The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
An R package implementing functions to assist in generating and plotting postestimation quantities after estimating Bayesian regression models using MCMC.
BayesPostEst contains functions to generate postestimation quantities
after estimating Bayesian regression models. The package was inspired by
a set of functions written originally for Johannes Karreth’s workshop on
Bayesian modeling at the ICPSR Summer
program. It has grown to include new functions (see
mcmcReg) and will continue to grow to support Bayesian
postestimation. For now, the package focuses mostly on generalized
linear regression models for binary outcomes (logistic and probit
regression).
To install the latest release on CRAN:
install.packages("BayesPostEst")The latest development version on GitHub can be installed with:
library("remotes")
install_github("ShanaScogin/BayesPostEst")Once you have installed the package, you can access it by calling:
library("BayesPostEst")After the package is loaded, check out the ?BayesPostEst
to see a help file.
Most functions in this package work with posterior distributions of
parameters. These distributions need to be converted into a matrix. The
mcmcTab function does this automatically for posterior
draws generated by JAGS, BUGS, MCMCpack, rstan, and rstanarm. For all
other functions, users must convert these objects into a matrix, where
rows represent iterations and columns represent parameters. The help
file for each function explains how to do this.
This vignette uses the Cowles dataset (Cowles and
Davis 1987, British Journal of Social Psychology 26(2): 97-102) from
the carData
package.
df <- carData::CowlesThis data frame contains information on 1421 individuals in the following variables:
Before proceeding, we convert the two factor variables
sex and volunteer into numeric variables. We
also means-center and standardize the two continuous variables by
dividing each by two standard deviations (Gelman and Hill 2007,
Cambridge University Press).
df$female <- (as.numeric(df$sex) - 2) * (-1)
df$volunteer <- as.numeric(df$volunteer) - 1
df$extraversion <- (df$extraversion - mean(df$extraversion)) / (2 * sd(df$extraversion))
df$neuroticism <- (df$neuroticism - mean(df$neuroticism)) / (2 * sd(df$neuroticism))We estimate a Bayesian generalized linear model with the inverse logit link function, where
\[ \text{Pr}\left(\text{Volunteering}_i\right) = \text{logit}^{-1}\left(\beta_1 + \beta_2 \text{Female}_i + \beta_3 \text{Neuroticism}_i + \beta_4 \text{Extraversion}_i\right) \]
BayesPostEst functions accommodate GLM estimates for both logit and
probit link functions. The examples proceed with the logit link
function. If we had estimated a probit regression, the corresponding
argument link in relevant function calls would need to be
set to link = "probit". Otherwise, it is set to
link = "logit" by default.
To use BayesPostEst, we first estimate a Bayesian regression model. The vignette demonstrates five tools for doing so: JAGS (via the R2jags and rjags packages), MCMCpack, and the two Stan interfaces rstan and rstanarm.
First, we prepare the data for JAGS (Plummer 2017). Users need to combine all variables into a list and specify any other elements, like in this case N, the number of observations.
dl <- as.list(df[, c("volunteer", "female", "neuroticism", "extraversion")])
dl$N <- nrow(df)We then write the JAGS model into the working directory.
mod.jags <- paste("
model {
for (i in 1:N){
volunteer[i] ~ dbern(p[i])
logit(p[i]) <- mu[i]
mu[i] <- b[1] + b[2] * female[i] + b[3] * neuroticism[i] + b[4] * extraversion[i]
}
for(j in 1:4){
b[j] ~ dnorm(0, 0.1)
}
}
")
writeLines(mod.jags, "mod.jags") We then define the parameters for which we wish to retain posterior distributions and provide starting values.
params.jags <- c("b")
inits1.jags <- list("b" = rep(0, 4))
inits.jags <- list(inits1.jags, inits1.jags, inits1.jags, inits1.jags)Now, fit the model.
library("R2jags")
set.seed(123)
fit.jags <- jags(data = dl, inits = inits.jags,
parameters.to.save = params.jags, n.chains = 4, n.iter = 2000,
n.burnin = 1000, model.file = "mod.jags")## Compiling model graph
## Resolving undeclared variables
## Allocating nodes
## Graph information:
## Observed stochastic nodes: 1421
## Unobserved stochastic nodes: 4
## Total graph size: 6864
##
## Initializing modelThe same data and model can be used to fit the model using the rjags package:
library("rjags")
mod.rjags <- jags.model(file = "mod.jags", data = dl, inits = inits.jags,
n.chains = 4, n.adapt = 1000)## Compiling model graph
## Resolving undeclared variables
## Allocating nodes
## Graph information:
## Observed stochastic nodes: 1421
## Unobserved stochastic nodes: 4
## Total graph size: 6864
##
## Initializing modelfit.rjags <- coda.samples(model = mod.rjags,
variable.names = params.jags,
n.iter = 2000)We estimate the same model using MCMCpack (Martin, Quinn, and Park 2011, Journal of Statistical Software 42(9): 1-22).
