The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
clinpubr is an R package designed to streamline the
workflow from clinical data processing to publication-ready outputs. It
provides tools for clinical data cleaning, significant result screening,
and generating tables/figures suitable for medical journals.
You can install clinpubr from CRAN with:
install.packages("clinpubr")Some functions require additional packages for full functionality. The package will automatically prompt you to install missing packages when needed. If you want to install the package with all dependencies, you can use:
install.packages("clinpubr", dependencies = TRUE)library(clinpubr)
# Sample messy data with various quality issues
messy_data <- data.frame(
id = 1:15,
# Numeric with outliers
bmi = c(
22.5, 23.1, 24.2, 21.8, 25.0, 23.5, 999, 24.1, 22.9, 23.8,
21.5, 24.3, 23.0, 22.7, 23.9
),
# Character with case inconsistency
city = c(
"Beijing", "BEIJING", "beijing", "Shanghai", "SHANGHAI",
"Guangzhou", "chengdu", "CHENGDU", "Shenzhen", "shenzhen",
"Beijing", "Shanghai", "Guangzhou", "Chengdu", "Shenzhen"
),
# Numeric with negative values in predominantly positive
height = c(
1.75, 1.80, 1.65, 1.70, 1.85, 1.78, 1.68, 1.72, 1.76, 1.82,
1.60, 1.62, 1.74, 179, -1
),
# Date with suspicious year
visit_date = as.Date(c(
"2020-01-15", "2020-02-20", "2020-03-10", "2019-05-18", "2020-06-22",
"2018-07-30", "2020-08-12", "2020-09-25", "2020-10-08", "2020-11-15",
"2020-12-20", "1900-01-01", "2030-02-28", "2020-03-15", "2020-04-20"
)),
# Numeric stored as character
age = c(
"25", "26", "27", "28", "29", "30", "31", "32", "33", "34",
"35", "unknown", "36", "37", "38"
),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
overview <- data_overview(messy_data)
#> === Data Overview Summary ===
#> Dataset: 15 rows, 6 columns
#>
#> Variable Types:
#> numeric : 3 variables
#> character : 2 variables
#> date : 1 variables
#>
#> Found 6 potential quality issues:
#> numeric_as_character : 1 cases
#> outliers : 2 cases
#> negative_in_positive : 1 cases
#> suspicious_dates : 1 cases
#> case_issues : 1 cases
#>
#> Recommendations:
#> - Consider converting these character variables to numeric: age
#> - Review outliers in these numeric variables: bmi, height
#> - Numeric variables with mostly positive values but containing negatives: height
#> - Review suspicious dates (year < 1910 or > current year) in: visit_date
#> - These character variables have case inconsistency issues: city - consider standardizing to lowercase or uppercase
print(overview$quality_issues$case_issues)
#> $city
#> $city$n_original
#> [1] 11
#>
#> $city$n_normalized
#> [1] 5
#>
#> $city$reduction
#> [1] 6
#>
#> $city$examples
#> $city$examples$beijing
#> [1] "Beijing" "BEIJING" "beijing"
#>
#> $city$examples$shanghai
#> [1] "Shanghai" "SHANGHAI"
#>
#> $city$examples$chengdu
#> [1] "chengdu" "CHENGDU" "Chengdu"# Sample messy data
messy_data <- data.frame(values = c("12.3", "0..45", " 67 ", "", "abandon"))
clean_data <- value_initial_cleaning(messy_data$values)
print(clean_data)
#> [1] "12.3" "0.45" "67" NA "abandon"# Sample messy data
x <- c("1.2(XXX)", "1.5", "0.82", "5-8POS", "NS", "FULL")
print(check_nonnum(x))
#> [1] "1.2(XXX)" "5-8POS" "NS" "FULL"This function filters out non-numerical values, which helps you choose the appropriate method to handle them.
# Sample messy data
x <- c("1.2(XXX)", "1.5", "0.82", "5-8POS", "NS", "FULL")
print(extract_num(x))
#> [1] 1.20 1.50 0.82 5.00 NA NA
print(extract_num(x,
res_type = "first", # Extract the first number
multimatch2na = TRUE, # Convert illegal multiple matches to NA
zero_regexp = "NEG|NS", # Convert "NEG" and "NS" (matched using regex) to 0
max_regexp = "FULL", # Convert "FULL" (matched using regex) to some specified quantile
max_quantile = 0.95
))
#> [1] 1.20 1.50 0.82 NA 0.00 1.47to_date(): Convert text to date, can handle
mixed format.unit_view() and
unit_standardize(): Provide a pipeline to
standardize conflicting units.cut_by(): Split numerics into factors, offers
a variety of splitting options and auto labeling.data(cancer, package = "survival")
# Screening for potential findings with regression models in the cancer dataset
scan_result <- regression_scan(cancer, y = "status", time = "time", save_table = FALSE)
#> Taking all variables as predictors
knitr::kable(scan_result)| predictor | nvalid | original.HR | original.pval | original.padj | logarithm.HR | logarithm.pval | logarithm.padj | categorized.HR | categorized.pval | categorized.padj | rcs.overall.pval | rcs.overall.padj | rcs.nonlinear.pval | rcs.nonlinear.padj | best.var.trans | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | ph.ecog | 227 | 1.6095320 | 0.0000269 | 0.0002154 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.0001530 | 0.0012237 | NA | NA | NA | NA | original |
| 6 | pat.karno | 225 | 0.9803456 | 0.0002824 | 0.0011296 | 0.2709544 | 0.0003071 | 0.0015356 | 0.5755627 | 0.0006608 | 0.0026431 | 0.0025848 | 0.0155086 | 0.5908952 | 0.8863427 | original |
| 3 | sex | 228 | 0.5880028 | 0.0014912 | 0.0039766 | NA | NA | NA | 0.5880028 | 0.0014912 | 0.0039766 | NA | NA | NA | NA | categorized |
| 5 | ph.karno | 227 | 0.9836863 | 0.0049579 | 0.0099157 | 0.3184168 | 0.0079468 | 0.0198669 | 0.6352465 | 0.0077670 | 0.0155339 | 0.0128462 | 0.0385385 | 0.2307961 | 0.6848245 | original |
| 2 | age | 228 | 1.0188965 | 0.0418531 | 0.0669650 | 3.0256773 | 0.0466926 | 0.0778209 | 1.1440790 | 0.3910647 | 0.3957558 | 0.0825447 | 0.1650894 | 0.3424123 | 0.6848245 | original |
| 1 | inst | 227 | 0.9903692 | 0.3459838 | 0.4613117 | 0.9292046 | 0.3181432 | 0.3976790 | 0.8384047 | 0.2600040 | 0.3466720 | 0.8175277 | 0.8707131 | 0.9839705 | 0.9839705 | categorized |
| 7 | meal.cal | 181 | 0.9998762 | 0.5929402 | 0.6776459 | 0.9141580 | 0.6128095 | 0.6128095 | 0.8620604 | 0.3957558 | 0.3957558 | 0.8707131 | 0.8707131 | 0.8227256 | 0.9839705 | categorized |
| 8 | wt.loss | 214 | 1.0013201 | 0.8281974 | 0.8281974 | NA | NA | NA | 1.3190185 | 0.0909098 | 0.1454557 | 0.1128907 | 0.1693361 | 0.0514936 | 0.3089618 | rcs.nonlinear |
cohort <- data.frame(
age = c(17, 25, 30, NA, 50, 60),
sex = c("M", "F", "F", "M", "F", "M"),
value = c(1, NA, 3, 4, 5, NA),
dementia = c(TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, FALSE)
)
res <- exclusion_count(
cohort,
age < 18,
is.na(value),
dementia == TRUE,
.criteria_names = c(
"Age < 18 years",
"Missing value",
"History of dementia"
)
)
#> Warning in exclusion_count(cohort, age < 18, is.na(value), dementia == TRUE, :
#> Criterion 'Age < 18 years' resulted in NA values. These rows have been excluded
#> by default. Consider adding an explicit check for missing values (e.g.,
#> is.na(variable)) as a preceding criterion.
