The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.

PieGlyph is an R package aimed at replacing points in a
plot with pie-chart glyphs, showing the relative proportions of
different categories. The pie-chart glyphs are invariant to the axes and
plot dimensions to prevent distortions when the plot dimensions are
changed.
You can install the released version of PieGlyph from CRAN by running:
install.packages("PieGlyph")Alternatively, you can install the development version of
PieGlyph from GitHub
with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("rishvish/PieGlyph")library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(PieGlyph)
library(ggiraph)set.seed(123)
plot_data <- data.frame(response = rnorm(30, 100, 30),
system = 1:30,
group = sample(size = 30, x = c('G1', 'G2', 'G3'), replace = T),
A = round(runif(30, 3, 9), 2),
B = round(runif(30, 1, 5), 2),
C = round(runif(30, 3, 7), 2),
D = round(runif(30, 1, 9), 2))The data has 30 observations and seven columns. response
is a continuous variable measuring system output while
system describes the 30 individual systems of interest.
Each system is placed in one of three groups shown in
group. Columns A, B,
C, and D measure system attributes.
head(plot_data)
#> response system group A B C D
#> 1 83.18573 1 G1 5.80 1.57 4.78 8.31
#> 2 93.09468 2 G3 6.07 3.76 3.87 8.21
#> 3 146.76125 3 G1 6.60 3.48 5.01 3.19