library("MCMCpack")
fit.MCMCpack <- MCMClogit(volunteer ~ female + neuroticism + extraversion,
data = df, burning = 1000, mcmc = 2000, seed = 123,
b0 = 0, B0 = 0.1)We write the same model in Stan language.
mod.stan <- paste("
data {
int<lower=0> N;
int<lower=0,upper=1> volunteer[N];
vector[N] female;
vector[N] neuroticism;
vector[N] extraversion;
}
parameters {
vector[4] b;
}
model {
volunteer ~ bernoulli_logit(b[1] + b[2] * female + b[3] * neuroticism + b[4] * extraversion);
for(i in 1:4){
b[i] ~ normal(0, 3);
}
}
")
writeLines(mod.stan, "mod.stan") We then load rstan…
library("rstan")
rstan_options(auto_write = TRUE)
options(mc.cores = parallel::detectCores())… and estimate the model, re-using the data in list format created for JAGS earlier.
fit.stan <- stan(file = "mod.stan",
data = dl,
pars = c("b"),
chains = 4,
iter = 2000,
seed = 123) Lastly, we use the rstanarm interface (Goodrich, Gabry, Ali, and Brilleman 2019) to estimate the same model again.
library("rstanarm")
fit.rstanarm <- stan_glm(volunteer ~ female + neuroticism + extraversion,
data = df, family = binomial(link = "logit"),
prior = normal(0, 3),
prior_intercept = normal(0, 3),
chains = 4,
iter = 2000,
seed = 123)mcmcTab generates a table summarizing the posterior
distributions of all parameters contained in the model object. This
table can then be used to summarize parameter quantities. The function
can directly process objects created by the following packages: R2jags,
runjags, rjags, R2WinBUGS, MCMCpack, rstan, rstanarm. This includes the
following object classes: jags, rjags,
bugs, mcmc, mcmc.list,
stanreg, stanfit. By default,
mcmcTab generates a dataframe with one row per parameter
and columns containing the median, standard deviation, and 95% credible
interval of each parameter’s posterior distribution.
mcmcTab(fit.jags)## Variable Median SD Lower Upper
## 1 b[1] -0.462 0.082 -0.622 -0.298
## 2 b[2] 0.238 0.112 0.017 0.455
## 3 b[3] 0.063 0.113 -0.158 0.283
## 4 b[4] 0.515 0.112 0.291 0.729
## 5 deviance 1909.455 2.875 1906.574 1917.541mcmcTab(fit.rjags)## Variable Median SD Lower Upper
## 1 b[1] -0.458 0.083 -0.623 -0.297
## 2 b[2] 0.233 0.112 0.015 0.459
## 3 b[3] 0.062 0.110 -0.154 0.281
## 4 b[4] 0.517 0.111 0.300 0.739mcmcTab(fit.MCMCpack)## Variable Median SD Lower Upper
## 1 (Intercept) -0.463 0.083 -0.612 -0.304
## 2 female 0.231 0.110 0.016 0.435
## 3 neuroticism 0.058 0.112 -0.147 0.321
## 4 extraversion 0.509 0.102 0.320 0.718mcmcTab(fit.stan)## Variable Median SD Lower Upper
## 1 b[1] -0.459 0.082 -0.624 -0.301
## 2 b[2] 0.234 0.112 0.020 0.459
## 3 b[3] 0.062 0.110 -0.157 0.284
## 4 b[4] 0.518 0.112 0.299 0.745
## 5 lp__ -954.763 1.419 -958.661 -953.298mcmcTab(fit.rstanarm)## Variable Median SD Lower Upper
## 1 (Intercept) -0.459 0.084 -0.624 -0.293
## 2 female 0.236 0.111 0.014 0.449
## 3 neuroticism 0.065 0.111 -0.149 0.280
## 4 extraversion 0.521 0.109 0.306 0.730Users can add a column to the table that calculates the percent of posterior draws that have the same sign as the median of the posterior distribution.
mcmcTab(fit.jags, Pr = TRUE)## Variable Median SD Lower Upper Pr
## 1 b[1] -0.462 0.082 -0.622 -0.298 1.000
## 2 b[2] 0.238 0.112 0.017 0.455 0.984
## 3 b[3] 0.063 0.113 -0.158 0.283 0.712
## 4 b[4] 0.515 0.112 0.291 0.729 1.000
## 5 deviance 1909.455 2.875 1906.574 1917.541 1.000Users can also define a “region of practical equivalence” (ROPE; Kruschke 2013, Journal of Experimental Psychology 143(2): 573-603). This region is a band of values around 0 that are “practically equivalent” to 0 or no effect. For this to be useful, all parameters (e.g. regression coefficients) must be on the same scale because mcmcTab accepts only one definition of ROPE for all parameters. Users can standardize regression coefficients to achieve this. Because we standardized variables earlier, the coefficients (except the intercept) are on a similar scale and we define the ROPE to be between -0.1 and 0.1.
