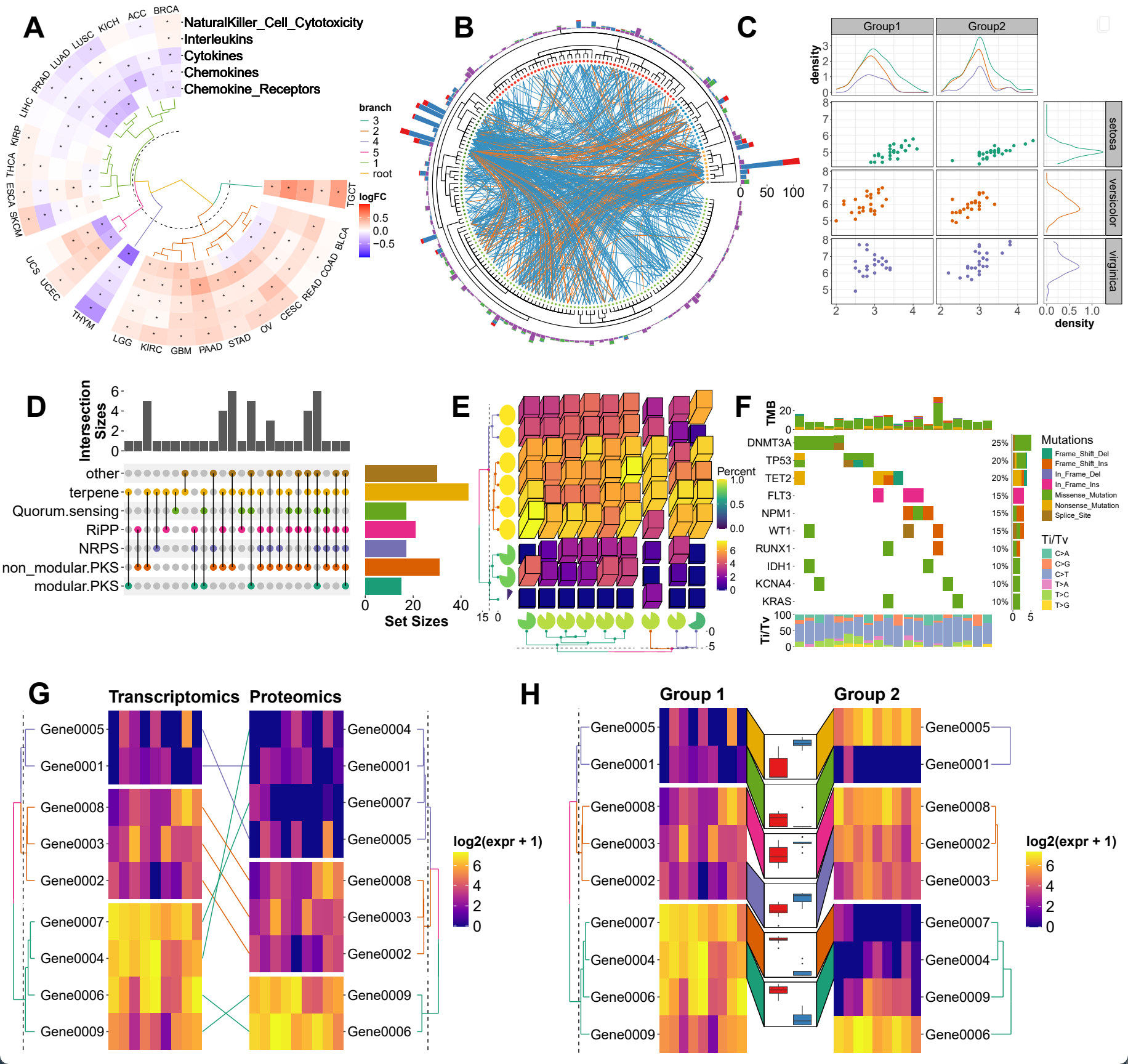
| StackLayout | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| QuadLayout | ✅ | ✅ | Heatmap Only (discrete variables) | |
| CircleLayout | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| Relationship | One-to-One | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| One-to-Many/Many-to-One | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| Many-to-Many | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| Crosswise | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| Annotate observations | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | |
| Fully Compatible with ggplot2 | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| Specification | ggalign |
marsilea |
ComplexHeatmap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reorder observations | ✅ | ✅ | Heatmap Only |
| Group observations into different panels | ✅ | ✅ | Heatmap Only |
| Clustering algorithm | Kmeans,Hierarchical Clustering and arbitary algorithm | ❌ | Kmeans,Hierarchical Clustering and arbitary algorithm |
| Legends Creation | Automatic | Automatic | Limited automatic, requires manual add |
| Legends Position | Anywhere; independently controllable per plot | Anywhere | Fixed to one of four sides |
| Dendrogram | Tree from both hclust or ape |
hclust only |
hclust only |
| Tanglegram | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| 3D Heatmap | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Oncoplot | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| UpSet plot | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to the contributors of
the ggplot2 project for providing a powerful and flexible
framework for data visualization in R. Their work laid the foundation
for the functionality and design of this package. I would also like to
thank the patchwork project, from which the core coding for
the plot composer was adapted. The patchwork library
provided a useful mechanism for combining and aligning plots, which was
modified to suit the needs of this package. Without the contributions of
these open-source projects, this package would not have been
possible.
Additionally, I would like to extend my heartfelt thanks to
@teunbrand, who has fulfilled my numerous feature requests,
and assisted with the integration of new functions into ggplot2.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.