The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
gdim estimates graph dimension using cross-validated
eigenvalues, via the graph-splitting technique developed in https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.03336. Theoretically, the
method works by computing a special type of cross-validated eigenvalue
which follows a simple central limit theorem. This allows users to
perform hypothesis tests on the rank of the graph.
You can install gdim from CRAN with:
install.packages("gdim")
# to get the development version from GitHub:
install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("RoheLab/gdim")eigcv() is the main function in gdim. The
single required parameter for the function is the maximum possible
dimension, k_max.
In the following example, we generate a random graph from the stochastic block model (SBM) with 1000 nodes and 5 blocks (as such, we would expect the estimated graph dimension to be 5).
library(fastRG)
#> Loading required package: Matrix
B <- matrix(0.1, 5, 5)
diag(B) <- 0.3
model <- sbm(
n = 1000,
B = B,
expected_degree = 40,
poisson_edges = FALSE,
allow_self_loops = FALSE
)
A <- sample_sparse(model)Here, A is the adjacency matrix.
Now, we call the eigcv() function with
k_max=10 to estimate graph dimension.
library(gdim)
eigcv_result <- eigcv(A, k_max = 10)
#> 'as(<dsCMatrix>, "dgCMatrix")' is deprecated.
#> Use 'as(., "generalMatrix")' instead.
#> See help("Deprecated") and help("Matrix-deprecated").
eigcv_result
#> Estimated graph dimension: 5
#>
#> Number of bootstraps: 10
#> Edge splitting probabaility: 0.1
#> Significance level: 0.05
#>
#> ------------ Summary of Tests ------------
#> k z pvals padj
#> 1 41.1972023 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00
#> 2 6.5483842 2.908147e-11 2.908147e-11
#> 3 6.2885741 1.601976e-10 1.601976e-10
#> 4 6.9601015 1.700138e-12 1.700138e-12
#> 5 7.1673010 3.824537e-13 3.824537e-13
#> 6 -0.3594110 6.403562e-01 6.403562e-01
#> 7 -0.2062852 5.817159e-01 5.817159e-01
#> 8 -0.6096004 7.289367e-01 7.289367e-01
#> 9 -0.7202233 7.643062e-01 7.643062e-01
#> 10 -0.6707828 7.488205e-01 7.488205e-01In this example, eigcv() suggests k=5.
To visualize the result, use plot() which returns a
ggplot object. The function displays the test statistic (z
score) for each hypothesized graph dimension.
plot(eigcv_result)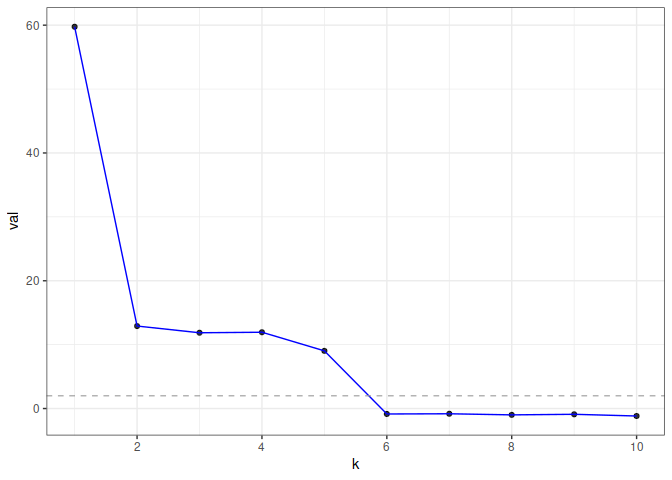
Chen, Fan, Sebastien Roch, Karl Rohe, and Shuqi Yu. “Estimating Graph Dimension with Cross-Validated Eigenvalues.” ArXiv:2108.03336 [Cs, Math, Stat], August 6, 2021. https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.03336.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.