mcmcTab(fit.jags, pars = c("b[2]", "b[3]", "b[4]"), ROPE = c(-0.1, 0.1))## This table contains an estimate for parameter values outside of the region of
## practical equivalence (ROPE). For this quantity to be meaningful, all parameters
## must be on the same scale (e.g. standardized coefficients or first differences).
## Variable Median SD Lower Upper PrOutROPE
## 1 b[2] 0.238 0.112 0.017 0.455 0.885
## 2 b[3] 0.063 0.113 -0.158 0.283 0.376
## 3 b[4] 0.515 0.112 0.291 0.729 1.000The mcmcReg function serves as an interface to
texreg and produces more polished and publication-ready
tables than mcmcTab in HTML or LaTeX format.
mcmcReg can produce tables with multiple models with each
model in a column and supports flexible renaming of parameters. However,
these tables are more similar to standard frequentist regression tables,
so they do not have a way to incorporate the percent of posterior draws
that have the same sign as the median of the posterior distribution or a
ROPE like mcmcTab is able to. Uncertainty intervals can be
either standard credible intervals or highest posterior density
intervals (Kruschke 2015) using the hpdi argument, and
their level can be set with the ci argument (default 95%).
Separately calculated goodness of fit statistics can be included with
the gof argument.
mcmcReg(fit.jags, format = 'html', doctype = F)mcmcReg supports limiting the parameters included in the
table via the pars argument. By default, all parameters
saved in the model object will be included. In the case of
fit.jags, this include the deviance estimate. If we wish to
exclude it, we can specify pars = 'b' which will capture
b[1]-b[4] using regular expression
matching.
mcmcReg(fit.jags, pars = 'b', format = 'html', doctype = F)If we only wish to exclude the intercept, we can do this by
explicitly specifying the parameters we wish to include as a vector.
Note that in this example we have to escape the []s in
pars because they are a reserved character in regular
expressions.
mcmcReg(fit.jags, pars = c('b\\[1\\]', 'b\\[3\\]', 'b\\[4\\]'), format = 'html', doctype = F)mcmcReg also supports partial regular expression
matching of multiple parameter family names as demonstrated below.
mcmcReg(fit.jags, pars = c('b', 'dev'), format = 'html', doctype = F)mcmcReg supports custom coefficient names to support
publication-ready tables. The simplest option is via the
coefnames argument. Note that the number of parameters and
the number of custom coefficient names must match, so it is a good idea
to use pars in tandem with coefnames.
mcmcReg(fit.jags, pars = 'b',
coefnames = c('(Constant)', 'Female', 'Neuroticism', 'Extraversion'),
format = 'html', doctype = F)A more flexible way to include custom coefficient names is via the
custom.coef.map argument, which accepts a named list, with
names as parameter names in the model and values as the custom
coefficient names.
mcmcReg(fit.jags, pars = 'b',
custom.coef.map = list('b[1]' = '(Constant)',
'b[2]' = 'Female',
'b[3]' = 'Nueroticism',
'b[4]' = 'Extraversion'),
format = 'html', doctype = F)The advantage of custom.coef.map is that it can flexibly
reorder and omit coefficients from the table based on their positions
within the list. Notice in the code below that deviance does not have to
be included in pars because its absence from
custom.coef.map omits it from the resulting table.
mcmcReg(fit.jags,
custom.coef.map = list('b[2]' = 'Female',
'b[4]' = 'Extraversion',
'b[1]' = '(Constant)'),
format = 'html', doctype = F)However, it is important to remember that mcmcReg will
look for the parameter names in the model object, so be sure to inspect
it for the correct parameter names. This is important because
stan_glm will produce a model object with variable names
instead of indexed parameter names.
mcmcReg accepts multiple model objects and will produce
a table with one model per column. To produce a table from multiple
models, pass a list of models as the mod argument to
mcmcReg.
mcmcReg(list(fit.stan, fit.stan), format = 'html', doctype = F)Note, however, that all model objects must be of the same class, so
it is not possible to generate a table from a jags
object and a stanfit object.
mcmcReg(list(fit.jags, fit.stan), format = 'html', doctype = F)When including multiple models, supplying scalars or vectors to arguments will result in them being applied to each model equally. Treating models differentially is possible by supplying a list of scalars or vectors instead.
mcmcReg(list(fit.rstanarm, fit.rstanarm),
pars = list(c('female', 'extraversion'), 'neuroticism'),
format = 'html', doctype = F)Texreg argumentsAlthough custom.coef.map is not an argument to
mcmcReg, it works because mcmcReg supports all
standard texreg arguments (a few have been overridden, but
they are explicit arguments to mcmcReg). This introduces a
high level of control over the output of mcmcReg, as
e.g. models can be renamed.
mcmcReg(fit.rstanarm, custom.model.names = 'Binary Outcome', format = 'html', doctype = F)mcmcAveProbTo evaluate the relationship between covariates and a binary outcome,
this function calculates the predicted probability (Pr(y = 1))
at pre-defined values of one covariate of interest (x), while
all other covariates are held at a “typical” value. This follows
suggestions outlined in King,
Tomz, and Wittenberg (2000, American Journal of Political Science 44(2):
347-361) and elsewhere, which are commonly adopted by users of GLMs.
