The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
The goal of STICr (pronounced “sticker”) is to provide a standardized
set of functions for working with data from Stream Temperature,
Intermittency, and Conductivity (STIC) loggers, first described in Chapin
et al. (2014). STICs and other intermittency sensors are becoming
more popular, but their raw data output is not in a form that allows for
convenient analysis. This package aims to provide a set of functions for
tidying the raw data from these loggers, as well as calibrating their
conductivity measurements to specific conductivity (SpC)
and classifying the conductivity data to generate a classified “wet/dry”
data set.
You can install STICr from CRAN or the development version of STICr from GitHub with:
# install.packages("STICr") # if needed: install package from CRAN
# devtools::install_github("HEAL-KGS/STICr") # if needed: install dev version from GitHub
library(STICr)This is an example workflow that shows the main functionality of the package. A more detailed version is available in the package vignette.
# read in raw HOBO data and tidy
df_tidy <- tidy_hobo_data(infile = "https://samzipper.com/data/raw_hobo_data.csv", outfile = FALSE)
head(df_tidy)
#> datetime condUncal tempC
#> 1 2021-07-16 22:00:00 88178.4 27.764
#> 2 2021-07-16 22:15:00 77156.1 28.655
#> 3 2021-07-16 22:30:00 74400.5 28.060
#> 4 2021-07-16 22:45:00 74400.5 27.764
#> 5 2021-07-16 23:00:00 74400.5 27.862
#> 6 2021-07-16 23:15:00 71644.9 27.370The second function is called get_calibration and is
demonstrated below. The function intakes a STIC calibration data frame
with columns standard and
conductivity_uncaland outputs a fitted model object
relating spc to the uncalibrated conductivity values
measured by the STIC.
# load calibration
lm_calibration <- get_calibration(calibration_standard_data)
# apply calibration
df_calibrated <- apply_calibration(
stic_data = df_tidy,
calibration = lm_calibration,
outside_std_range_flag = T
)
head(df_calibrated)
#> datetime condUncal tempC SpC outside_std_range
#> 1 2021-07-16 22:00:00 88178.4 27.764 857.3845
#> 2 2021-07-16 22:15:00 77156.1 28.655 752.0820
#> 3 2021-07-16 22:30:00 74400.5 28.060 725.7561
#> 4 2021-07-16 22:45:00 74400.5 27.764 725.7561
#> 5 2021-07-16 23:00:00 74400.5 27.862 725.7561
#> 6 2021-07-16 23:15:00 71644.9 27.370 699.4302# classify data
df_classified <- classify_wetdry(
stic_data = df_calibrated,
classify_var = "SpC",
threshold = 100,
method = "absolute"
)
head(df_classified)
#> datetime condUncal tempC SpC outside_std_range wetdry
#> 1 2021-07-16 22:00:00 88178.4 27.764 857.3845 wet
#> 2 2021-07-16 22:15:00 77156.1 28.655 752.0820 wet
#> 3 2021-07-16 22:30:00 74400.5 28.060 725.7561 wet
#> 4 2021-07-16 22:45:00 74400.5 27.764 725.7561 wet
#> 5 2021-07-16 23:00:00 74400.5 27.862 725.7561 wet
#> 6 2021-07-16 23:15:00 71644.9 27.370 699.4302 wet# apply qaqc function
df_qaqc <-
qaqc_stic_data(
stic_data = df_classified,
spc_neg_correction = T,
inspect_deviation = T,
deviation_size = 2,
window_size = 96
)
head(df_qaqc)
#> datetime condUncal tempC SpC wetdry QAQC
#> 1 2021-07-16 22:00:00 88178.4 27.764 857.3845 wet
#> 2 2021-07-16 22:15:00 77156.1 28.655 752.0820 wet
#> 3 2021-07-16 22:30:00 74400.5 28.060 725.7561 wet
#> 4 2021-07-16 22:45:00 74400.5 27.764 725.7561 wet
#> 5 2021-07-16 23:00:00 74400.5 27.862 725.7561 wet
#> 6 2021-07-16 23:15:00 71644.9 27.370 699.4302 wet
table(df_qaqc$QAQC)
#>
#> DO O
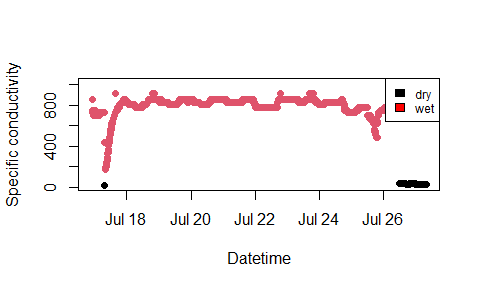
#> 916 1 83# plot SpC through time, colored by wetdry
plot(df_classified$datetime, df_classified$SpC,
col = as.factor(df_classified$wetdry),
pch = 16,
lty = 2,
xlab = "Datetime",
ylab = "Specific conductivity"
)
legend("topright", c("dry", "wet"),
fill = c("black", "red"), cex = 0.75
)
# create validation data frame
stic_validation <-
validate_stic_data(
stic_data = classified_df,
field_observations = field_obs,
max_time_diff = 30,
join_cols = NULL,
get_SpC = TRUE,
get_QAQC = FALSE
)
# compare the field observations and classified STIC data in table
head(stic_validation)
#> datetime wetdry_obs SpC_obs condUncal_STIC wetdry_STIC SpC_STIC
#> 1 2021-07-16 18:03:00 wet 612.1672 74400.5 wet 725.7561
#> 2 2021-07-19 15:01:00 wet 589.4157 88178.4 wet 857.3845
#> 3 2021-07-21 02:44:00 dry 599.6622 85422.8 wet 831.0587
#> 4 2021-07-23 13:55:00 wet 916.8215 88178.4 wet 857.3845
#> 5 2021-07-25 16:27:00 wet 631.9857 77156.1 wet 752.0820
#> timediff_min
#> 1 3
#> 2 1
#> 3 -1
#> 4 -5
#> 5 -3
# calculate percent classification accuracy
sum(stic_validation$wetdry_obs == stic_validation$wetdry_STIC) / length(stic_validation$wetdry_STIC)
#> [1] 0.8
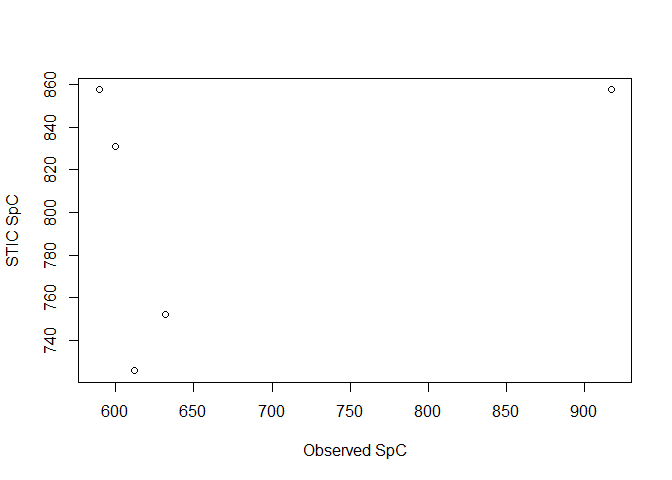
# compare SpC as a plot
plot(stic_validation$SpC_obs, stic_validation$SpC_STIC,
xlab = "Observed SpC", ylab = "STIC SpC"
)
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.