The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
The goal of aplms is fitting Additive partial linear
models with symmetric autoregressive errors (APLMS), proposed by Chou-Chen et al.,
(2024). This framework models a time series response variable using
both linear and nonlinear structures of a set of explanatory variables,
with the nonparametric components approximated by natural cubic splines
or P-splines. It also accounts for autoregressive error terms with
distributions that have lighter or heavier tails than the normal
distribution.
You can install the package with:
install.packages("aplms")or the development version of aplms from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("shuwei325/aplms")The details of the model and its assumptions are given in Chou-Chen et al., (2024).
This package provides two datasets to illustrate the model fitting procedure. To load the package:
library(aplms)The first dataset temperature:
data(temperature)
# Create dataframe object to fit the model
datos = data.frame(temperature,time=1:length(temperature))
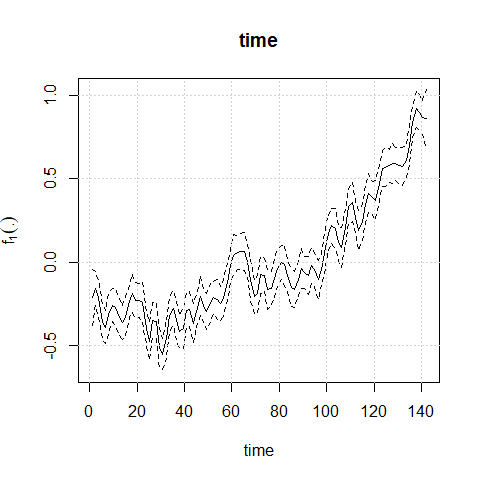
mod1<-aplms::aplms(temperature ~ 1,
npc=c("time"), basis=c("cr"),Knot=c(60),
data=datos,family=Powerexp(k=0.3),p=1,
control = list(tol = 0.001,
algorithm1 = c("P-GAM"),
algorithm2 = c("BFGS"),
Maxiter1 = 20,
Maxiter2 = 25),
lam=c(10))summary(mod1)
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------
#> Additive partial linear models with symmetric errors
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------
#> Sample size: 142
#> -------------------------- Model ---------------------------
#>
#> aplms::aplms(formula = temperature ~ 1, npc = c("time"), basis = c("cr"),
#> Knot = c(60), data = datos, family = Powerexp(k = 0.3), p = 1,
#> control = list(tol = 0.001, algorithm1 = c("P-GAM"), algorithm2 = c("BFGS"),
#> Maxiter1 = 20, Maxiter2 = 25), lam = c(10))
#>
#> ------------------- Parametric component -------------------
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> intercept 0.056619 0.0041 13.8905 < 2.2e-16 ***
#>
#> ----------------- Non-parametric component ------------------
#>
#> Wald df Pr(>.)
#> time 7589.838 58.583 < 2.2e-16 ***
#>
#> --------------- Autoregressive and Scale parameter ----------------
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error Wald Pr(>|t|)
#> phi 0.0022992 0.0003 7.3902 1.242e-11 ***
#> rho1 -0.2571215 0.0662 -3.8866 0.0001568 ***
#>
#>
#> ------ Penalized Log-likelihood and Information criterion------
#>
#> Log-lik: 200.07
#> AIC : -276.97
#> AICc : -274.46
#> BIC : -94.94
#> GCV : 0.01
#>
#> --------------------------------------------------------------------plot(mod1)
To perform diagnostic and influence analyses, execute:
aplms.diag.plot(mod1)
influenceplot.aplms(mod1, perturbation = c("case-weight"))The second dataset hospitalization:
data(hospitalization)
mod2<-aplms::aplms(formula = y ~
MP10_avg + NO_avg + O3_avg + TEMP_min + ampl_max + RH_max,
npc=c("tdate","epi.week"), basis=c("cr","cc"),Knot=c(60,12),
data=hospitalization,family=Powerexp(k=0.3),p=3,
control = list(tol = 0.001,
algorithm1 = c("P-GAM"),
algorithm2 = c("BFGS"),
Maxiter1 = 20,
Maxiter2 = 25),
lam=c(100,10))summary(mod2)
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------
#> Additive partial linear models with symmetric errors
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------
#> Sample size: 932
#> -------------------------- Model ---------------------------
#>
#> aplms::aplms(formula = y ~ MP10_avg + NO_avg + O3_avg + TEMP_min +
#> ampl_max + RH_max, npc = c("tdate", "epi.week"), basis = c("cr",
#> "cc"), Knot = c(60, 12), data = hospitalization, family = Powerexp(k = 0.3),
#> p = 3, control = list(tol = 0.001, algorithm1 = c("P-GAM"),
#> algorithm2 = c("BFGS"), Maxiter1 = 20, Maxiter2 = 25),
#> lam = c(100, 10))
#>
#> ------------------- Parametric component -------------------
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> intercept 83.317951 14.8082 5.6265 2.44e-08 ***
#> MP10_avg 0.276500 0.0673 4.1057 4.39e-05 ***
#> NO_avg -0.071118 0.0909 -0.7821 0.4344
#> O3_avg -0.050675 0.0632 -0.8014 0.4231
#> TEMP_min 0.073164 0.2201 0.3324 0.7397
#> ampl_max -0.174587 0.2640 -0.6613 0.5086
#> RH_max -0.071845 0.1382 -0.5199 0.6032
#>
#> ----------------- Non-parametric component ------------------
#>
#> Wald df Pr(>.)