knitr::kable(res) # Display the table| Criteria | N |
|---|---|
| Initial N | 6 |
| Age < 18 years | 2 |
| Missing value | 2 |
| History of dementia | 1 |
| Final N | 1 |
var_types <- get_var_types(mtcars, strata = "vs") # Automatically infer variable types
print(var_types)
#> $factor_vars
#> [1] "cyl" "vs" "am" "gear"
#>
#> $exact_vars
#> [1] "cyl" "gear"
#>
#> $nonnormal_vars
#> [1] "drat" "carb"
#>
#> $omit_vars
#> NULL
#>
#> $strata
#> [1] "vs"
#>
#> attr(,"class")
#> [1] "var_types"
tables <- baseline_table(mtcars,
var_types = var_types, contDigits = 1, save_table = FALSE,
filename = "baseline.csv", seed = 1 # set seed for simulated fisher exact test
)
knitr::kable(tables$baseline) # Display the table| Overall | vs: 0 | vs: 1 | p | test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 32 | 18 | 14 | ||
| mpg (mean (SD)) | 20.1 (6.0) | 16.6 (3.9) | 24.6 (5.4) | <0.001 | |
| cyl (%) | <0.001 | exact | |||
| 4 | 11 (34.4) | 1 (5.6) | 10 (71.4) | ||
| 6 | 7 (21.9) | 3 (16.7) | 4 (28.6) | ||
| 8 | 14 (43.8) | 14 (77.8) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| disp (mean (SD)) | 230.7 (123.9) | 307.1 (106.8) | 132.5 (56.9) | <0.001 | |
| hp (mean (SD)) | 146.7 (68.6) | 189.7 (60.3) | 91.4 (24.4) | <0.001 | |
| drat (median [IQR]) | 3.7 [3.1, 3.9] | 3.2 [3.1, 3.7] | 3.9 [3.7, 4.1] | 0.013 | nonnorm |
| wt (mean (SD)) | 3.2 (1.0) | 3.7 (0.9) | 2.6 (0.7) | 0.001 | |
| qsec (mean (SD)) | 17.8 (1.8) | 16.7 (1.1) | 19.3 (1.4) | <0.001 | |
| am = 1 (%) | 13 (40.6) | 6 (33.3) | 7 (50.0) | 0.556 | |
| gear (%) | 0.001 | exact | |||
