The hardware and bandwidth for this mirror is donated by dogado GmbH, the Webhosting and Full Service-Cloud Provider. Check out our Wordpress Tutorial.
If you wish to report a bug, or if you are interested in having us mirror your free-software or open-source project, please feel free to contact us at mirror[@]dogado.de.
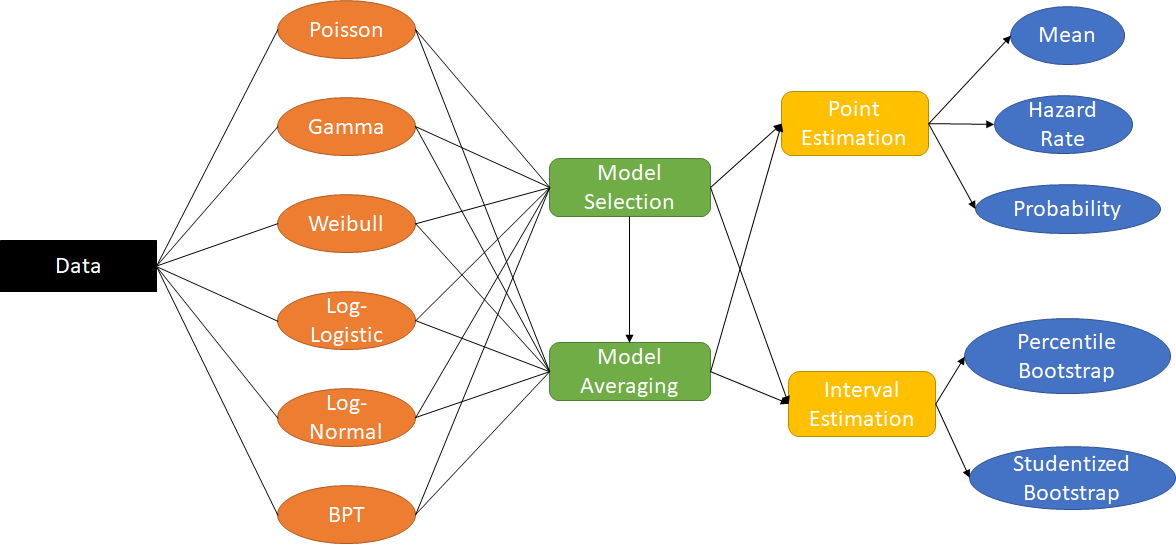
An R package to apply model-averaging on renewal process.
You can install the released version of marp from GitHub with:
if(!require(devtools)){
install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
}
devtools::install_github("kanji709/marp")Here is a basic example which shows you how to use
marp:
# load R package - marp
library(marp)
# generate a small dataset
data <- rgamma(100,3,0.01)
# set parameters
m <- 10 # number of iterations for MLE optimization
t <- seq(100,200,by=10) # time intervals
B <- 99 # number of bootstraps
BB <- 99 # number of double-bootstrapps
alpha <- 0.05 # confidence level
y <- 304 # cut-off time point for probablity estimation
model_gen <- 2 # specifying the data generating model (if known)
# step one: fitting differnt renewal models
res1 <- marp::poisson_rp(dat,t,y)
res2 <- marp::gamma_rp(dat,t,m,y)
res3 <- marp::loglogis_rp(dat,t,m,y)
res4 <- marp::weibull_rp(dat,t,m,y)
res5 <- marp::lognorm_rp(dat,t,y)
res6 <- marp::bpt_rp(dat,t,m,y)
# step two: model selection and obtain model-averaged estimates
res <- marp::marp(dat,t,m,y,which.model = 2)
# step three: construct different confidence intervals (including model-averaged CIs)
ci <- marp::marp_confint(dat,m,t,B,BB,alpha,y,model_gen)These binaries (installable software) and packages are in development.
They may not be fully stable and should be used with caution. We make no claims about them.
Health stats visible at Monitor.