#> 4 102.11525 4 G2 5.00 4.57 4.42 3.57
#> 5 103.87863 5 G1 5.93 3.69 5.60 8.89
#> 6 151.45195 6 G1 8.73 3.95 4.50 5.96We can plot the outputs for each system as a scatterplot and replace the points with pie-chart glyphs showing the relative proportions of the four system attributes.
ggplot(data = plot_data, aes(x = system, y = response))+
geom_pie_glyph(slices = c('A', 'B', 'C', 'D'))+
theme_classic()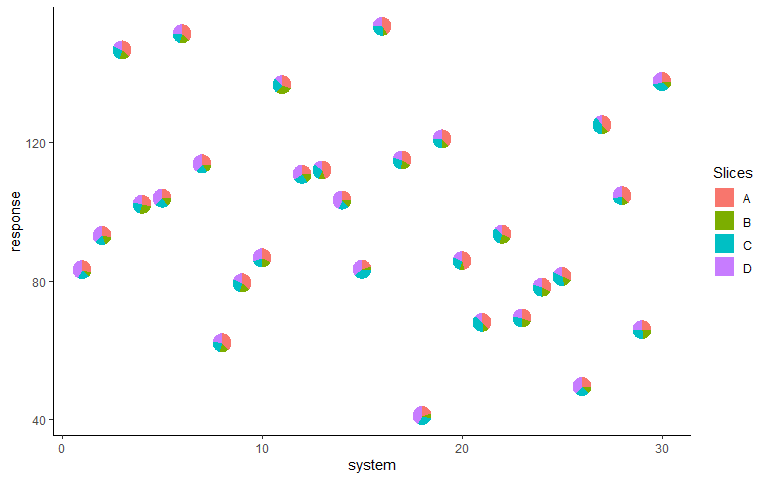
ggplot(data = plot_data, aes(x = system, y = response))+
# Can also specify slices as column indices
geom_pie_glyph(slices = 4:7, colour = 'black', radius = 0.5)+
theme_classic()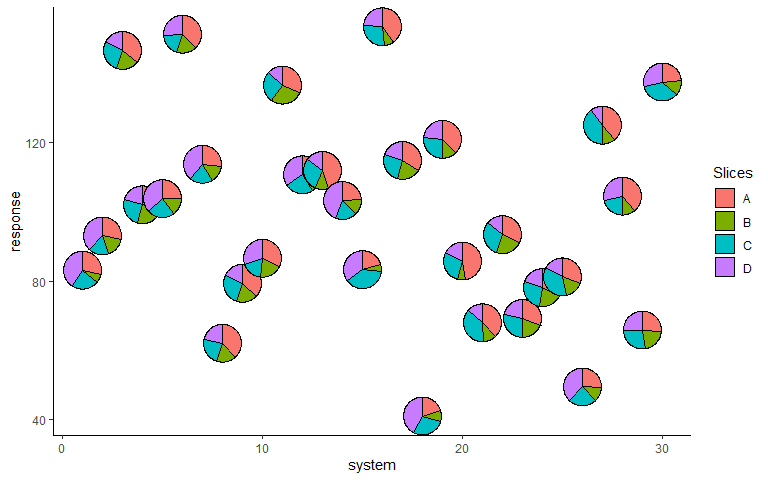
p <- ggplot(data = plot_data, aes(x = system, y = response))+
geom_pie_glyph(aes(radius = group),
slices = c('A', 'B', 'C', 'D'),
colour = 'black')+
theme_classic()
p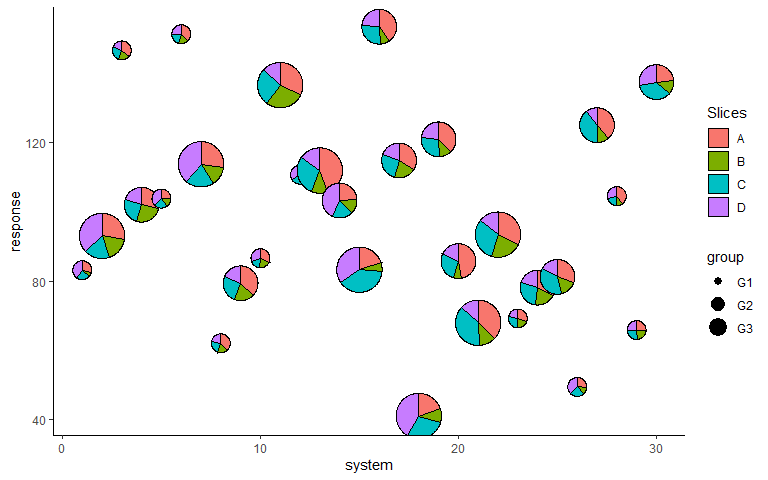
p <- p + scale_radius_manual(values = c(0.25, 0.5, 0.75), unit = 'cm')
p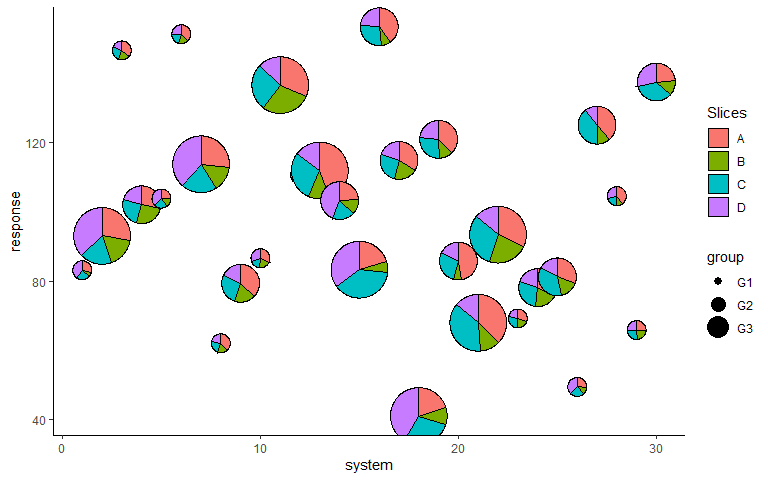
p <- p + labs(x = 'System', y = 'Response', fill = 'Attributes', radius = 'Group')
p
p + scale_fill_manual(values = c('#56B4E9', '#CC79A7', '#F0E442', '#D55E00'))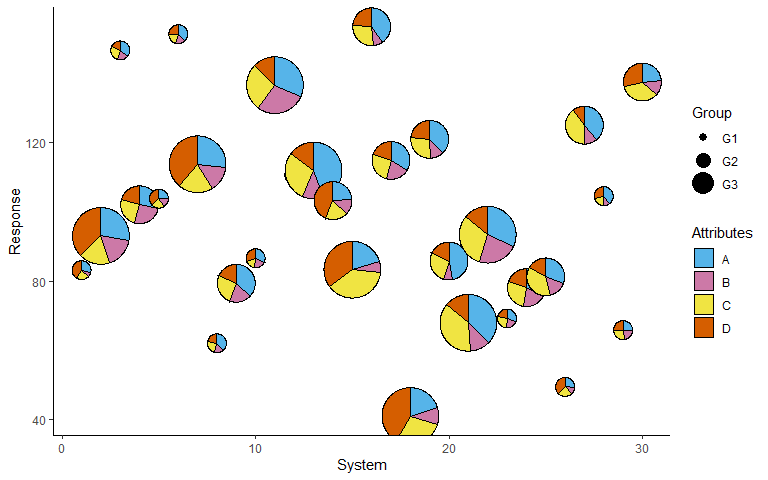
The attributes can also be stacked into one column to generate the
plot. This variant of the function is useful for situations when the
data is in tidy format. See vignette('tidy-data') and
vignette('pivot') for more information.