| 3 | 15 (46.9) | 12 (66.7) | 3 (21.4) | ||
| 4 | 12 (37.5) | 2 (11.1) | 10 (71.4) | ||
| 5 | 5 (15.6) | 4 (22.2) | 1 (7.1) | ||
| carb (median [IQR]) | 2.0 [2.0, 4.0] | 4.0 [2.2, 4.0] | 1.5 [1.0, 2.0] | <0.001 | nonnorm |
data(cancer, package = "survival")
# Performing cox regression, which is inferred by `y` and `time`
p <- rcs_plot(cancer, x = "age", y = "status", time = "time", covars = c("sex", "ph.karno"), save_plot = FALSE)
#> Warning in predictor_effect_plot(data = data, x = x, y = y, time = time, : 1
#> incomplete cases excluded.
plot(p)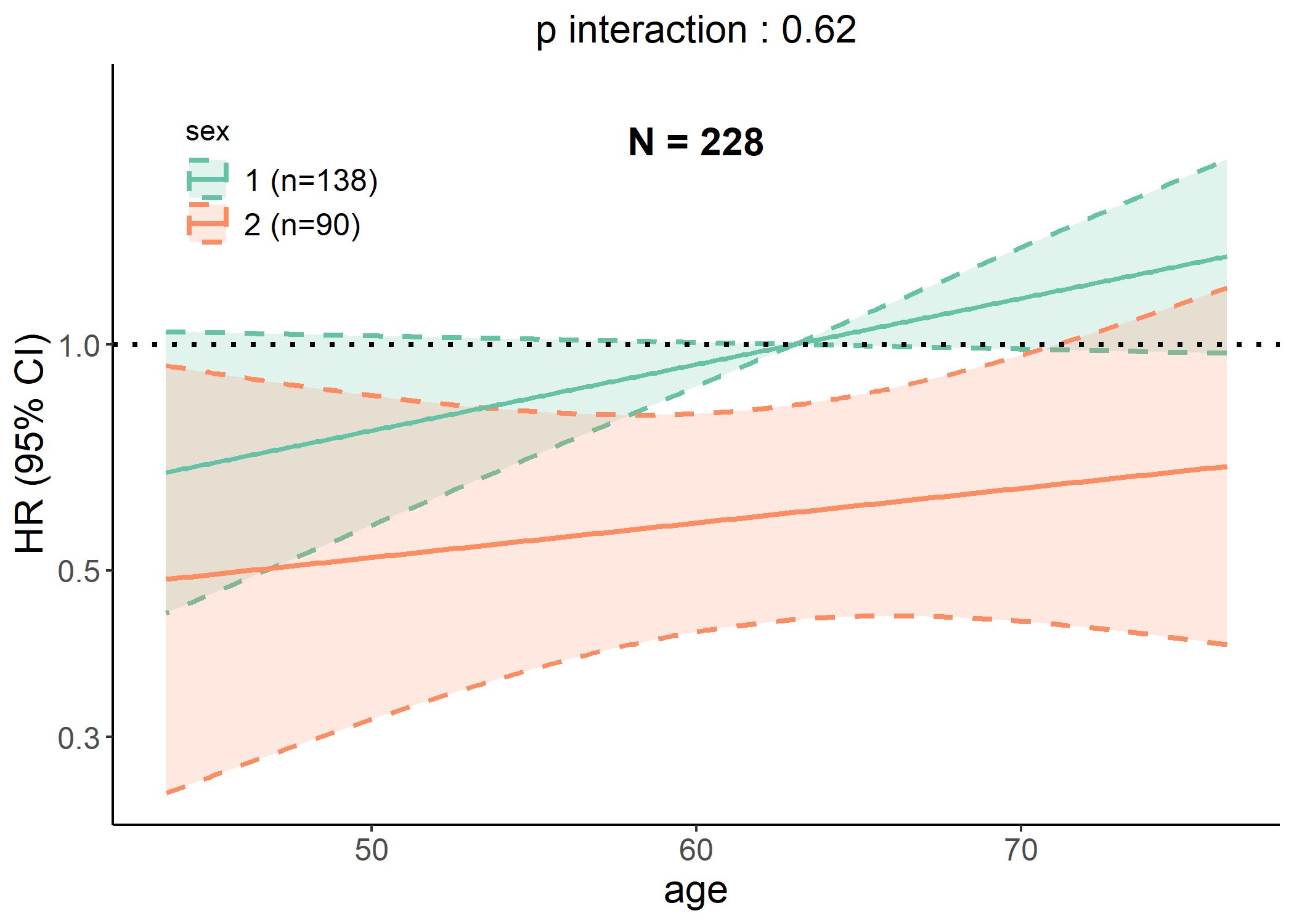
data(cancer, package = "survival")
# Generating interaction plot of both linear and RCS models
p <- interaction_plot(cancer,
y = "status", time = "time", predictor = "age",
group_var = "sex", save_plot = FALSE
)
