
The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
The goal of edar is to provide some convenient functions to facilitate common tasks in exploratory data analysis.
Sou T (2025). edar: Convenient Functions for Exploratory Data Analysis. R package version 0.0.5.9000, https://github.com/soutomas/edar.
citation("edar")
#> To cite package 'edar' in publications use:
#>
#> Sou T (2025). _edar: Convenient Functions for Exploratory Data
#> Analysis_. R package version 0.0.5.9000, https://github.com/soutomas/edar/,
#> <https://soutomas.github.io/edar/>.
#>
#> A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
#>
#> @Manual{,
#> title = {edar: Convenient Functions for Exploratory Data Analysis},
#> author = {Tomas Sou},
#> note = {R package version 0.0.5.9000, https://github.com/soutomas/edar/},
#> url = {https://soutomas.github.io/edar/},
#> }# From CRAN
install.packages("edar")
# From GitHub - for the development version
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("soutomas/edar")It is often helpful to see a quick summary of the dataset.
library(edar)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'edar'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter
# Data
dat = mtcars |> mutate(across(c(am,carb,cyl,gear,vs),factor))
# Summaries of all continuous variables.
dat |> summ_by()
#> NB: Non-numeric variables are dropped.
#> Dropped: cyl vs am gear carb
#> Adding missing grouping variables: `name`
#> # A tibble: 6 × 10
#> name n nNA Mean SD Min P25 Med P75 Max
#> <chr> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 disp 32 0 231. 124. 71.1 121. 196. 326 472
#> 2 drat 32 0 3.60 0.535 2.76 3.08 3.70 3.92 4.93
#> 3 hp 32 0 147. 68.6 52 96.5 123 180 335
#> 4 mpg 32 0 20.1 6.03 10.4 15.4 19.2 22.8 33.9
#> 5 qsec 32 0 17.8 1.79 14.5 16.9 17.7 18.9 22.9
#> 6 wt 32 0 3.22 0.978 1.51 2.58 3.32 3.61 5.42
# Summaries of a selected variable after grouping.
dat |> summ_by(mpg,vs)
#> Adding missing grouping variables: `vs`
#> # A tibble: 2 × 10
#> vs n nNA Mean SD Min P25 Med P75 Max
#> <fct> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0 18 0 16.6 3.86 10.4 14.8 15.6 19.1 26
#> 2 1 14 0 24.6 5.38 17.8 21.4 22.8 29.6 33.9
# Summaries of all categorical variables.
dat |> summ_cat()
#> NB: Numeric variables are dropped.
#> Dropped: mpg disp hp drat wt qsec
#> $cyl
#> cyl n percent
#> 4 11 0.34375
#> 6 7 0.21875
#> 8 14 0.43750
#> Total 32 1.00000
#>
#> $vs
#> vs n percent
#> 0 18 0.5625
#> 1 14 0.4375
#> Total 32 1.0000
#>
#> $am
#> am n percent
#> 0 19 0.59375
#> 1 13 0.40625
#> Total 32 1.00000
#>
#> $gear
#> gear n percent
#> 3 15 0.46875
#> 4 12 0.37500
#> 5 5 0.15625
#> Total 32 1.00000
#>
#> $carb
#> carb n percent
#> 1 7 0.21875
#> 2 10 0.31250
#> 3 3 0.09375
#> 4 10 0.31250
#> 6 1 0.03125
#> 8 1 0.03125
#> Total 32 1.00000Results can be viewed directly in a flextable object.
# Show data frame as a flextable object.
dat |> summ_by(mpg,vs) |> ft()
#> Adding missing grouping variables: `vs`
Variables can be quickly visualised for exploratory graphical analysis.
# Histograms of all continuous variables.
dat |> gghist()
#> NB: Non-numeric variables are dropped.
#> Dropped: cyl vs am gear carb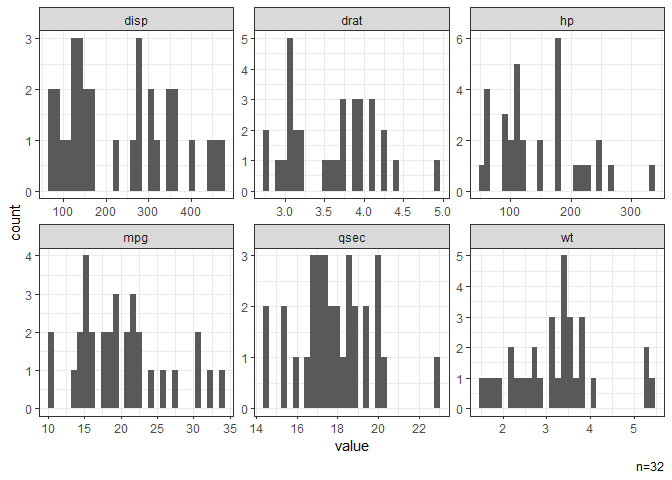
# Box plots stratified by categorical variables.
dat |> ggbox(mpg)
#> NB: Numeric variables are dropped.