The mcmcAveProb function by default calculates the median
value of all covariates other than x as “typical” values.
Before moving on, we show how create a matrix of posterior draws of
coefficients to pass onto these functions. Eventually, each function
will contain code similar to the first section of mcmcTab
to do this as part of the function.
mcmcmat.jags <- as.matrix(coda::as.mcmc(fit.jags))
mcmcmat.MCMCpack <- as.matrix(fit.MCMCpack)
mcmcmat.stan <- as.matrix(fit.stan)
mcmcmat.rstanarm <- as.matrix(fit.rstanarm)Next, we generate the model matrix to pass on to the function. A model matrix contains as many columns as estimated regression coefficients. The first column is a vector of 1s (corresponding to the intercept); the remaining columns are the observed values of covariates in the model. Note: the order of columns in the model matrix must correspond to the order of columns in the matrix of posterior draws.
mm <- model.matrix(volunteer ~ female + neuroticism + extraversion,
data = df)We can now generate predicted probabilities for different values of a covariate of interest.
First, we generate full posterior distributions of the predicted
probability of volunteering for a typical female and a typical male. In
this function and mcmcObsProb, users specify the range of
x (here 0 and 1) as well as the number of the column of
x in the matrix of posterior draws as well as the model
matrix.
aveprob.female.jags <- mcmcAveProb(modelmatrix = mm,
mcmcout = mcmcmat.jags[, 1:ncol(mm)],
xcol = 2,
xrange = c(0, 1),
link = "logit",
ci = c(0.025, 0.975),
fullsims = TRUE)Users can then visualize this posterior distribution using the ggplot2 and ggridges packages.
library("ggplot2")
library("ggridges")
ggplot(data = aveprob.female.jags,
aes(y = factor(x), x = pp)) +
stat_density_ridges(quantile_lines = TRUE,
quantiles = c(0.025, 0.5, 0.975), vline_color = "white") +
scale_y_discrete(labels = c("Male", "Female")) +
ylab("") +
xlab("Estimated probability of volunteering") +
labs(title = "Probability based on average-case approach") +
theme_minimal()## Picking joint bandwidth of 0.00327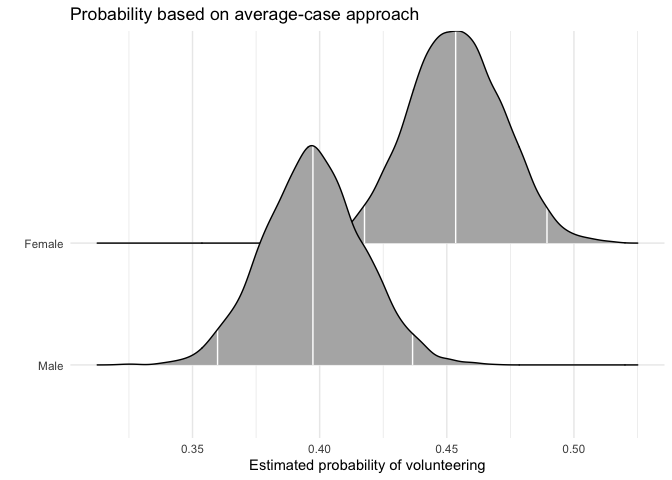
For continuous variables of interest, users may want to set
fullsims = FALSE to obtain the median predicted probability
along the range of x as well as a lower and upper bound of
choice (here, the 95% credible interval).
aveprob.extra.jags <- mcmcAveProb(modelmatrix = mm,
mcmcout = mcmcmat.jags[, 1:ncol(mm)],
xcol = 4,
xrange = seq(min(df$extraversion), max(df$extraversion), length.out = 20),
link = "logit",
ci = c(0.025, 0.975),
fullsims = FALSE)Users can then plot the resulting probabilities using any plotting functions, such as ggplot2.
ggplot(data = aveprob.extra.jags,
aes(x = x, y = median_pp)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = lower_pp, ymax = upper_pp), fill = "gray") +
geom_line() +
xlab("Extraversion") +
ylab("Estimated probability of volunteering") +
ylim(0, 1) +
labs(title = "Probability based on average-case approach") +
theme_minimal()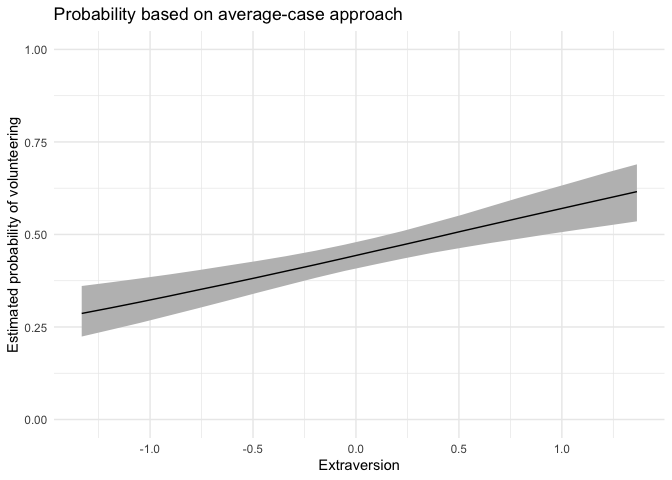
mcmcObsProbAs an alternative to probabilities for “typical” cases, Hanmer and Kalkan (2013, American Journal of Political Science 57(1): 263-277) suggest to calculate predicted probabilities for all observed cases and then derive an “average effect”. In their words, the goal of this postestimation “is to obtain an estimate of the average effect in the population … rather than seeking to understand the effect for the average case.”