plot(p$lin)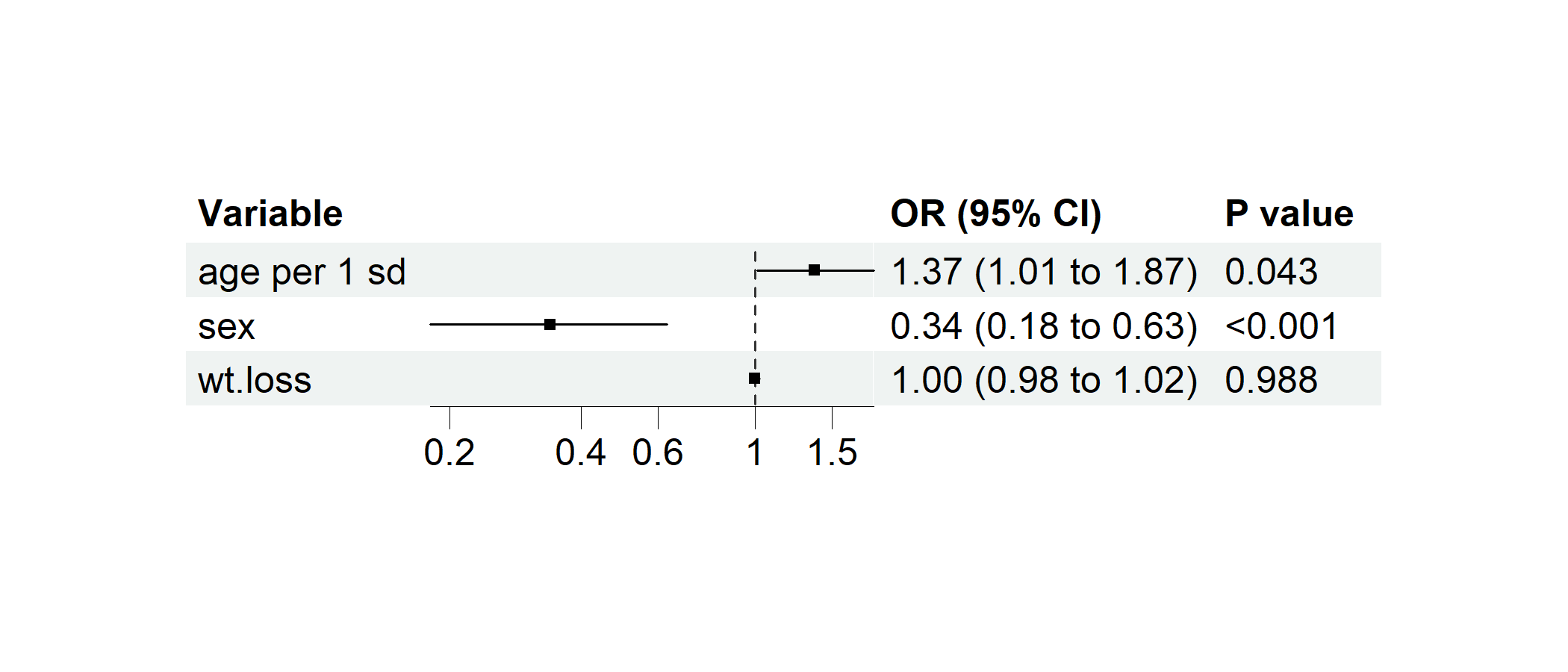
plot(p$rcs)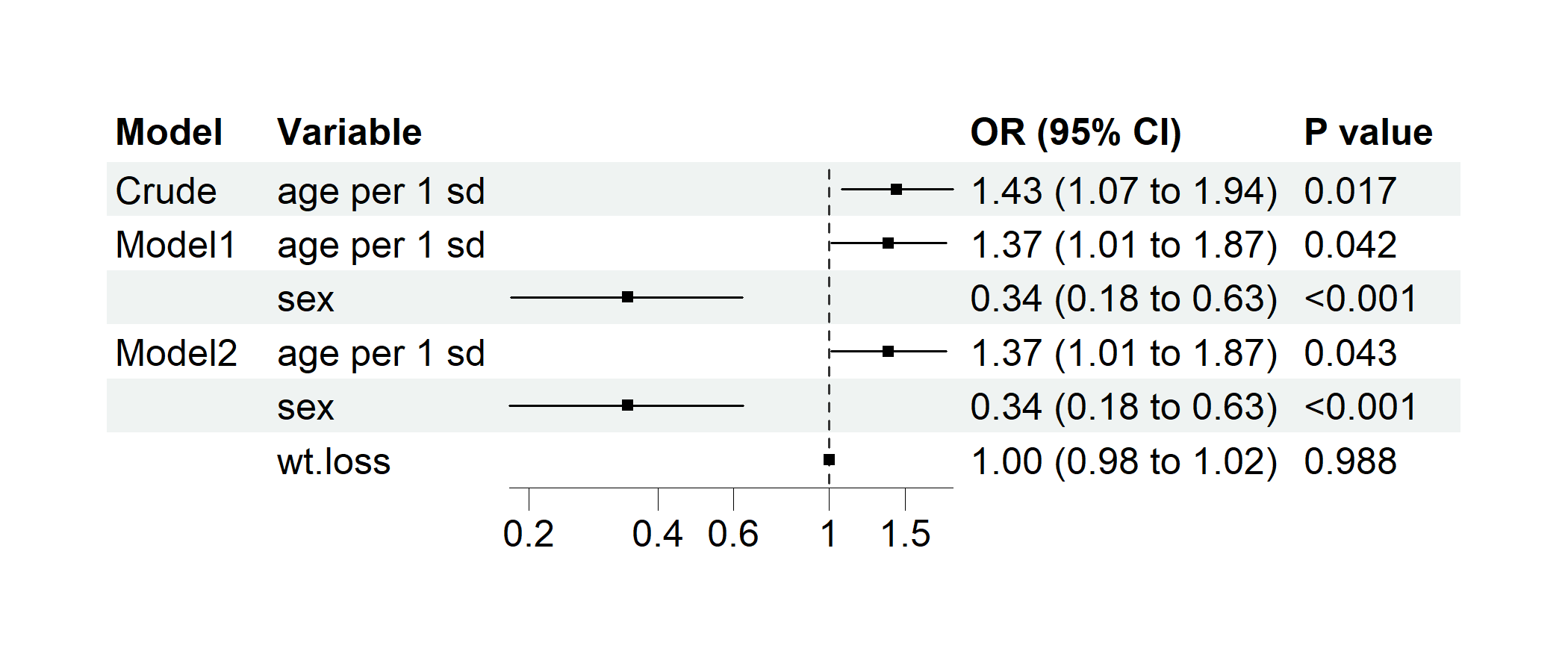
data(cancer, package = "survival")
cancer$dead <- cancer$status == 2 # Preparing a binary variable for logistic regression
cancer$`age per 1 sd` <- c(scale(cancer$age)) # Standardizing age
# Performing multivairate logistic regression
p1 <- regression_forest(cancer,
model_vars = c("age per 1 sd", "sex", "wt.loss"), y = "dead",
as_univariate = FALSE, save_plot = FALSE
)
plot(p1)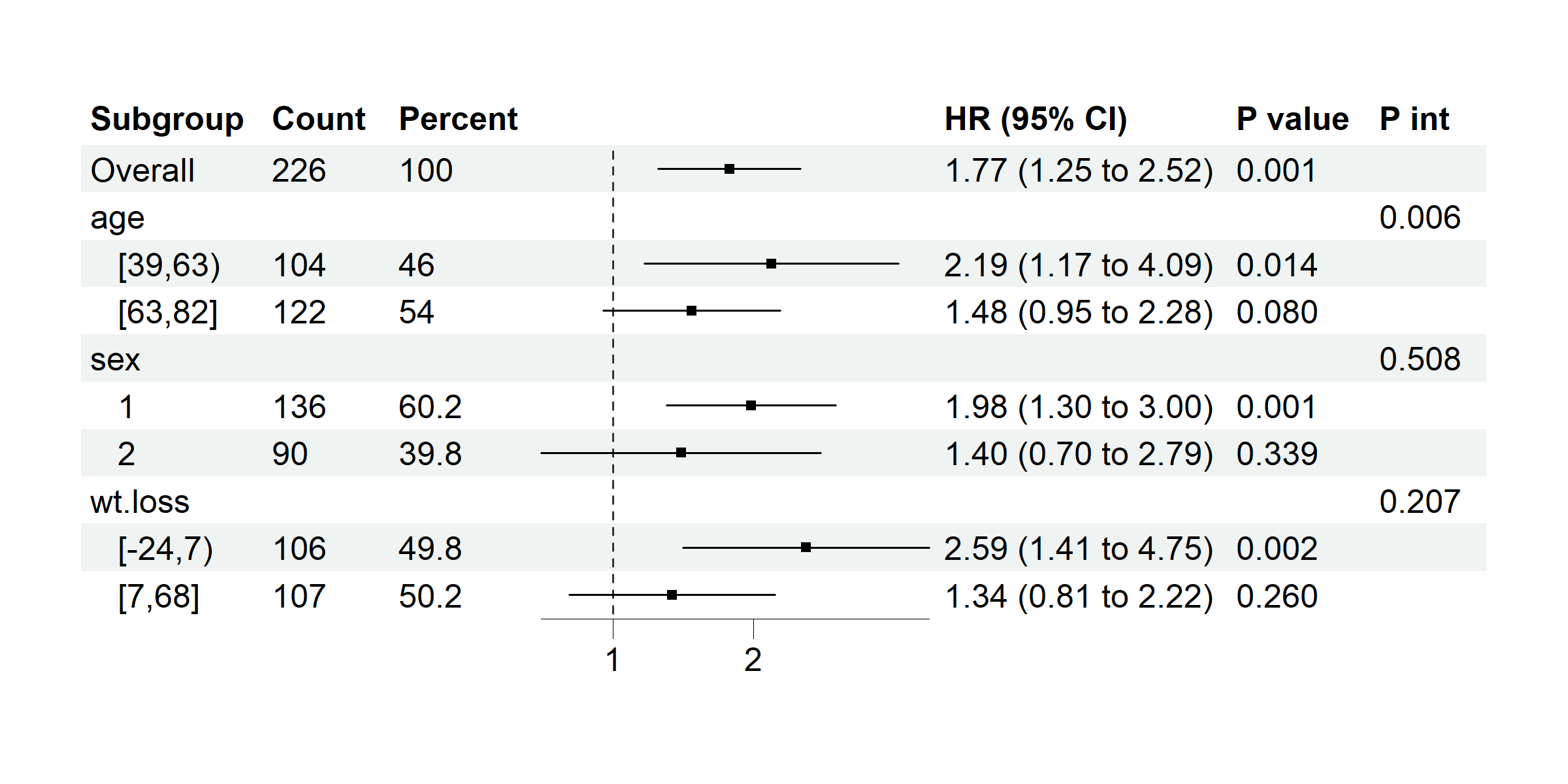
p2 <- regression_forest(
cancer,
model_vars = list(
Crude = c("age per 1 sd"),
Model1 = c("age per 1 sd", "sex"),
Model2 = c("age per 1 sd", "sex", "wt.loss")
),
y = "dead",
save_plot = FALSE
)
plot(p2)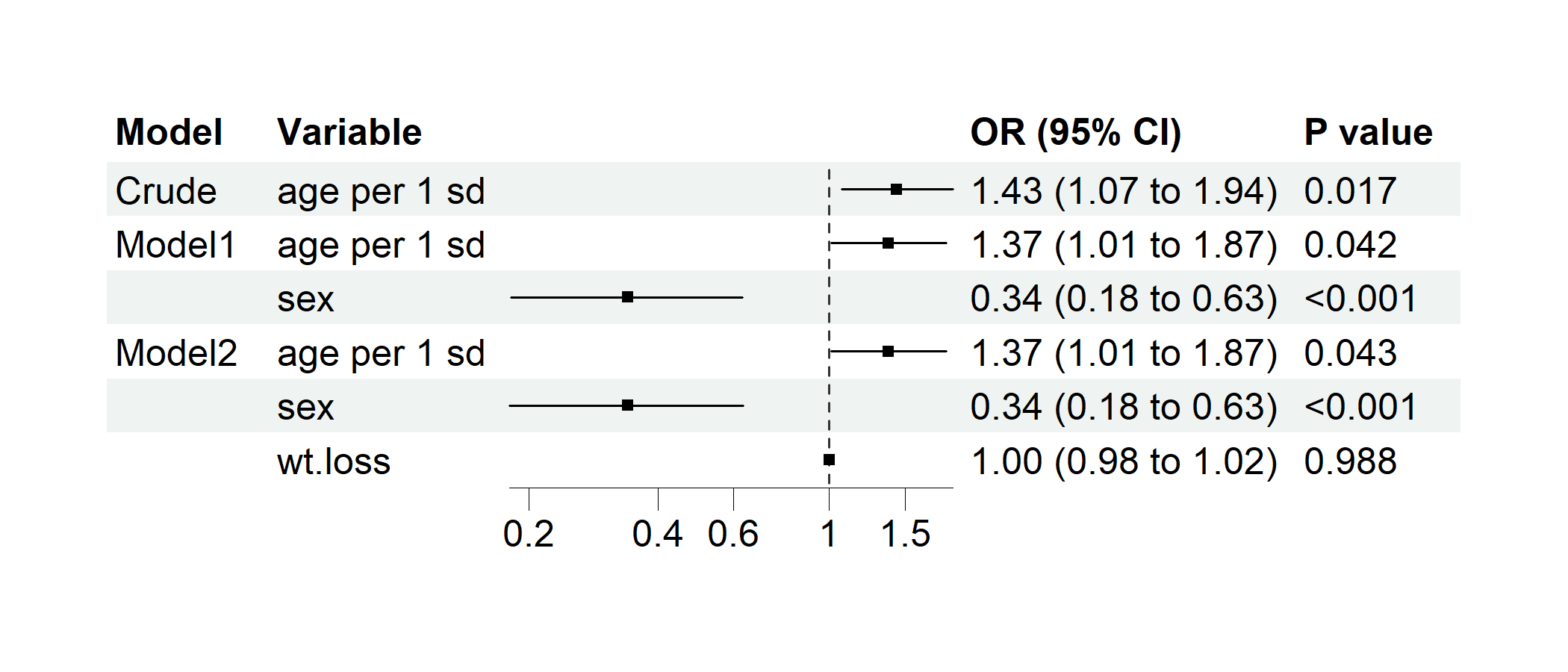
data(cancer, package = "survival")