#> Dropped: disp hp drat wt qsec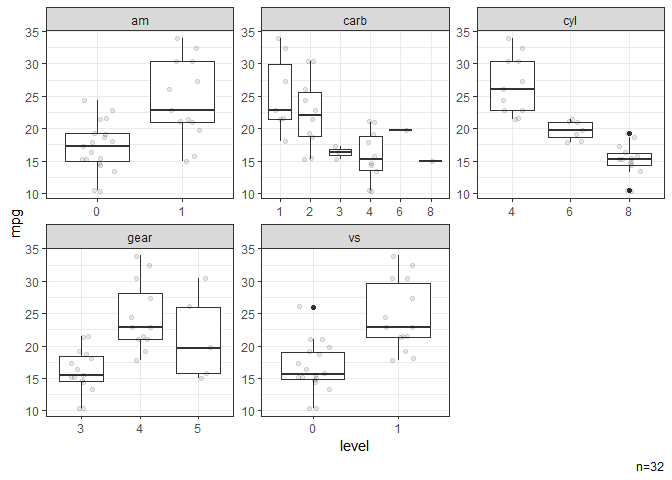
# Violin plots stratified by categorical variables.
dat |> ggvio(mpg)
#> NB: Numeric variables are dropped.
#> Dropped: disp hp drat wt qsec
#> Warning: Groups with fewer than two datapoints have been dropped.
#> ℹ Set `drop = FALSE` to consider such groups for position adjustment purposes.
#> Groups with fewer than two datapoints have been dropped.
#> ℹ Set `drop = FALSE` to consider such groups for position adjustment purposes.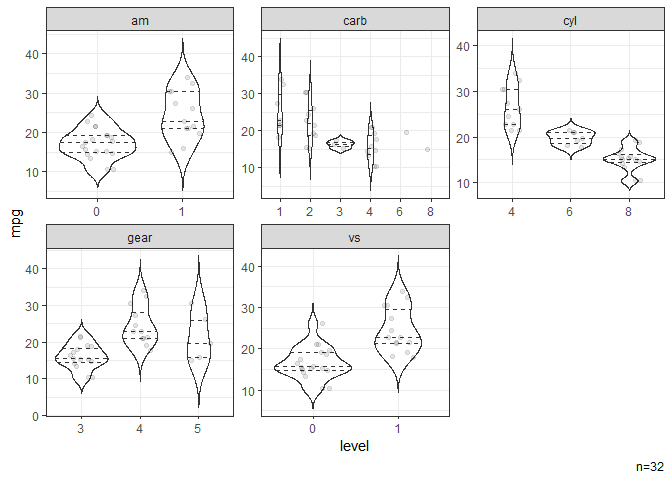
# Scatter plot showing correlation.
dat |> ggxy(hp,disp)
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'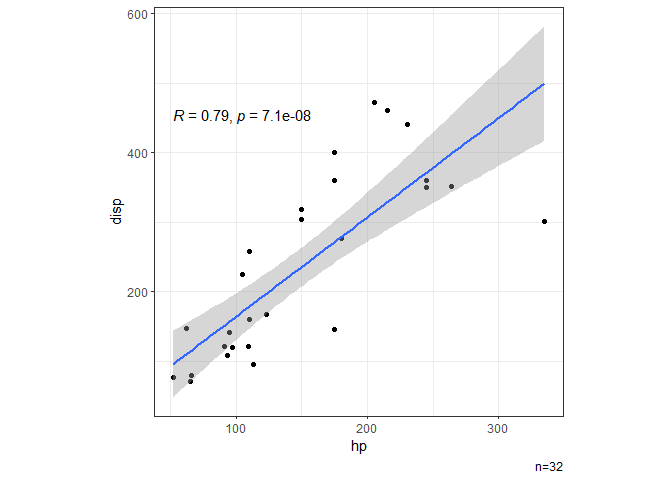
A label indicating the current source file with a time stamp can be easily generated for annotation.
# To generate a source file label for annotation.
lab = label_src()# A source file label can be directly added to the flextable output.
dat |> summ_by(mpg,vs) |> ft(src=1)# A source file label can be directly added to a ggplot object.
p = dat |> ggxy(hp,disp)
p |> ggsrc()These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.