We first calculate the average “effect” of sex on volunteering, again
generating a full posterior distribution. Again, xcol
represents the position of the covariate of interest, and
xrange specifies the values for which Pr(y = 1) is
to be calculated.
obsprob.female.jags <- mcmcObsProb(modelmatrix = mm,
mcmcout = mcmcmat.jags[, 1:ncol(mm)],
xcol = 2,
xrange = c(0, 1),
link = "logit",
ci = c(0.025, 0.975),
fullsims = TRUE)Users can again plot the resulting densities.
ggplot(data = obsprob.female.jags,
aes(y = factor(x), x = pp)) +
stat_density_ridges(quantile_lines = TRUE,
quantiles = c(0.025, 0.5, 0.975), vline_color = "white") +
scale_y_discrete(labels = c("Male", "Female")) +
ylab("") +
xlab("Estimated probability of volunteering") +
labs(title = "Probability based on observed-case approach") +
theme_minimal()## Picking joint bandwidth of 0.00318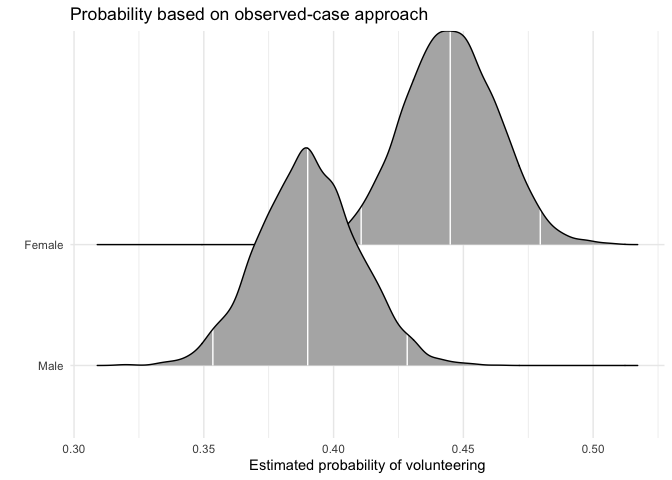
For this continuous predictor, we use
fullsims = FALSE.
obsprob.extra.jags <- mcmcObsProb(modelmatrix = mm,
mcmcout = mcmcmat.jags[, 1:ncol(mm)],
xcol = 4,
xrange = seq(min(df$extraversion), max(df$extraversion), length.out = 20),
link = "logit",
ci = c(0.025, 0.975),
fullsims = FALSE)We then plot the resulting probabilities across observed cases.
ggplot(data = obsprob.extra.jags,
aes(x = x, y = median_pp)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = lower_pp, ymax = upper_pp), fill = "gray") +
geom_line() +
xlab("Extraversion") +
ylab("Estimated probability of volunteering") +
ylim(0, 1) +
labs(title = "Probability based on observed-case approach") +
theme_minimal()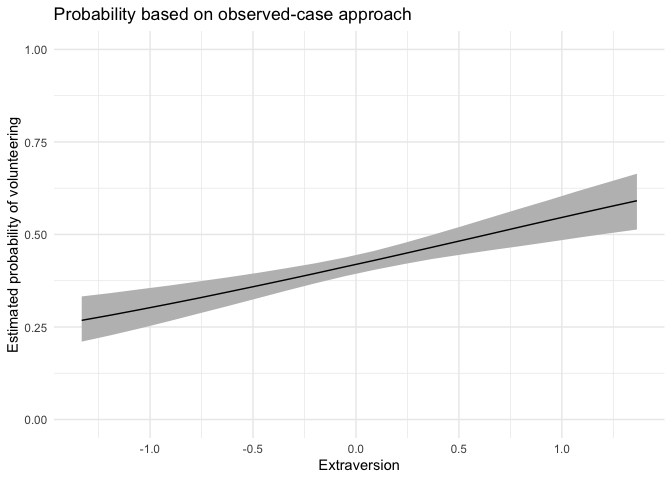
mcmcFDTo summarize typical effects across covariates, we generate “first differences” (Long 1997, Sage Publications; King, Tomz, and Wittenberg 2000, American Journal of Political Science 44(2): 347-361). This quantity represents, for each covariate, the difference in predicted probabilities for cases with low and high values of the respective covariate. For each of these differences, all other variables are held constant at their median.