#> tdate 13.8541 3.5398 0.005221 **
#> epi.week 16.9563 1.5178 9.978e-05 ***
#>
#> --------------- Autoregressive and Scale parameter ----------------
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error Wald Pr(>|t|)
#> phi 96.19593 5.0808 18.9331 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> rho1 0.45783 0.0318 14.4155 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> rho2 0.23190 0.0345 6.7186 3.211e-11 ***
#> rho3 0.16820 0.0323 5.2017 2.434e-07 ***
#>
#>
#> ------ Penalized Log-likelihood and Information criterion------
#>
#> Log-lik: -3706.73
#> AIC : 7445.58
#> AICc : 7446.61
#> BIC : 7523.26
#> GCV : 99.57
#>
#> --------------------------------------------------------------------plot(mod2)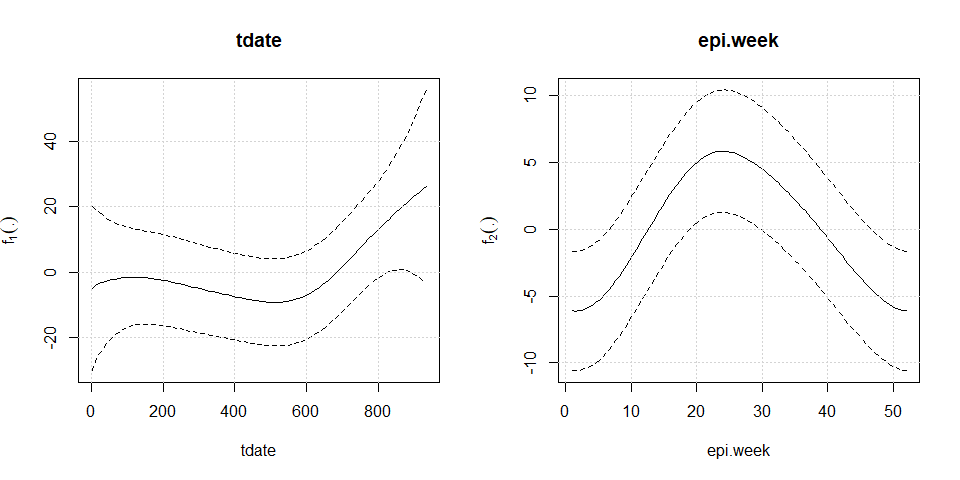
To perform diagnostic and influence analyses, execute:
aplms.diag.plot(mod2)and
influenceplot.aplms(mod2, perturbation = c("case-weight"))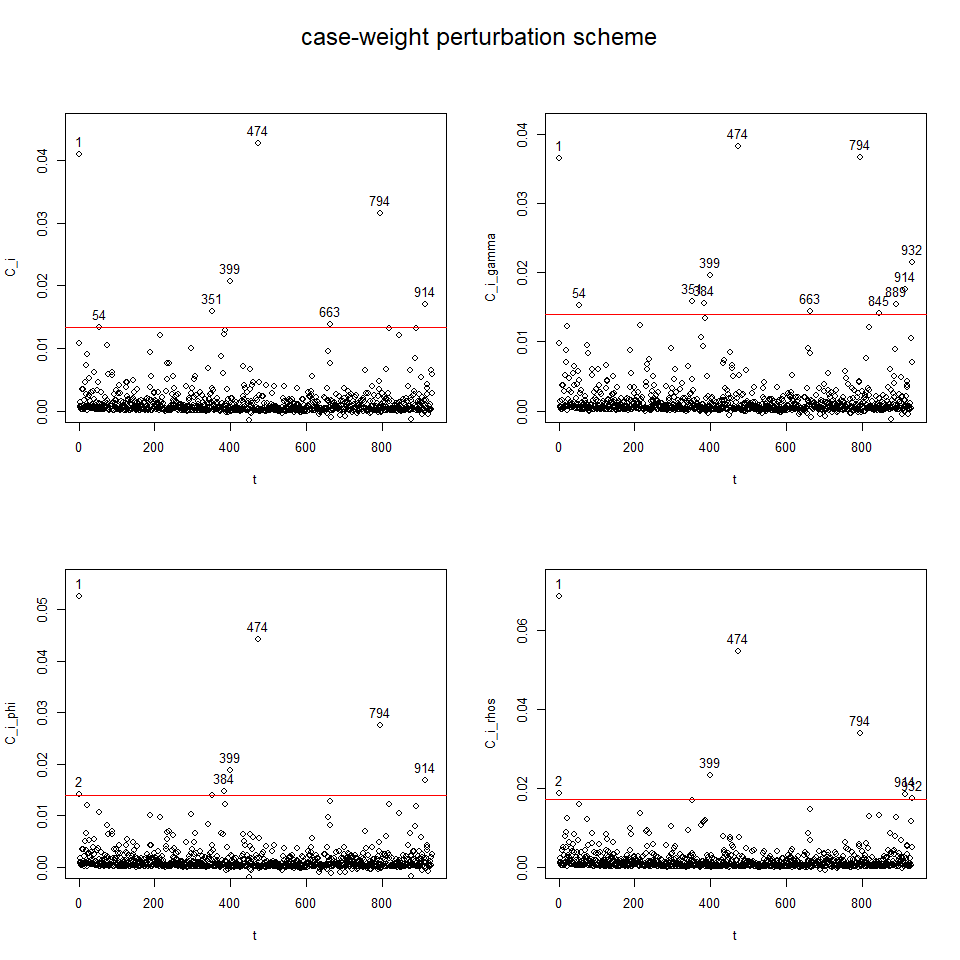
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.