# coxph model with time assigned
p <- subgroup_forest(cancer,
subgroup_vars = c("age", "sex", "wt.loss"), x = "ph.ecog", y = "status",
time = "time", covars = "ph.karno", ticks_at = c(1, 2), save_plot = FALSE
)
plot(p)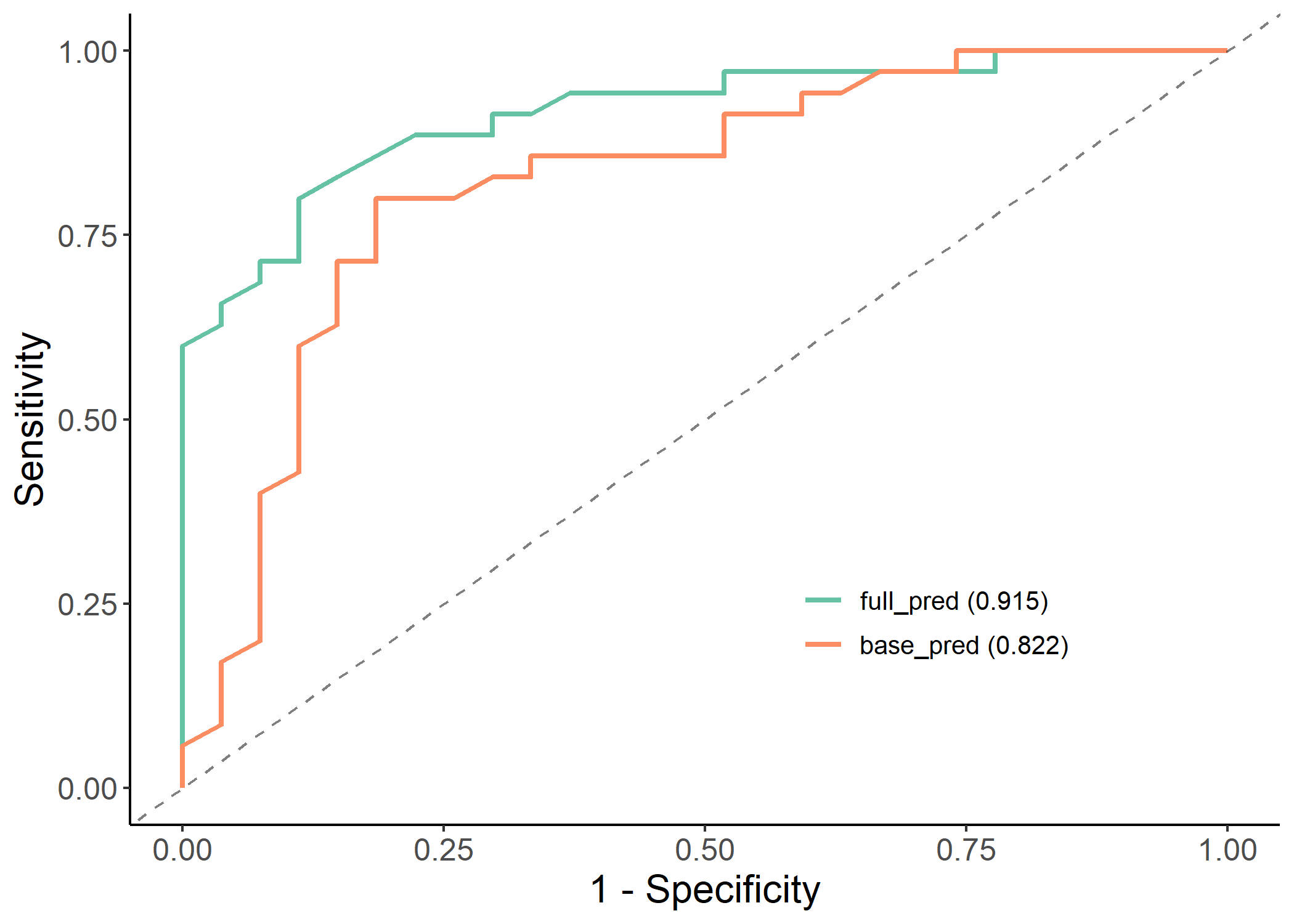
# Building models with example data
data(cancer, package = "survival")
df <- kidney
df$dead <- ifelse(df$time <= 100 & df$status == 0, NA, df$time <= 100)
df <- na.omit(df[, -c(1:3)])
model0 <- glm(dead ~ age + frail, family = binomial(), data = df)
model1 <- glm(dead ~ ., family = binomial(), data = df)
df$base_pred <- predict(model0, type = "response")
df$full_pred <- predict(model1, type = "response")
# Generating most of the useful plots and metrics for model comparison
results <- classif_model_compare(df, "dead", c("base_pred", "full_pred"), save_output = FALSE)