fdfull.jags <- mcmcFD(modelmatrix = mm,
mcmcout = mcmcmat.jags[, 1:ncol(mm)],
link = "logit",
ci = c(0.025, 0.975),
fullsims = TRUE)
summary(fdfull.jags)## female neuroticism extraversion
## Min. :-0.04432 Min. :-0.055522 Min. :0.01957
## 1st Qu.: 0.03972 1st Qu.:-0.002247 1st Qu.:0.06957
## Median : 0.05795 Median : 0.011224 Median :0.08132
## Mean : 0.05779 Mean : 0.011263 Mean :0.08124
## 3rd Qu.: 0.07619 3rd Qu.: 0.024511 3rd Qu.:0.09313
## Max. : 0.15245 Max. : 0.080707 Max. :0.14269The posterior distribution can be summarized as above, or users can
directly obtain a summary when setting fullsims to
FALSE.
fdsum.jags <- mcmcFD(modelmatrix = mm,
mcmcout = mcmcmat.jags[, 1:ncol(mm)],
link = "logit",
ci = c(0.025, 0.975),
fullsims = FALSE)
fdsum.jags## median_fd lower_fd upper_fd VarName VarID
## female 0.05794760 0.004299115 0.11073472 female 1
## neuroticism 0.01122442 -0.028097810 0.05008092 neuroticism 2
## extraversion 0.08132383 0.045716391 0.11482003 extraversion 3Users can plot the median and credible intervals of the summary of the first differences.
ggplot(data = fdsum.jags,
aes(x = median_fd, y = VarName)) +
geom_point() +
geom_segment(aes(x = lower_fd, xend = upper_fd, yend = VarName)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0) +
xlab("Change in Pr(Volunteering)") +
ylab("") +
theme_minimal()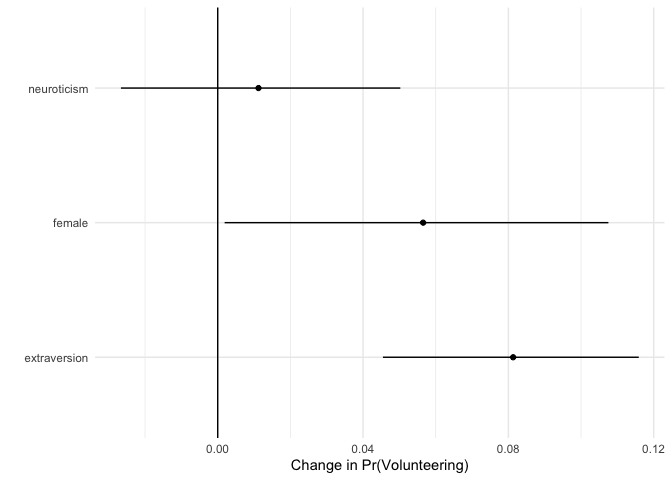
mcmcFD
objectsTo make use of the full posterior distribution of first differences,
we provide a dedicated plotting method, plot.mcmcFD, which
returns a ggplot2 object that can be further customized. The function is
modeled after Figure 1 in Karreth (2018,
International Interactions 44(3): 463-490). Users can specify a
region of practical equivalence and print the percent of posterior draws
to the right or left of the ROPE. If ROPE is not specified, the figure
automatically prints the percent of posterior draws to the left or right
of 0.
plot(fdfull.jags, ROPE = c(-0.01, 0.01))## Picking joint bandwidth of 0.37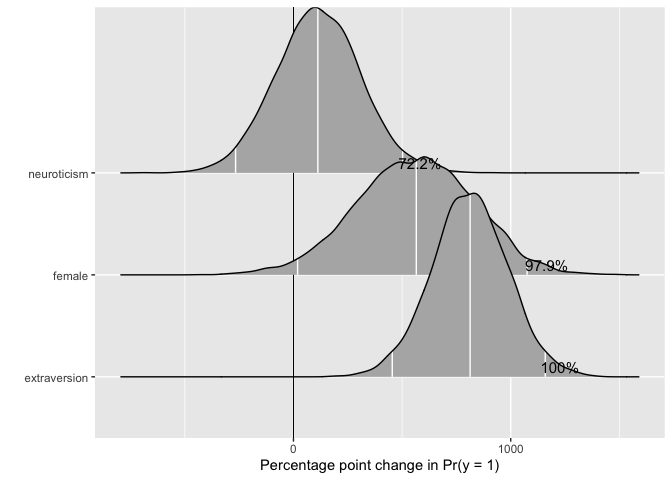
The user can further customize the plot.
