The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
The goal of drpop is to provide users doubly robust and efficient estimates of population size and the confidence intervals for a capture-recapture problem.
You can install the released version of drpop from CRAN with:
install.packages("drpop")And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("mqnjqrid/drpop")This is a basic example which shows you how to solve a common problem:
library(drpop)
#> Registered S3 methods overwritten by 'tibble':
#> method from
#> format.tbl pillar
#> print.tbl pillar
n = 1000
x = matrix(rnorm(n*3, 2, 1), nrow = n)
expit = function(xi) {
exp(sum(xi))/(1 + exp(sum(xi)))
}
y1 = unlist(apply(x, 1, function(xi) {sample(c(0, 1), 1, replace = TRUE, prob = c(1 - expit(-0.6 + 0.4*xi), expit(-0.6 + 0.4*xi)))}))
y2 = unlist(apply(x, 1, function(xi) {sample(c(0, 1), 1, replace = TRUE, prob = c(1 - expit(-0.6 + 0.3*xi), expit(-0.6 + 0.3*xi)))}))
datacrc = cbind(y1, y2, exp(x/2))[y1+y2 > 0, ]
estim <- popsize(data = datacrc, func = c("gam"), nfolds = 2, K = 2)
#> Warning: package 'dplyr' was built under R version 4.0.5
#> Loading required package: tidyr
#> Loaded gam 1.20
#> Warning in popsize_base(data, K = K, j0 = j, k0 = k, filterrows = filterrows, :
#> Plug-in variance is not well-defined. Returning variance evaluated using DR
#> estimator formula
# The population size estimates are 'n' and the standard deviations are 'sigman'
print(estim)
#> listpair model method psi sigma n sigman cin.l cin.u
#> 1 1,2 gam DR 0.820 1.015 955 31.886 893 1018
#> 2 1,2 gam PI 0.810 1.015 967 32.150 904 1030
#> 3 1,2 gam TMLE 0.822 0.921 953 29.515 895 1010
## basic example codeThe following shows the confidence interval of estimates for a toy data. Real population size is 3000.
library(drpop)
n = 3000
x = matrix(rnorm(n*3, 2,1), nrow = n)
expit = function(xi) {
exp(sum(xi))/(1 + exp(sum(xi)))
}
y1 = unlist(apply(x, 1, function(xi) {sample(c(0, 1), 1, replace = TRUE, prob = c(1 - expit(-0.6 + 0.4*xi), expit(-0.6 + 0.4*xi)))}))
y2 = unlist(apply(x, 1, function(xi) {sample(c(0, 1), 1, replace = TRUE, prob = c(1 - expit(-0.6 + 0.3*xi), expit(-0.6 + 0.3*xi)))}))
datacrc = cbind(y1, y2, exp(x/2))[y1+y2>0,]
estim <- popsize(data = datacrc, func = c("gam", "rangerlogit"), nfolds = 2, margin = 0.01)
