The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
Topic modeling in R via reticulate + the Python
BERTopic ecosystem (version 0.17.x). Provides helpers for
training, persistence, topic inspection, and visualization; see the Quarto
notebook and the vignettes
for an end-to-end workflow.
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("tpetric7/bertopicr")A. Install inside R via reticulate
Requires Python installed and discoverable by the R package
reticulate. Install Python from python.org and restart R on
Windows.
Installation with the setup_python_environment()
function:
library(bertopicr)
library(reticulate)
setup_python_environment(
envname = "r-bertopic",
method = "virtualenv" # or "conda"
)
# Point reticulate at the environment you just created
use_virtualenv("r-bertopic", required = TRUE)
# or use_condaenv("r-bertopic", required = TRUE)
py_config() # confirm reticulate sees the chosen envAlternatively, setup with the following lines of code:
library(reticulate)
# Choose ONE of these depending on what you created
target_env <- "r-bertopic"
use_virtualenv(target_env, required = TRUE) # for virtualenv
# use_condaenv(target_env, required = TRUE) # for conda
req <- system.file("requirements.txt", package = "bertopicr")
# If req is "", reinstall/upgrade the package so the file is available.
py_install(packages = c("-r", req), envname = target_env, method = "auto", pip = TRUE)
py_config() # confirm reticulate sees the chosen envB. Virtualenv (base Python)
python -m venv r-bertopic
# Windows
r-bertopic\Scripts\activate
# macOS/Linux
source r-bertopic/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r inst/requirements.txtC. Conda
conda create -n r-bertopic python=3.10
conda activate r-bertopic
pip install -r inst/requirements.txt(Requirements are bundled at inst/requirements.txt. If
you have a GPU, install a matching CUDA build of PyTorch in the same
env,
e.g. pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118.)
If reticulate fails to load Python libraries on macOS, install
Homebrew zlib and set the fallback library path once per
session:
bertopicr::configure_macos_homebrew_zlib()You can install zlib with Homebrew:
brew install zlibThe package includes helpers for setup, training, and persistence. You can still use your own BERTopic training code, then pass the Python model and outputs into the R helpers.
library(reticulate)
library(bertopicr)
# Point reticulate to the env you prepared
use_virtualenv("r-bertopic", required = TRUE)
# use_condaenv("r-bertopic", required = TRUE)
# Example: train in R (use a real sample to avoid tiny-N failures)
sample_path <- system.file("extdata", "spiegel_sample.rds", package = "bertopicr")
df <- readr::read_rds(sample_path)
texts <- df$text_clean[seq_len(500)]
topic_model <- train_bertopic_model(
texts,
embedding_model = "Qwen/Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B",
top_n_words = 3L
)
# Note: tiny datasets can trigger UMAP spectral warnings/errors; using a
# realistic sample size and a smaller top_n_words avoids that.
save_bertopic_model(topic_model, "topic_model")
loaded <- load_bertopic_model("topic_model")
model <- loaded$model
probs <- loaded$extras$probabilities
# Use the R helpers
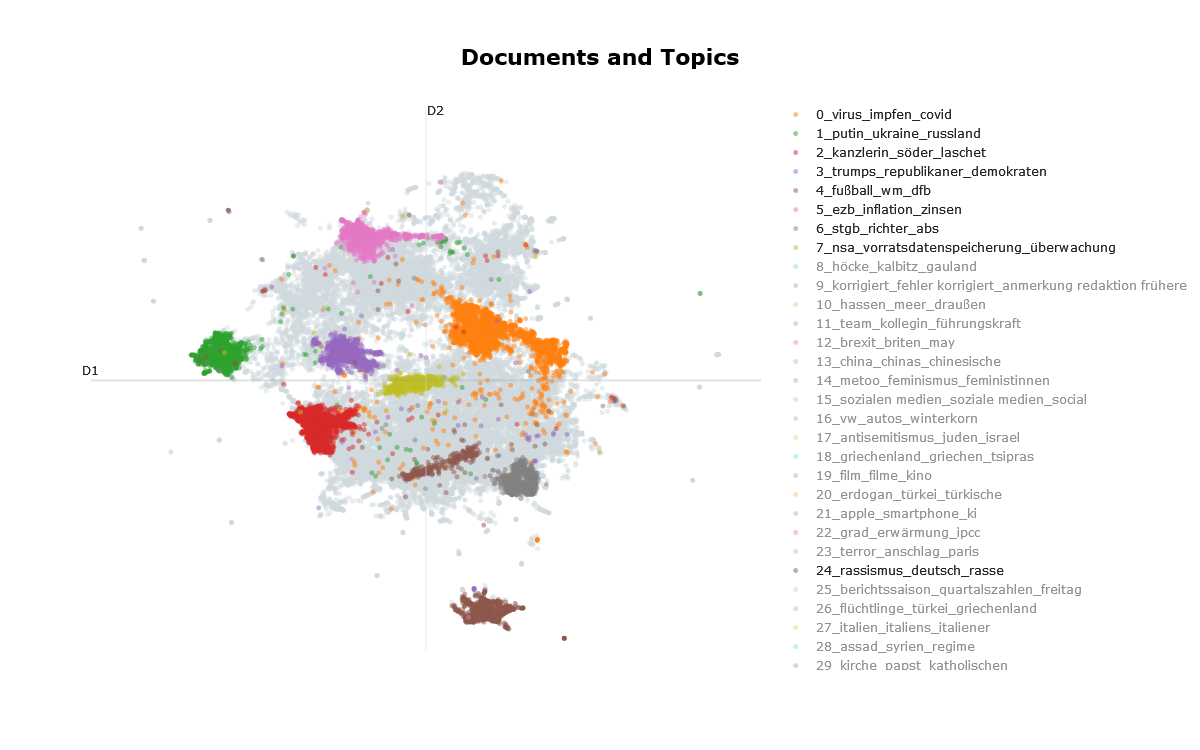
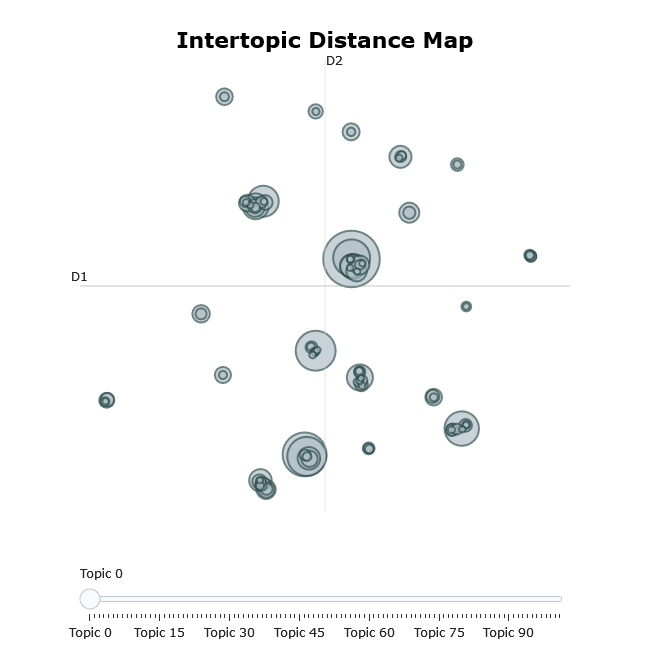
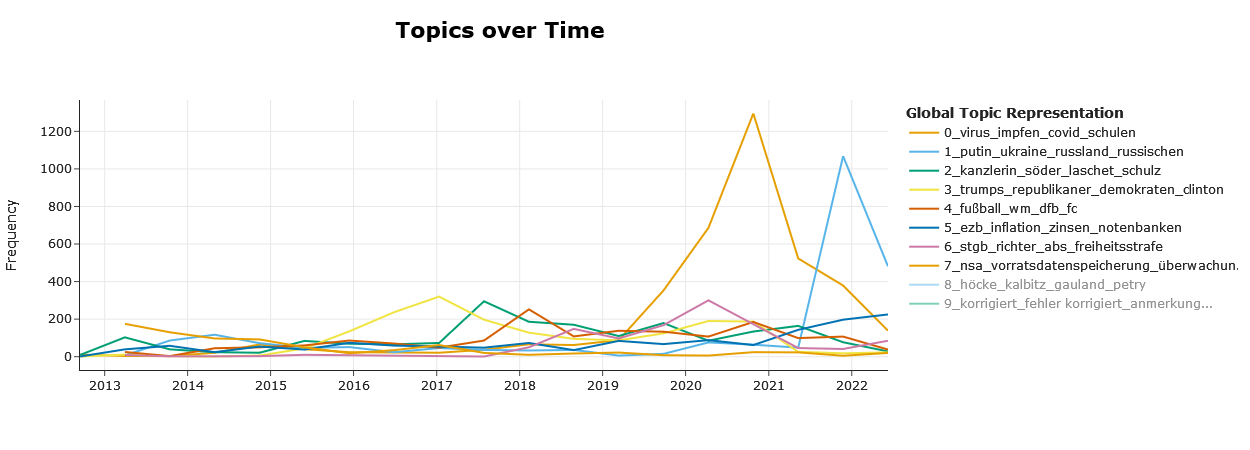
visualize_topics(model, filename = "intertopic_distance_map", auto_open = FALSE)
visualize_distribution(model, text_id = 1, probabilities = probs, auto_open = FALSE)See the vignettes
(including train_and_save_model.Rmd and
load_and_reuse_model.Rmd) or the Quarto
tutorial for a complete workflow (training, representation models
[keyBERT, ollama models, …], dimensionality reduction, clustering, and
visualizations).
The demo script is available at
inst/scripts/train_model_function_demo.R and shows
end-to-end training, saving, loading, and reuse.
BERTopic is described in:
@article{grootendorst2022bertopic,
title={BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure},
author={Grootendorst, Maarten},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.05794},
year={2022}
}This package is licensed under the MIT License. You are free to use, modify, and distribute this software, provided that proper attribution is given to the original author.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.