p <- plot(fdfull.jags, ROPE = c(-0.01, 0.01))
p + labs(title = "First differences") +
ggridges::theme_ridges()## Picking joint bandwidth of 0.37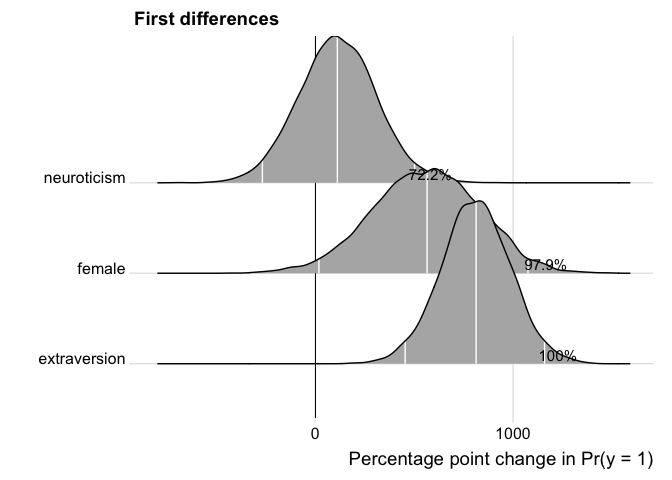
mcmcRocPrcOne way to assess model fit is to calculate the area under the
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) and Precision-Recall curves. A
short description of these curves and their utility for model assessment
is provided in Beger
(2016). The mcmcRocPrc function produces an object with
four elements: the area under the ROC curve, the area under the PR
curve, and two dataframes to plot each curve. When fullsims
is set to FALSE, the elements represent the median of the
posterior distribution of each quantity.
mcmcRocPrc currently requires an “rjags” object (a model
fitted in R2jags) as input. Future package versions will generalize this
input to allow for model objects fit with any of the other packages used
in BayesPostEst.
fitstats <- mcmcRocPrc(object = fit.jags,
yname = "volunteer",
xnames = c("female", "neuroticism", "extraversion"),
curves = TRUE,
fullsims = FALSE)Users can then print the area under the each curve:
fitstats$area_under_roc## V1
## 0.5840611fitstats$area_under_prc## V1
## 0.4867844Users can also plot the ROC curve…
ggplot(data = as.data.frame(fitstats, what = "roc"), aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_line() +
geom_abline(intercept = 0, slope = 1, color = "gray") +
labs(title = "ROC curve") +
xlab("1 - Specificity") +
ylab("Sensitivity") +
theme_minimal()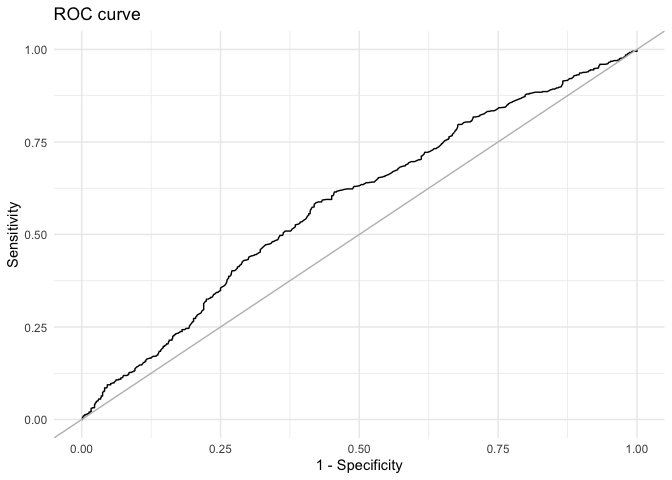
… as well as the precision-recall curve.
ggplot(data = as.data.frame(fitstats, what = "prc"), aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_line() +
labs(title = "Precision-Recall curve") +
xlab("Recall") +
ylab("Precision") +
theme_minimal()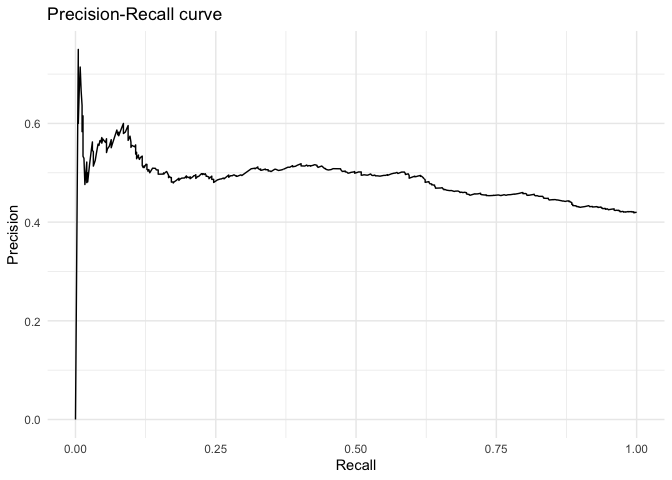
To plot the posterior distribution of the area under the curves,
users set the fullsims argument to TRUE.
