The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
arcgisutils is the foundational infrastructure package that powers the R-ArcGIS Bridge Data and Location Service ecosystem. It provides sophisticated, production-ready tools for interacting with ArcGIS Online, ArcGIS Enterprise, and ArcGIS Platform via their REST APIs.
🔐 Comprehensive Authentication:
auth_code(),
auth_client())arcgisbinding🌐 Portal Integration:
⚙️ Geoprocessing Services:
arc_gp_job) with real-time
status tracking and built-in result parsing📄 Esri JSON Ecosystem:
sf integration🛠️ Developer Utilities:
arc_base_req(),
arc_paginate_req()){arcgisutils} is part of the {arcgis}
metapackage, which provides the complete R-ArcGIS Bridge toolkit. For
most users, installing the metapackage is recommended:
install.packages("arcgis")You can also install {arcgisutils} individually from
CRAN:
install.packages("arcgisutils")To install the development version:
pak::pak("r-arcgis/arcgisutils")Authorization tokens are provided through the functions
auth_code(), auth_client(),
auth_user(), auth_key(), and
auth_binding(). Additional token validation functions are
provided via refresh_token() and
validate_or_refresh_token().
auth_code() can be used for integrating into Shiny
applications, for example, to have individual users log in. We recommend
using auth_key() for authenticating in non-interactive
environments (for example scheduled scripts or deployments).
Tokens are managed using set_arc_token() and
unset_arc_token(). They are fetched using
arc_token(). set_arc_token() can set the token
globally or set multiple named environments. Here is a minimal
example:
library(arcgisutils)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'arcgisutils'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> %||%key <- auth_key()
set_arc_token(key)Alternatively, tokens can be set based on a key-value pair for multiple environments:
set_arc_token("production" = prod_token, "development" = dev_token)And fetched based on their name via
arc_token("production")Search and discover content across your ArcGIS organization:
# Search for feature services containing "crime" data
crime_items <- search_items(
query = "crime",
item_type = "Feature Service",
max_pages = 1
)
crime_items
#> # A data frame: 50 × 46
#> id owner created modified guid name title type
#> * <chr> <chr> <dttm> <dttm> <lgl> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 ea0cfe… Toro… 2023-03-28 15:02:39 2025-01-22 18:27:48 NA Neig… Neig… Feat…
#> 2 0a239a… Toro… 2023-03-27 18:59:00 2025-08-06 14:01:27 NA Majo… Majo… Feat…
#> 3 5e055d… JASo… 2023-04-04 17:36:59 2023-09-07 19:05:06 NA <NA> Sher… Feat…
#> 4 64691a… Temp… 2024-01-17 20:01:43 2024-01-17 20:04:45 NA hate… Hate… Feat…
#> 5 7c2b78… JASo… 2023-04-04 17:49:30 2023-06-02 22:27:11 NA <NA> Sher… Feat…
#> 6 e0992d… balt… 2023-07-31 20:27:01 2025-01-22 21:21:01 NA Part… Part… Feat…
#> 7 c749e3… open… 2024-02-23 19:36:34 2025-09-04 17:08:47 NA <NA> Crim… Feat…
#> 8 2cb53d… KASU… 2019-12-10 19:06:39 2019-12-10 19:14:27 NA Viol… Viol… Feat…
#> 9 30644d… MyCi… 2025-03-14 14:55:06 2025-08-20 13:55:24 NA HPD_… HPD … Feat…
#> 10 5dc4e6… iwat… 2023-06-23 22:07:21 2023-08-09 15:33:46 NA <NA> Prop… Feat…
#> # ℹ 40 more rows
#> # ℹ 38 more variables: typeKeywords <list>, description <chr>, tags <list>,
#> # snippet <chr>, thumbnail <chr>, documentation <lgl>, extent <list>,
#> # categories <list>, spatialReference <chr>, accessInformation <chr>,
#> # classification <lgl>, licenseInfo <chr>, culture <chr>, properties <list>,
#> # advancedSettings <lgl>, url <chr>, proxyFilter <lgl>, access <chr>,
#> # size <int>, subInfo <int>, appCategories <list>, industries <list>, …# Get detailed item information for a portal item
arc_item(crime_items$id[1])
#> <PortalItem<Feature Service>>
#> id: ea0cfecdb1de416884e6b0bf08a9e195
#> title: Neighbourhood Crime Rates Open Data
#> owner: TorontoPoliceServiceAlways use arc_base_req() as this will handle setting
the user agent and authorization token. The function creates a
standardized httr2 request object:
# defaults to arcgis.com
host <- arc_host()
req <- arc_base_req(host)
req
#> <httr2_request>
#> GET https://www.arcgis.com
#> Body: empty
#> Options:
#> * useragent: "arcgisutils v0.3.3.9000"To handle paginated services and requests use
arc_paginate_req() to automatically handle fetching
pages.