#> Assuming 'TRUE' is [Event] and 'FALSE' is [non-Event]
knitr::kable(results$metric_table)| Model | AUC | PRAUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Pos Pred Value | Neg Pred Value | F1 | Kappa | Brier | cutoff | Youden | HosLem | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | full_pred | 0.915 (0.847, 0.984) | 0.885 | 0.839 | 0.8 | 0.889 | 0.903 | 0.774 | 0.848 | 0.677 | 0.114 | 0.626 | 0.689 | 0.944 |
| 1 | base_pred | 0.822 (0.711, 0.933) | 0.766 | 0.806 | 0.8 | 0.815 | 0.848 | 0.759 | 0.824 | 0.610 | 0.171 | 0.490 | 0.615 | 0.405 |
plot(results$roc_plot)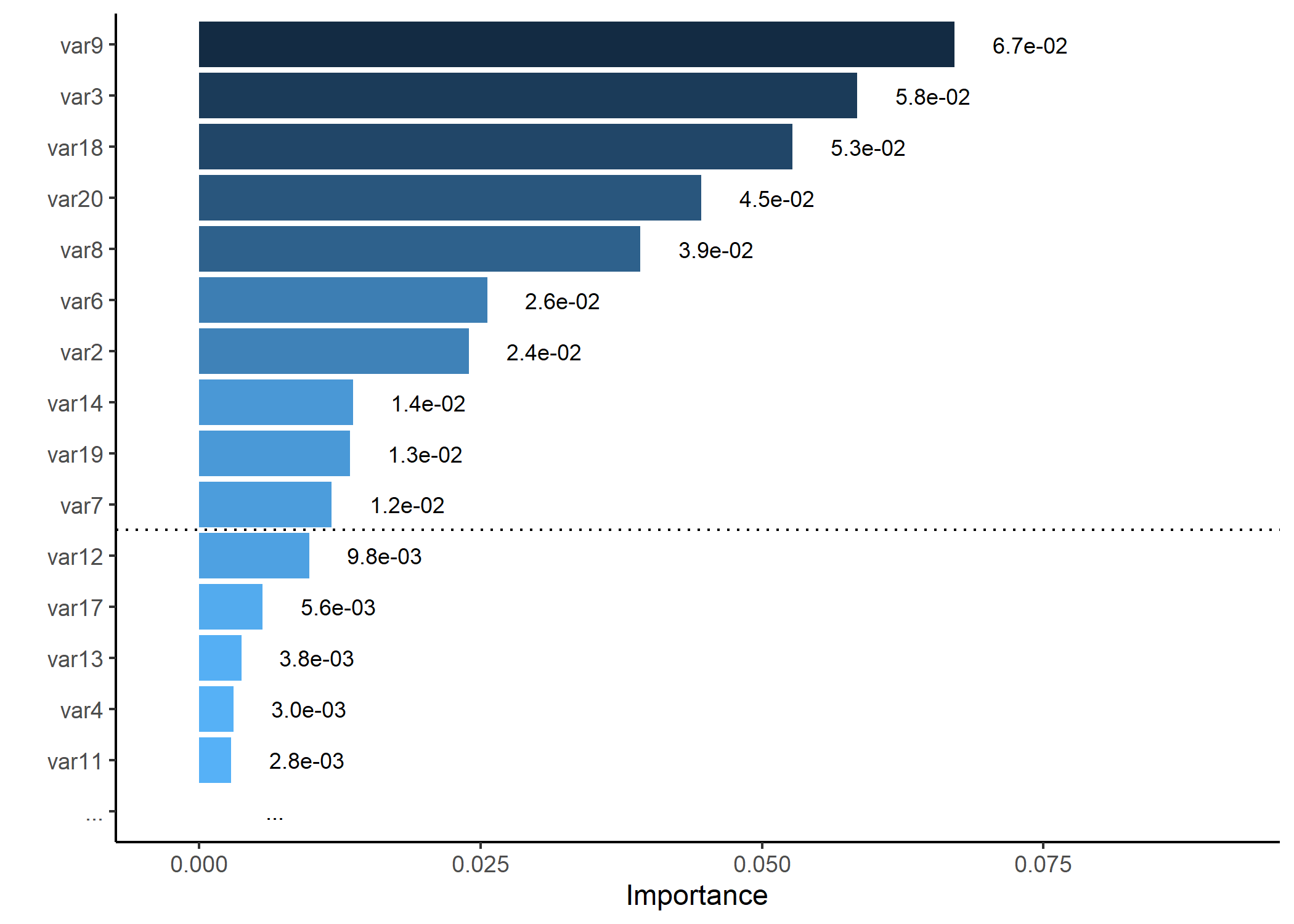
plot(results$pr_plot)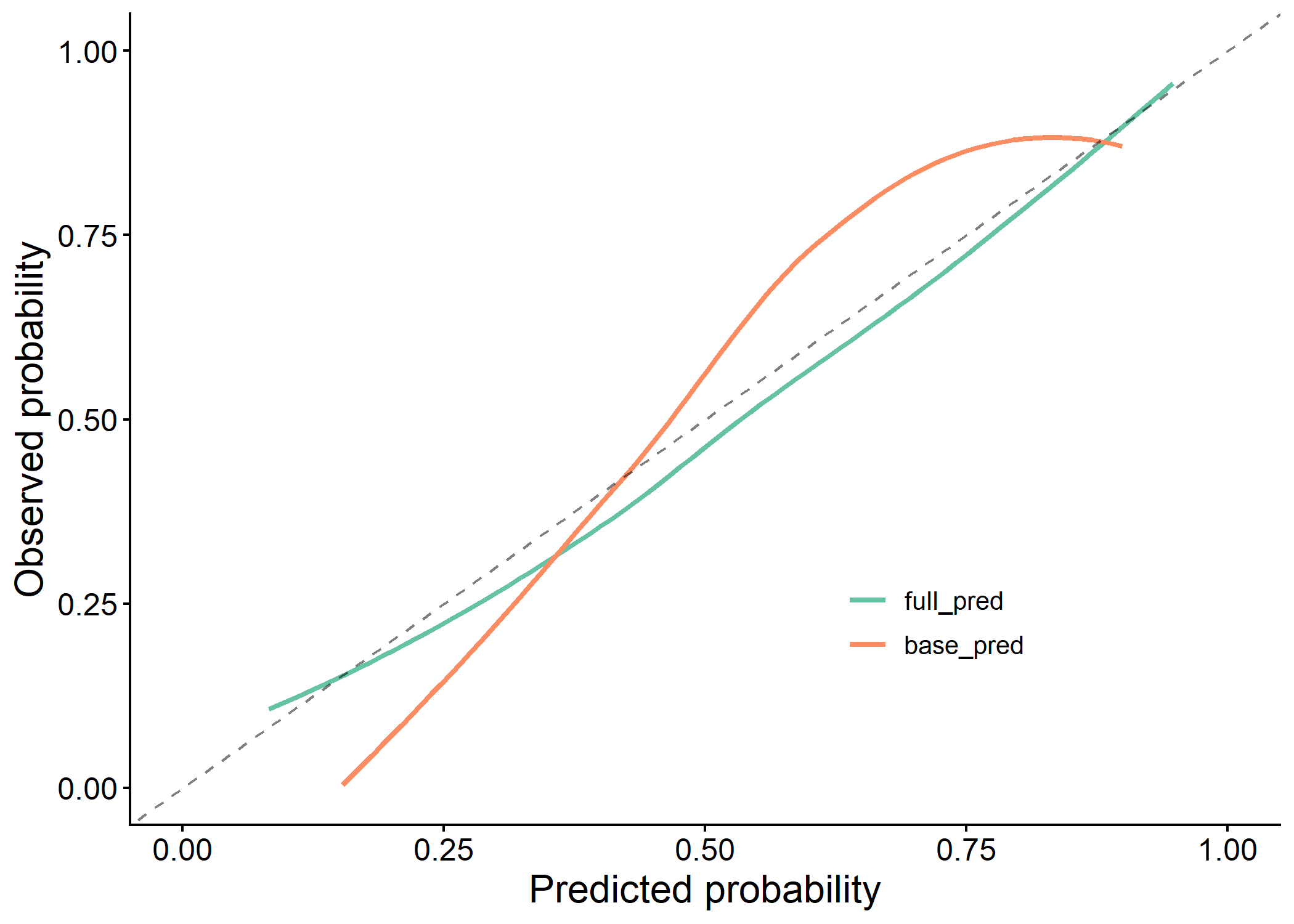
plot(results$calibration_plot)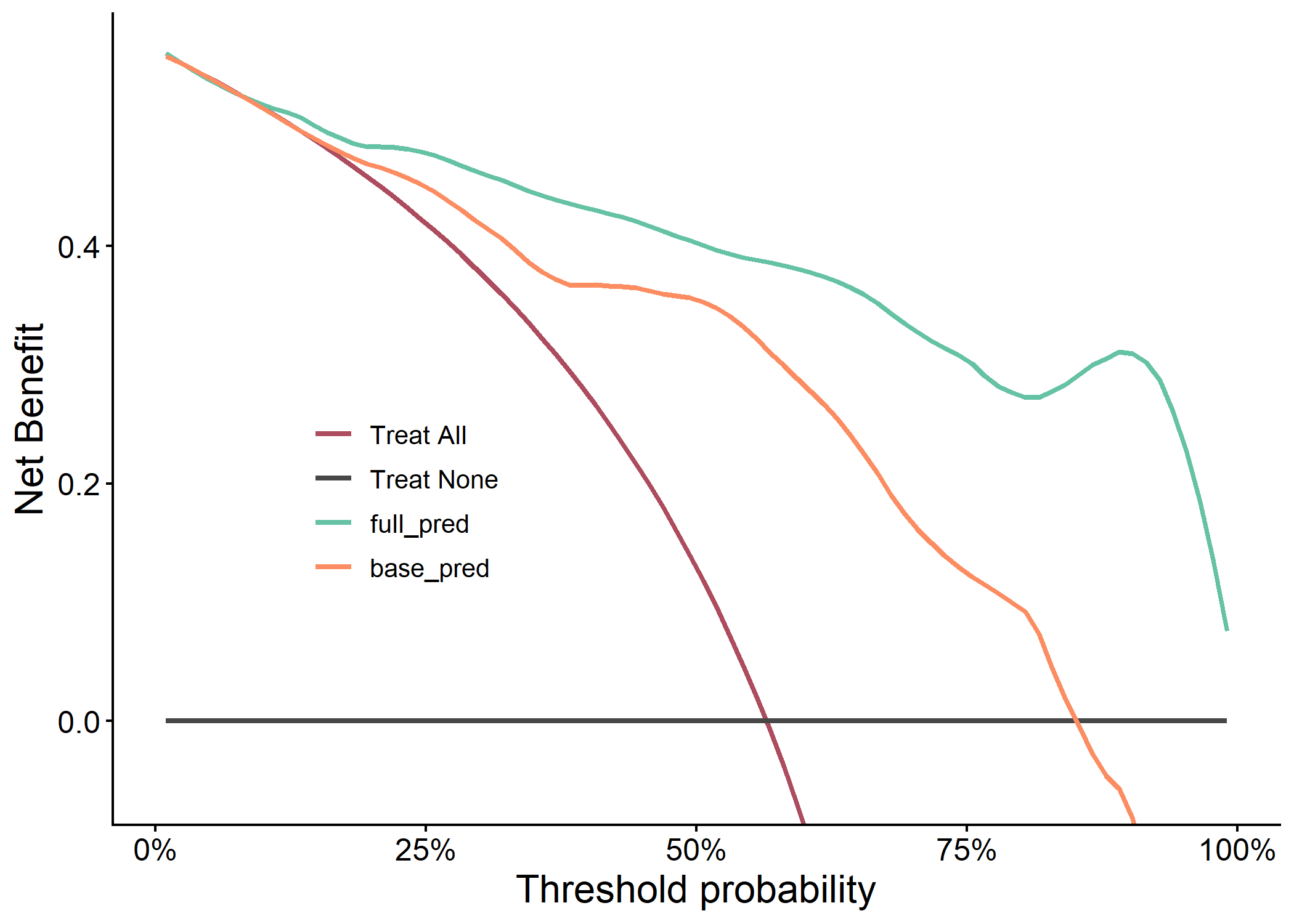