plot_data_stacked <- plot_data %>%
pivot_longer(cols = c('A','B','C','D'),
names_to = 'Attributes',
values_to = 'values')
head(plot_data_stacked, 8)
#> # A tibble: 8 × 5
#> response system group Attributes values
#> <dbl> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 83.2 1 G1 A 5.8
#> 2 83.2 1 G1 B 1.57
#> 3 83.2 1 G1 C 4.78
#> 4 83.2 1 G1 D 8.31
#> 5 93.1 2 G3 A 6.07
#> 6 93.1 2 G3 B 3.76
#> 7 93.1 2 G3 C 3.87
#> 8 93.1 2 G3 D 8.21ggplot(data = plot_data_stacked, aes(x = system, y = response))+
# Along with categories column, values column is also needed now
geom_pie_glyph(slices = 'Attributes', values = 'values')+
theme_classic()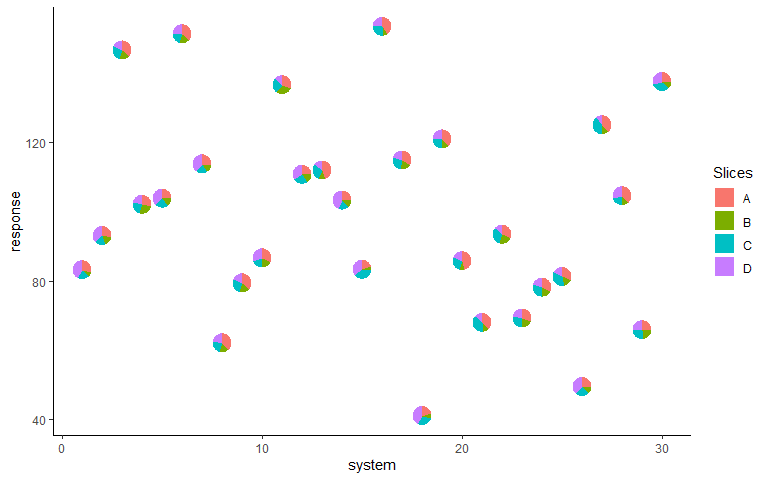
It is also possible to create interactive pie-chart scatterplots
using the geom_pie_interactive function via the ggiraph framework.
Hovering over a pie-chart glyph will show a tooltip containing
information about the raw counts and percentages of the categories
(system attributes in this example) shown in the pie-charts. All
additional features by ggiraph are also supported. See the ggiraph book and
vignette("interactive-pie-glyphs") for more
information.
plot_obj <- ggplot(data = plot_data)+
geom_pie_interactive(aes(x = system, y = response,
data_id = system),
slices = c("A", "B", "C", "D"),
colour = "black")+
theme_classic()
girafe(ggobj = plot_obj, height_svg = 6, width_svg = 8)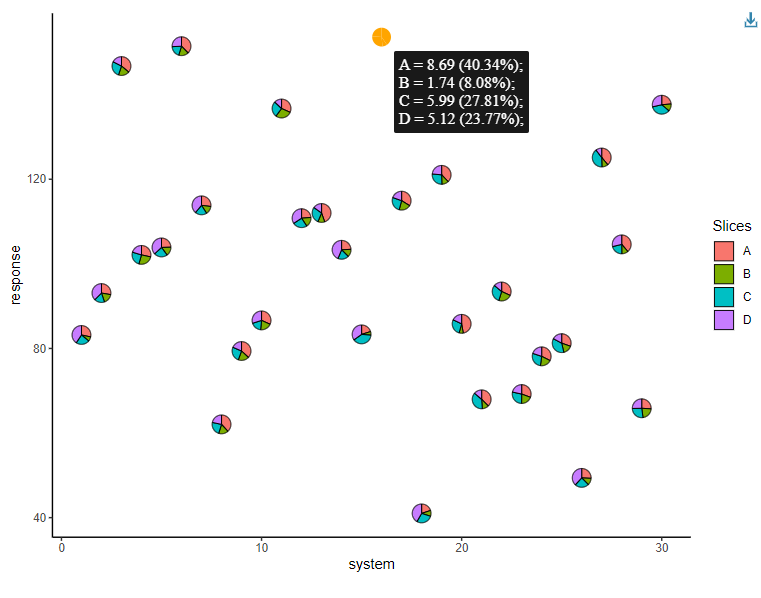
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.