There are also a number of utility functions for creating and parsing
Esri JSON. For example we can create an Esri FeatureSet
json string using as_esri_featureset() directly from an
sf object.
library(sf)
# load the NC SIDS dataset and extract centroids
# of the first few rows
nc <- system.file("shape/nc.shp", package = "sf") |>
st_read(quiet = TRUE) |>
st_centroid()
# convert to json
nc_json <- as_esri_featureset(nc[1:2, 1:3])
jsonify::pretty_json(nc_json)
#> {
#> "geometryType": "esriGeometryPoint",
#> "spatialReference": {
#> "wkid": 4267
#> },
#> "features": [
#> {
#> "geometry": {
#> "x": -81.4982290095261,
#> "y": 36.43139560823758
#> },
#> "attributes": {
#> "AREA": 0.114,
#> "CNTY_": 1825.0,
#> "PERIMETER": 1.442
#> }
#> },
#> {
#> "geometry": {
#> "x": -81.12512977849917,
#> "y": 36.49110847237506
#> },
#> "attributes": {
#> "AREA": 0.061,
#> "CNTY_": 1827.0,
#> "PERIMETER": 1.231
#> }
#> }
#> ]
#> }Feature set json can also be parsed using
parse_esri_json().
parse_esri_json(nc_json)
#> Simple feature collection with 2 features and 3 fields
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -81.49823 ymin: 36.4314 xmax: -81.12513 ymax: 36.49111
#> Geodetic CRS: NAD27
#> AREA CNTY_ PERIMETER geometry
#> 1 0.114 1825 1.442 POINT (-81.49823 36.4314)
#> 2 0.061 1827 1.231 POINT (-81.12513 36.49111)Additionally, sf’s crs object can be converted to a spatialReference
JSON object using validate_crs(). Convert these to json
with yyjsonr or jsonify.
crs <- validate_crs(27700)
jsonify::pretty_json(crs, unbox = TRUE)
#> {
#> "spatialReference": {
#> "wkid": 27700
#> }
#> }The geoprocessing service framework is completely supported in
{arcgisutils}. Here we combine the functionality of the
geoprocessing job framework with utilities such as
as_esri_featureset() to call the Trace
DownStream Elevation Service
trace_downstream <- function(
input_points,
point_id_field = NULL,
resolution = NULL,
generalize = FALSE,
token = arc_token()
) {
# create a list of parameters
params <- compact(list(
InputPoints = as_esri_featureset(input_points),
PointIdField = point_id_field,
DataSourceResolution = resolution,
Generalize = as.character(generalize),
f = "json"
))
service_url <- "https://hydro.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/Tools/Hydrology/GPServer/TraceDownstream"
arc_gp_job$new(
base_url = service_url,
params = params,
result_fn = parse_gp_feature_record_set,
token
)
}This new function can be called to start a new job:
# create input points
input_points <- st_sfc(
st_point(c(-159.548936, 21.955888)),
crs = 4326
)
# initialze an empty job
job <- trace_downstream(
input_points,
token = auth_user()
)
# start the job
job$start()
#> <arc_gp_job>
#> Job ID: jd9f76de1e62e4d8a877f3e6859fdb7b2
#> Status: not started
#> Resource: /TraceDownstream
#> Params:
#> • InputPoints
#> • Generalize
#> • fJobs run asynchronously so we can check the status with
job$status
job$status
#> <arcgisutils::arc_job_status>
#> @ status: chr "esriJobSubmitted"Then, when the job is complete, we can fetch the results applying the
result function which is parse_gp_feature_record_set() in
this case.
job$results
#> $param_name
#> [1] "OutputTraceLine"
#>
#> $data_type
#> [1] "GPFeatureRecordSetLayer"
#>
#> $geometry
#> Simple feature collection with 1 feature and 6 fields
#> Geometry type: MULTILINESTRING
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: 438895 ymin: 2422310 xmax: 443325 ymax: 2428045
#> Projected CRS: NAD83 / UTM zone 4N + Unknown VCS
#> OBJECTID PourPtID Description DataResolution LengthKm
#> 1 1 1 NED 10m processed by Esri 10.0 9.489823
#> Shape_Length geometry
#> 1 9489.823 MULTILINESTRING ((443325 24...
# store and view the results
res <- job$results
res
#> $param_name
#> [1] "OutputTraceLine"
#>
#> $data_type
#> [1] "GPFeatureRecordSetLayer"
#>
#> $geometry
#> Simple feature collection with 1 feature and 6 fields
#> Geometry type: MULTILINESTRING
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: 438895 ymin: 2422310 xmax: 443325 ymax: 2428045
#> Projected CRS: NAD83 / UTM zone 4N + Unknown VCS
#> OBJECTID PourPtID Description DataResolution LengthKm
#> 1 1 1 NED 10m processed by Esri 10.0 9.489823
#> Shape_Length geometry
#> 1 9489.823 MULTILINESTRING ((443325 24...
# plot the resultant geometry
plot(st_geometry(res$geometry))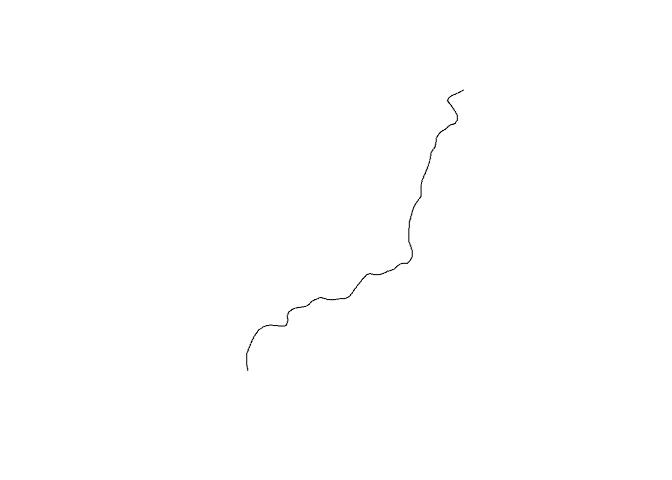
To learn more about the R-ArcGIS Bridge project visit the developer documentation.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.