Unless a user wishes to plot credible intervals around the ROC and PR
curves themselves, we recommend keeping curves at
FALSE to avoid long computation time.
fitstats.fullsims <- mcmcRocPrc(object = fit.jags,
yname = "volunteer",
xnames = c("female", "neuroticism", "extraversion"),
curves = FALSE,
fullsims = TRUE)We can then plot the posterior density of the area under each curve.
ggplot(as.data.frame(fitstats.fullsims),
aes(x = area_under_roc)) +
geom_density() +
labs(title = "Area under the ROC curve") +
theme_minimal()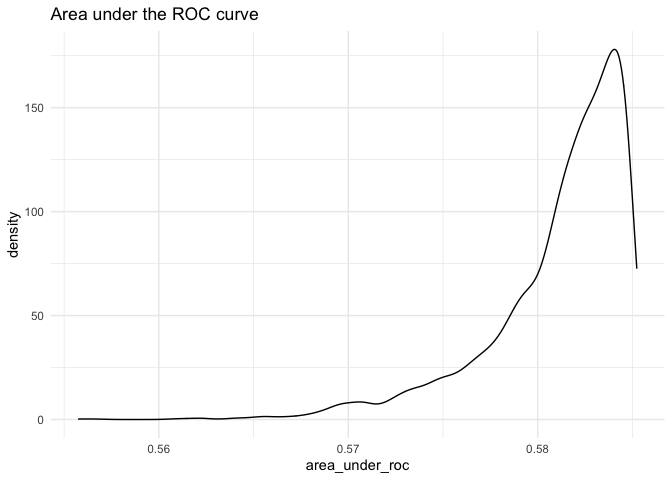
ggplot(as.data.frame(fitstats.fullsims),
aes(x = area_under_prc)) +
geom_density() +
labs(title = "Area under the Precision-Recall curve") +
theme_minimal()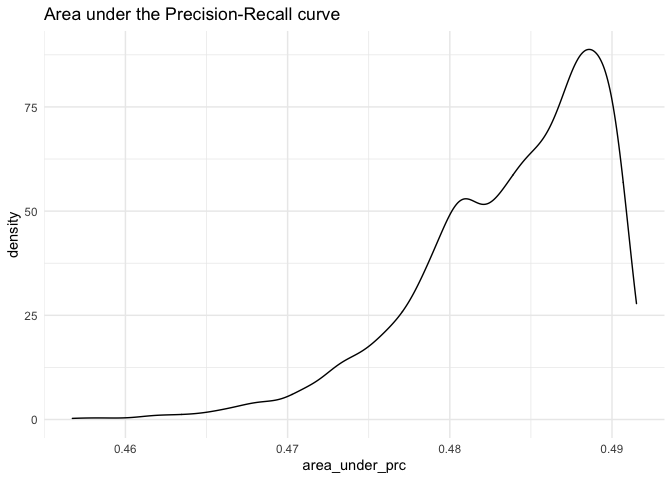
Please submit an issue if you encounter any bugs with or have suggestions for the package. Feel free to check out Johannes Karreth’s website for more resources on Bayesian estimation.
Beger, Andreas. 2016. “Precision-Recall Curves.” Available at: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2765419.
Cowles, Michael, and Caroline Davis. 1987. “The Subject Matter of Psychology: Volunteers.” British Journal of Social Psychology 26 (2): 97–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8309.1987.tb00769.x.
Fox, John, Sanford Weisberg, and Brad Price. 2018. CarData: Companion to Applied Regression Data Sets. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=carData.
Gelman, Andrew, and Jennifer Hill. 2007. Data Analysis Using Regression and Multilevel/Hierarchical Models. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Goodrich, Ben, Jonah Gabry, Imad Ali, and Sam Brilleman. 2019. Rstanarm: Bayesian Applied Regression Modeling via Stan. https://mc-stan.org/.
Hanmer, Michael J., and Kerem Ozan Kalkan. 2013. “Behind the Curve: Clarifying the Best Approach to Calculating Predicted Probabilities and Marginal Effects from Limited Dependent Variable Models.” American Journal of Political Science 57 (1): 263–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5907.2012.00602.x.
Karreth, Johannes. 2018. “The Economic Leverage of International Organizations in Interstate Disputes.” International Interactions 44 (3): 463–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/03050629.2018.1389728.
King, Gary, Michael Tomz, and Jason Wittenberg. 2000. “Making the Most of Statistical Analyses: Improving Interpretation and Presentation.” American Journal of Political Science 44 (2): 347–61. https://doi.org/10.2307/2669316.
Kruschke, John K. 2013. “Bayesian Estimation Supersedes the T-Test.” Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 142 (2): 573–603. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029146.
Kruschke, John K. 2015. Doing Bayesian Data Analysis: A Tutorial with R, JAGS, and Stan. Amsterdam: Academic Press. 978-0-12-405888-0
Long, J. Scott. 1997. Regression Models for Categorical and Limited Dependent Variables. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Martin, Andrew D., Kevin M. Quinn, and Jong Hee Park. 2011. “MCMCpack: Markov Chain Monte Carlo in R.” Journal of Statistical Software 42 (9): 22. https://www.jstatsoft.org/v42/i09/.
Plummer, Martyn. 2017. “JAGS Version 4.3.0 User Manual.” https://mcmc-jags.sourceforge.io/.
Stan Development Team. 2019. RStan: The R Interface to Stan. https://mc-stan.org/.
These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.