plot(results$dca_plot)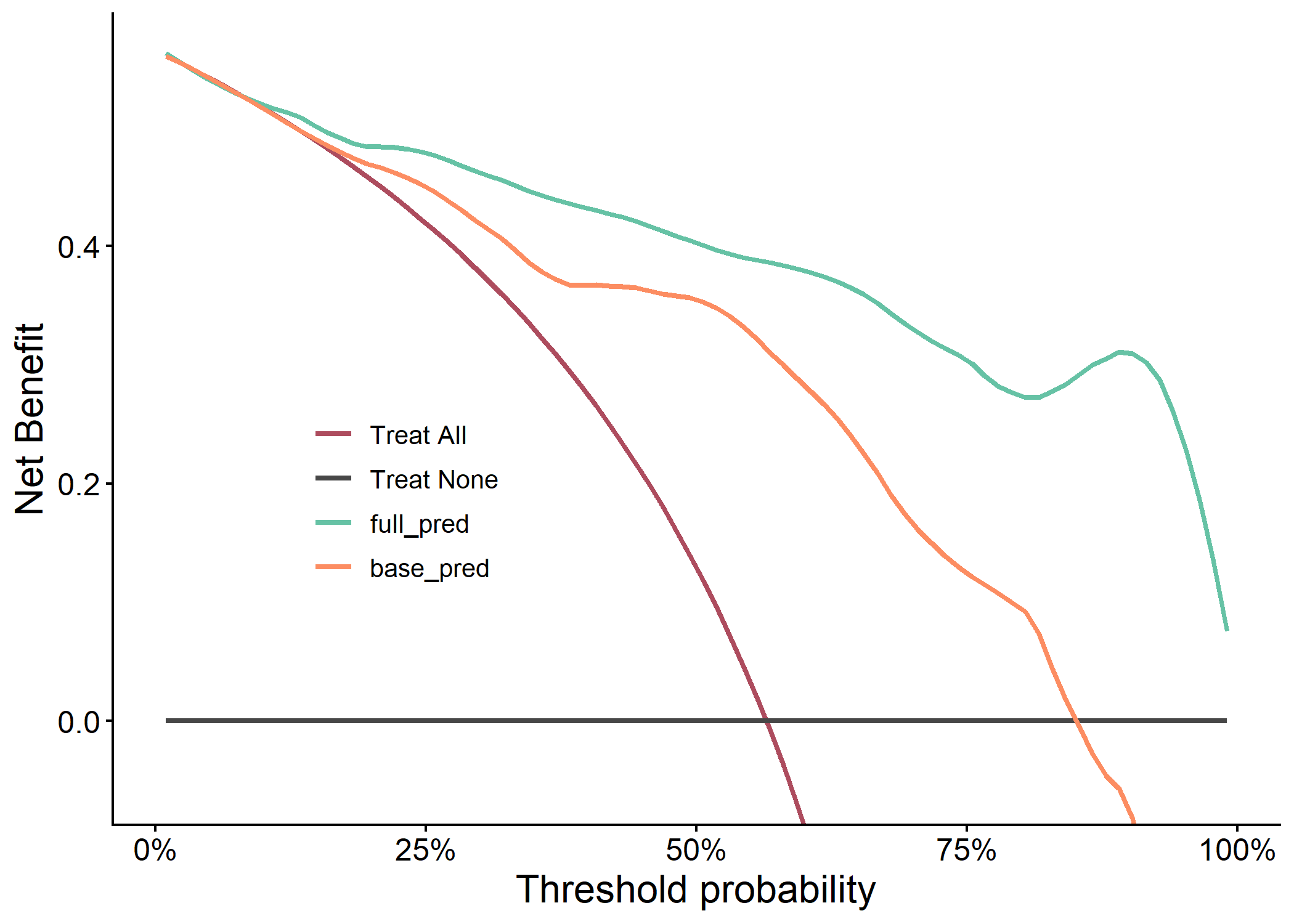
# Generating a dummy importance vector
set.seed(5)
dummy_importance <- runif(20, 0.2, 0.6)^5
names(dummy_importance) <- paste0("var", 1:20)
# Plotting variable importance, keeping only top 15 and splitting at 10
p <- importance_plot(dummy_importance, top_n = 15, split_at = 10, save_plot = FALSE)
plot(p)
#> Warning: Removed 1 row containing missing values or values outside the scale range
#> (`geom_bar()`).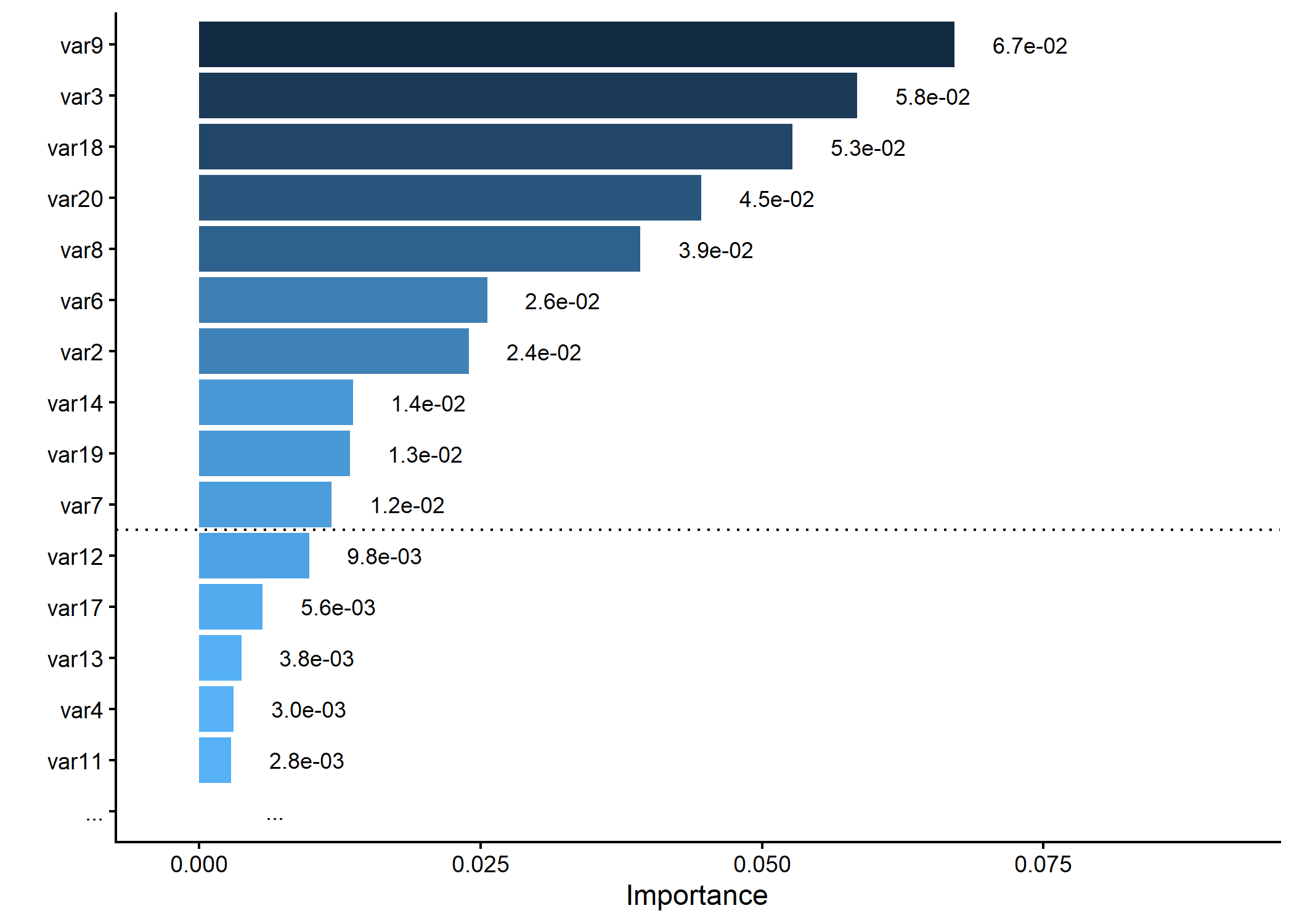
For detailed usage, refer to the package vignettes (coming soon) or the GitHub repository.
Bug reports and feature requests are welcome via the issue tracker.
clinpubr is licensed under GPL (>= 3).
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.