#> Warning in popsize_base(data, K = K, j0 = j, k0 = k, filterrows = filterrows, :
#> Plug-in variance is not well-defined. Returning variance evaluated using DR
#> estimator formula
print(estim)
#> listpair model method psi sigma n sigman cin.l cin.u
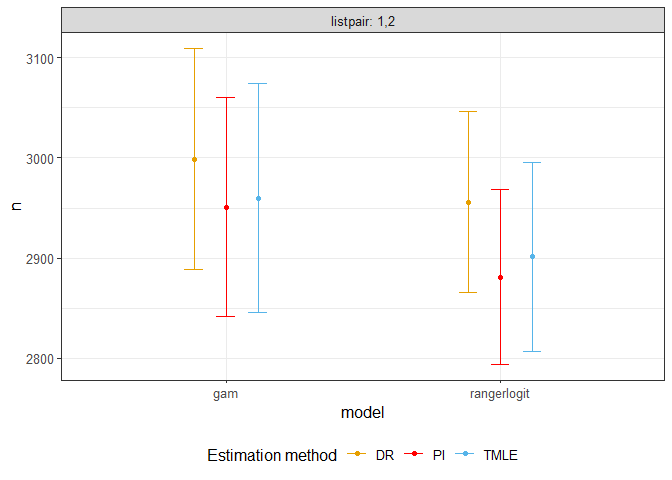
#> 1 1,2 gam DR 0.794 1.001 2999 56.258 2889 3109
#> 2 1,2 gam PI 0.807 1.001 2951 55.612 2842 3060
#> 3 1,2 gam TMLE 0.805 1.059 2960 58.228 2846 3074
#> 4 1,2 rangerlogit DR 0.806 0.764 2956 45.880 2866 3046
#> 5 1,2 rangerlogit PI 0.827 0.764 2881 44.678 2794 2969
#> 6 1,2 rangerlogit TMLE 0.821 0.841 2902 48.147 2807 2996
plotci(estim)
#> Warning: package 'ggplot2' was built under R version 4.0.4
#result = melt(as.data.frame(estim), variable.name = "estimator", value.name = "population_size")
#ggplot(result, aes(x = population_size - n, fill = estimator, color = estimator)) +
# geom_density(alpha = 0.4) +
# xlab("Bias on n")The following shows confidence interval of estimates for toy data with a categorical covariate. Real population size is 10000.
library(drpop)
n = 10000
x = matrix(rnorm(n*3, 2, 1), nrow = n)
expit = function(xi) {
exp(sum(xi))/(1 + exp(sum(xi)))
}
catcov = sample(c('m','f'), n, replace = TRUE, prob = c(0.45, 0.55))
y1 = unlist(apply(x, 1, function(xi) {sample(c(0, 1), 1, replace = TRUE, prob = c(1 - expit(-0.6 + 0.4*xi), expit(-0.6 + 0.4*xi)))}))
y2 = sapply(1:n, function(i) {sample(c(0, 1), 1, replace = TRUE, prob = c(1 - expit(-0.6 + 0.3*(catcov[i] == 'm') + 0.3*x[i,]), expit(-0.6 + 0.3*(catcov[i] == 'm') + 0.3*x[i,])))})
datacrc = cbind.data.frame(y1, y2, exp(x/2), catcov)[y1+y2>0,]
result = popsize_cond(data = datacrc, condvar = 'catcov')
#> Warning in popsize_base(data = datasub, K = K, filterrows = filterrows, : Plug-
#> in variance is not well-defined. Returning variance evaluated using DR estimator
#> formula
#> Warning in popsize_base(data = datasub, K = K, filterrows = filterrows, : Plug-
#> in variance is not well-defined. Returning variance evaluated using DR estimator
#> formula
fig = plotci(result)
fig + geom_hline(yintercept = table(catcov), color = "brown", linetype = "dashed")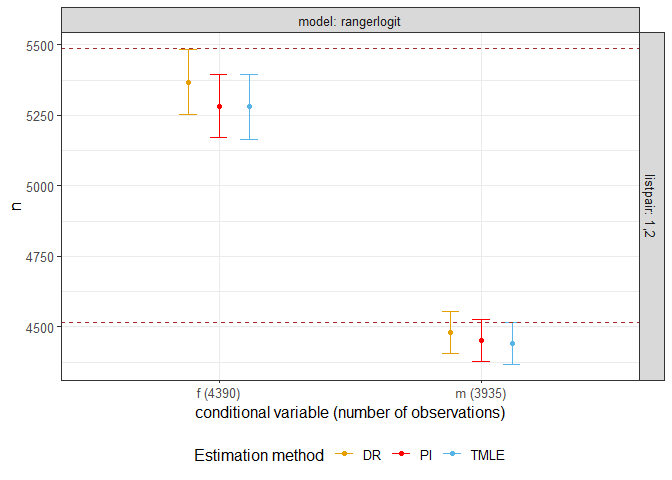
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.