The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
RegEnRF is the implementation of the Regression-Enhanced
Random Forests algorithm as described in Zhang et
al. (2019).
You can install RegEnRF like so:
install.packages("RegEnRF")or the development version like so:
devtools::install_github("umbe1987/regenrf")This is an example showing how to perform Regression-Enhanced Random
Forests with RegEnRF. It demonstrates how
RegEnRF can extrapolate beyond the training domain, as
opposed to randomForest.
library(RegEnRF)
set.seed(111)
data(co2)
x <- matrix(c(time(co2), cycle(co2)), ncol = 2)
y <- as.numeric(co2)
mod <- RegEnRF(x, y, lambda = 0.1)
#> Warning in rfout$mse/(var(y) * (n - 1)/n): Recycling array of length 1 in vector-array arithmetic is deprecated.
#> Use c() or as.vector() instead.
freq <- frequency(co2)
startt <- tsp(co2)[2] + 1 / freq
xnew.t <- seq(startt, by = 1 / freq, length.out = freq * 3)
xnew <- matrix(c(xnew.t, cycle(tail(co2, freq * 3))), ncol = 2)
pred <- predict(mod, xnew)
pred.ts <- ts(pred, start = startt, frequency = freq)
plot(ts.union(co2, pred.ts), plot.type = "single", col = c("black", "red"))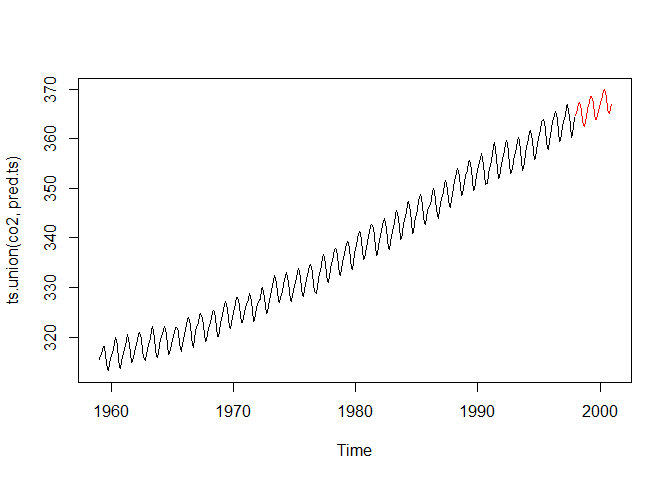
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.